Financial risk involves the potential loss of capital due to factors such as market fluctuations, credit defaults, or liquidity crises. Effective management of these risks requires identifying, assessing, and mitigating exposure to protect your investments and ensure long-term stability. Explore the rest of the article to understand strategies for safeguarding your financial future.
Table of Comparison
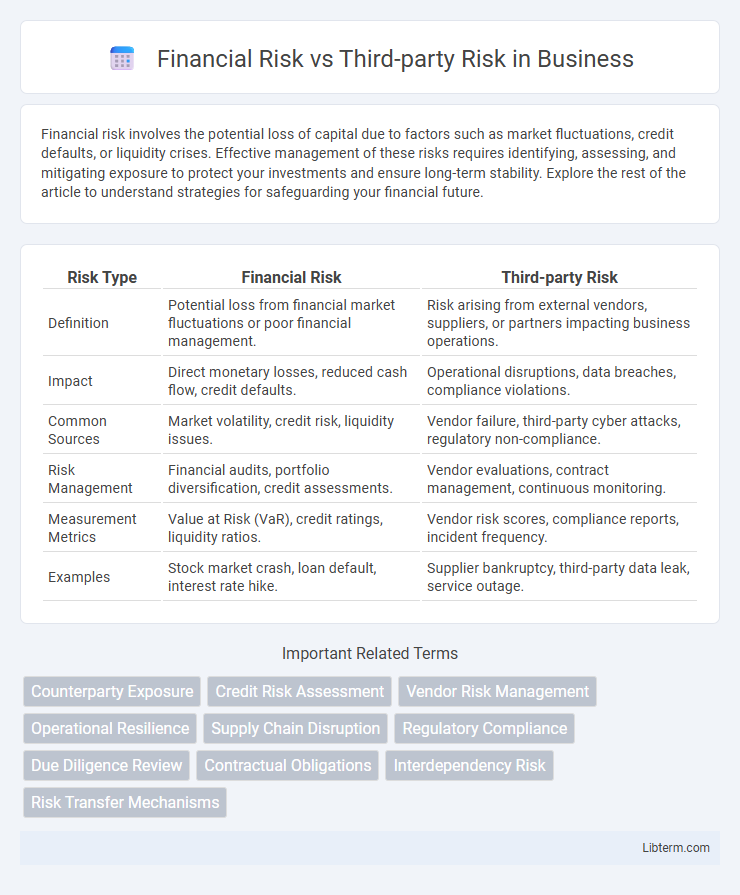
| Risk Type | Financial Risk | Third-party Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Potential loss from financial market fluctuations or poor financial management. | Risk arising from external vendors, suppliers, or partners impacting business operations. |
| Impact | Direct monetary losses, reduced cash flow, credit defaults. | Operational disruptions, data breaches, compliance violations. |
| Common Sources | Market volatility, credit risk, liquidity issues. | Vendor failure, third-party cyber attacks, regulatory non-compliance. |
| Risk Management | Financial audits, portfolio diversification, credit assessments. | Vendor evaluations, contract management, continuous monitoring. |
| Measurement Metrics | Value at Risk (VaR), credit ratings, liquidity ratios. | Vendor risk scores, compliance reports, incident frequency. |
| Examples | Stock market crash, loan default, interest rate hike. | Supplier bankruptcy, third-party data leak, service outage. |
Introduction to Financial Risk and Third-party Risk
Financial risk involves potential losses due to factors like market fluctuations, credit defaults, or liquidity shortages that directly impact an organization's financial health. Third-party risk arises from the reliance on external vendors or partners whose operational, compliance, or security failures can indirectly lead to financial, reputational, or regulatory damage. Understanding both risks requires evaluating internal financial controls alongside the monitoring of third-party relationships to ensure comprehensive risk management.
Defining Financial Risk
Financial risk refers to the potential for losses resulting from an organization's financial activities, including credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk, and operational risk. It encompasses uncertainties in cash flow, investment returns, and the capacity to meet debt obligations. Understanding financial risk is crucial for managing exposure to factors that could negatively impact a company's financial stability and performance.
Understanding Third-party Risk
Third-party risk involves potential financial losses and operational disruptions arising from external vendors, suppliers, or partners, making it a critical component of overall financial risk management. Understanding third-party risk requires evaluating the financial stability, compliance adherence, cybersecurity measures, and reputational factors of these external entities. Effective third-party risk management reduces vulnerabilities by implementing robust due diligence, continuous monitoring, and clear contract terms to mitigate impacts on financial performance.
Key Differences Between Financial Risk and Third-party Risk
Financial risk involves potential losses due to internal financial mismanagement, market fluctuations, or credit defaults, directly impacting an organization's monetary stability. Third-party risk arises from external vendors or partners whose actions or failures could compromise operational continuity, compliance, or data security. Key differences include the origin of risk--internal financial factors versus external entities--and the scope, with financial risk focusing on fiscal impacts and third-party risk emphasizing supply chain and reputational vulnerabilities.
Common Sources of Financial Risk
Common sources of financial risk include market volatility, credit defaults, liquidity shortages, and operational failures that can impact an organization's financial stability. Third-party risk often arises from reliance on external vendors, suppliers, or partners whose financial health, compliance issues, or service disruptions directly affect the company's financial outcomes. Effective risk management requires continuous monitoring of these risks to mitigate potential losses and ensure business continuity.
Main Causes of Third-party Risk
Main causes of third-party risk include lack of thorough due diligence, insufficient monitoring of vendor performance, and inadequate cybersecurity measures implemented by external partners. Financial risk often arises when third parties fail to meet contractual obligations, leading to potential losses, compliance violations, and operational disruptions. Supply chain dependencies and the complexity of outsourcing further amplify these risks, requiring organizations to implement robust risk management strategies.
Impact of Financial Risk on Organizations
Financial risk significantly affects organizations by exposing them to potential losses from market fluctuations, credit defaults, and liquidity shortages, which can threaten operational stability and profitability. These risks can impair cash flow, reduce capital availability, and increase borrowing costs, directly impacting strategic decision-making and growth opportunities. Managing financial risk is crucial to maintaining investor confidence and ensuring long-term financial health.
Consequences of Third-party Risk Exposure
Third-party risk exposure can lead to significant financial losses, data breaches, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage for organizations. These consequences often surpass direct financial risks by impacting operational continuity and client trust, resulting in longer-term revenue declines. Effective third-party risk management is crucial to mitigate these risks and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Strategies for Managing Financial and Third-party Risk
Implement robust due diligence processes to assess financial stability and compliance of third-party vendors, reducing exposure to potential losses. Employ continuous monitoring tools and key risk indicators (KRIs) to track financial health and contractual adherence, ensuring timely identification of emerging risks. Integrate risk management frameworks like ISO 31000 or COSO to align financial and third-party risk strategies, promoting comprehensive mitigation and resilience.
Building a Holistic Risk Management Framework
A holistic risk management framework integrates financial risk and third-party risk to ensure comprehensive organizational protection by identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats across internal and external domains. Effective frameworks utilize risk data analytics, continuous monitoring, and cross-functional collaboration to address credit, market, operational, and vendor risks cohesively. Embedding risk governance, compliance controls, and regular audits strengthens resilience against financial losses and third-party disruptions.
Financial Risk Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com