Acquisition drives growth by enabling companies to expand their market presence and access new customer bases. Effective acquisition strategies involve thorough due diligence, strategic alignment, and integration planning to maximize value. Explore the rest of the article to learn how your business can leverage acquisitions for sustainable success.
Table of Comparison
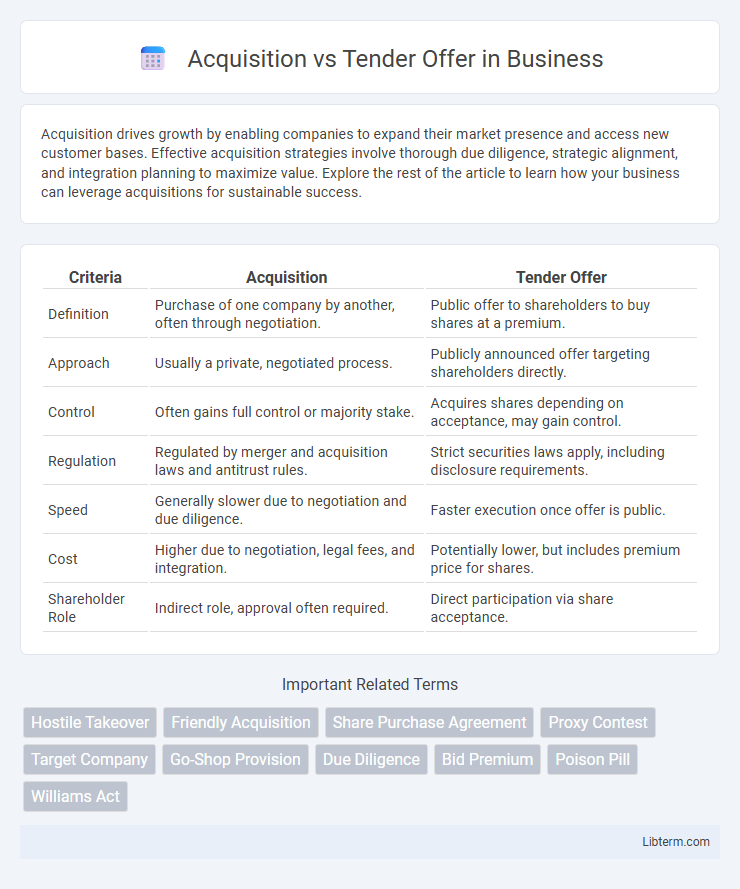
| Criteria | Acquisition | Tender Offer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Purchase of one company by another, often through negotiation. | Public offer to shareholders to buy shares at a premium. |
| Approach | Usually a private, negotiated process. | Publicly announced offer targeting shareholders directly. |
| Control | Often gains full control or majority stake. | Acquires shares depending on acceptance, may gain control. |
| Regulation | Regulated by merger and acquisition laws and antitrust rules. | Strict securities laws apply, including disclosure requirements. |
| Speed | Generally slower due to negotiation and due diligence. | Faster execution once offer is public. |
| Cost | Higher due to negotiation, legal fees, and integration. | Potentially lower, but includes premium price for shares. |
| Shareholder Role | Indirect role, approval often required. | Direct participation via share acceptance. |
Understanding Acquisitions and Tender Offers
Acquisitions involve one company purchasing another to gain control, often through negotiated agreements or stock purchases, while tender offers are public bids to shareholders, typically at a premium, to buy shares directly for acquiring control. Understanding acquisitions requires analyzing due diligence, valuation metrics, and regulatory approvals, whereas tender offers necessitate familiarity with offer conditions, shareholder rights, and possible defensive measures. Both strategies aim to consolidate ownership but differ in execution, timing, and legal complexity within corporate finance.
Key Definitions: Acquisition vs Tender Offer
An acquisition involves one company obtaining control of another through the purchase of assets or shares, often negotiated privately. A tender offer is a public, open bid by an acquirer to purchase shares from shareholders at a specified price, usually at a premium to the market value. While acquisitions encompass broader corporate control strategies, tender offers specifically target shareholder approval for direct stock purchase.
Types of Acquisition Methods
Acquisition methods primarily include direct purchase, merger, and tender offer, each varying in structure and control implications. Tender offers involve a bidder directly appealing to shareholders to buy shares at a premium, bypassing management, while mergers consolidate companies through mutual agreement, and direct purchases focus on acquiring assets or equity through negotiation. Understanding these distinctions helps companies select the most strategic acquisition method based on control, cost, and regulatory considerations.
How Tender Offers Work
Tender offers function as a public bid by an acquiring company to purchase shares directly from shareholders at a premium price, typically above the market value. The offer specifies the number of shares sought and the price per share, binding shareholders to sell within a set timeframe if they accept. Shareholders can decide individually whether to tender their shares, allowing the acquirer to gain control without negotiating with the company's board.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Acquisition and tender offer processes are governed by distinct legal and regulatory frameworks, with acquisitions often undergoing comprehensive due diligence and regulatory approvals under antitrust laws. Tender offers must comply with securities regulations such as the Williams Act, requiring public disclosures to protect shareholders and ensuring fair pricing in the offer. Both approaches are subject to oversight by regulatory bodies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to prevent fraud and ensure transparency in corporate transactions.
Advantages of Acquisitions
Acquisitions offer companies the advantage of full control over the target business, enabling seamless integration of operations and strategic alignment. They typically result in long-term value creation through synergies in cost savings, increased market share, and expanded product lines. Furthermore, acquisitions can be structured flexibly, allowing for negotiated terms that address both parties' interests and minimize regulatory hurdles.
Benefits of Tender Offers
Tender offers provide shareholders the opportunity for a premium price compared to the current market value, incentivizing them to sell their shares quickly. They offer a direct and transparent transaction method, bypassing lengthy negotiations typically involved in acquisitions. This approach can accelerate the acquisition process, reducing uncertainty and increasing the likelihood of a successful takeover.
Challenges and Risks in Both Approaches
Acquisition challenges include integration difficulties, cultural clashes, and regulatory obstacles that may delay or derail transactions. Tender offers risk shareholder rejection, price volatility, and potential litigation, complicating deal completion. Both approaches face uncertainties in valuation accuracy, financing issues, and market reactions impacting overall success.
Strategic Factors Influencing Choice
Strategic factors influencing the choice between acquisition and tender offer include the level of control desired, speed of transaction, and market reaction management. Acquisitions often involve negotiated agreements that enable comprehensive due diligence and integration planning, suitable for long-term strategic alignment. Tender offers provide a faster route to gaining control, appealing in hostile or competitive scenarios where swift shareholder approval is critical.
Acquisition vs Tender Offer: Which is Right for Your Business?
Acquisition and tender offer are strategic methods for business growth, where an acquisition involves purchasing a company outright, while a tender offer is a public proposal to buy shares from shareholders at a premium. Acquisitions provide complete control and integration but require extensive negotiation and due diligence, whereas tender offers offer a quicker route to gain significant ownership without immediate full control. Choosing the right approach depends on factors like desired control level, speed of transaction, shareholder structure, and long-term business goals.
Acquisition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com