Outsourcing streamlines business operations by delegating tasks to external experts, reducing costs, and enhancing efficiency. Companies leverage outsourcing to access specialized skills and focus on core activities without the burden of managing every function internally. Discover how your business can benefit from outsourcing strategies tailored to maximize growth and competitiveness in the full article.
Table of Comparison
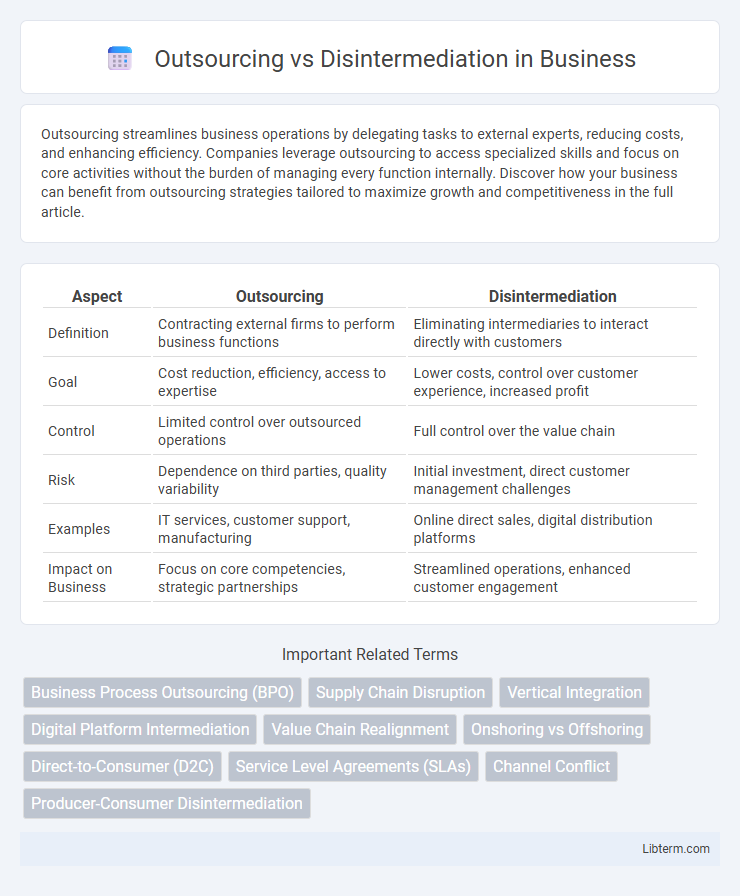
| Aspect | Outsourcing | Disintermediation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contracting external firms to perform business functions | Eliminating intermediaries to interact directly with customers |
| Goal | Cost reduction, efficiency, access to expertise | Lower costs, control over customer experience, increased profit |
| Control | Limited control over outsourced operations | Full control over the value chain |
| Risk | Dependence on third parties, quality variability | Initial investment, direct customer management challenges |
| Examples | IT services, customer support, manufacturing | Online direct sales, digital distribution platforms |
| Impact on Business | Focus on core competencies, strategic partnerships | Streamlined operations, enhanced customer engagement |
Understanding Outsourcing and Disintermediation
Outsourcing involves delegating specific business processes or services to third-party providers to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Disintermediation refers to the removal of intermediaries in a supply chain or service delivery, allowing direct interaction between producers and consumers. Both strategies impact operational control and customer relationships, with outsourcing emphasizing external partnerships and disintermediation focusing on streamlining distribution channels.
Key Differences Between Outsourcing and Disintermediation
Outsourcing involves contracting third-party providers to perform specific business functions or services, enhancing cost efficiency and access to specialized expertise. Disintermediation refers to the elimination of intermediaries in a supply chain or distribution channel, enabling direct interaction between producers and consumers. Key differences include outsourcing's reliance on external vendors for support roles, whereas disintermediation removes middlemen to streamline processes and reduce transaction costs.
Benefits of Outsourcing for Businesses
Outsourcing enables businesses to reduce operational costs by leveraging specialized external expertise and scalable resources, enhancing efficiency and focus on core competencies. It provides access to advanced technologies and skilled talent pools that may be unavailable in-house, fostering innovation and competitive advantage. Furthermore, outsourcing offers flexibility in managing workload fluctuations, improving service quality and accelerating time-to-market for products and services.
Advantages of Disintermediation in the Digital Economy
Disintermediation in the digital economy eliminates intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing transaction speed. It empowers businesses to have direct access to customers, enhancing personalized marketing and improving customer experience. This direct engagement facilitates better data collection and analytics, driving more informed decision-making and innovation.
Risks and Challenges of Outsourcing
Outsourcing poses risks such as loss of control over critical business processes, potential data security breaches, and dependency on third-party vendors which can lead to service disruptions. Challenges include managing communication barriers, ensuring quality compliance, and navigating cultural differences that may impact project outcomes. Companies must implement robust governance frameworks and risk mitigation strategies to address these vulnerabilities effectively.
Drawbacks and Concerns with Disintermediation
Disintermediation eliminates intermediaries, reducing costs but raises significant concerns such as increased operational complexity and the loss of expertise provided by middlemen. This approach may lead to challenges in maintaining quality control, managing direct customer relationships, and handling supply chain logistics, which intermediaries typically streamline. Companies risk exposure to higher financial and legal liabilities without the protective buffer intermediaries offer.
Impact on Cost Efficiency and Operational Flexibility
Outsourcing enables companies to reduce operational costs by leveraging specialized external providers, often leading to significant savings in labor and infrastructure expenses while enhancing operational flexibility through scalable resource allocation. Disintermediation removes intermediaries from the supply chain, which can lower costs by cutting out middleman fees but may require firms to invest in internal capabilities, potentially impacting short-term flexibility. Both strategies influence cost efficiency and operational adaptability differently: outsourcing tends to offer immediate cost reduction with flexible service levels, whereas disintermediation offers long-term cost control at the potential expense of reduced agility during transition periods.
Influence on Vendor and Customer Relationships
Outsourcing often strengthens vendor-customer relationships by establishing formal contracts and ongoing collaboration, enabling vendors to become strategic partners rather than mere suppliers. Disintermediation removes intermediaries, allowing direct interactions between vendors and customers, which can increase transparency and customize service but may also increase risk due to the loss of established support mechanisms. Both outsourcing and disintermediation reshape power dynamics, where outsourcing may enhance vendor influence through dependency, while disintermediation empowers customers with greater control and access to real-time information.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications and Outcomes
Case studies reveal that outsourcing enables companies like IBM and Accenture to leverage specialized expertise, reduce operational costs, and focus on core competencies, resulting in increased efficiency and innovation. Disintermediation, demonstrated by platforms like Airbnb and Tesla, removes traditional intermediaries, enhances direct customer interactions, and improves profit margins through streamlined supply chains. Real-world applications highlight that outsourcing suits scalable service demands, while disintermediation drives disruptive market models and consumer empowerment.
Choosing the Right Strategy: Outsourcing or Disintermediation?
Choosing the right strategy between outsourcing and disintermediation depends on a company's core competencies and goals for efficiency and control. Outsourcing enables businesses to delegate non-core functions to specialized third parties, reducing operational costs and leveraging external expertise. Disintermediation removes intermediaries to streamline processes and enhance direct customer relationships, ideal for companies aiming to increase transparency and reduce dependence on middlemen.
Outsourcing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com