Venture capital drives innovation by providing funding to early-stage startups with high growth potential. It connects ambitious entrepreneurs with investors who offer not only capital but also strategic guidance and industry expertise. Discover how venture capital can transform your startup and learn key strategies by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
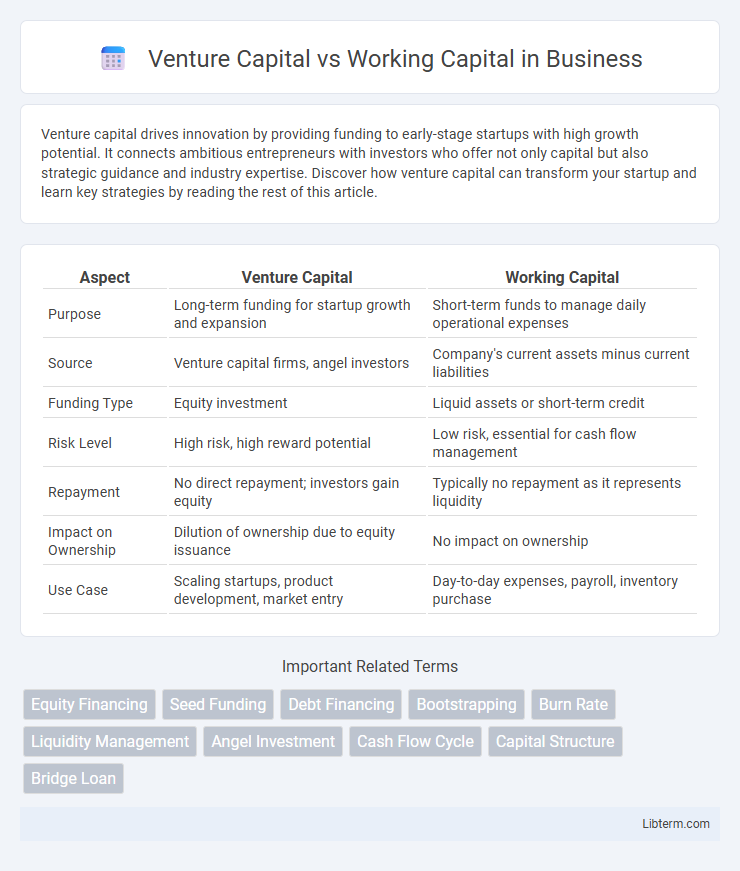
| Aspect | Venture Capital | Working Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Long-term funding for startup growth and expansion | Short-term funds to manage daily operational expenses |
| Source | Venture capital firms, angel investors | Company's current assets minus current liabilities |
| Funding Type | Equity investment | Liquid assets or short-term credit |
| Risk Level | High risk, high reward potential | Low risk, essential for cash flow management |
| Repayment | No direct repayment; investors gain equity | Typically no repayment as it represents liquidity |
| Impact on Ownership | Dilution of ownership due to equity issuance | No impact on ownership |
| Use Case | Scaling startups, product development, market entry | Day-to-day expenses, payroll, inventory purchase |
Introduction to Venture Capital and Working Capital
Venture capital represents funds invested in early-stage, high-potential startups in exchange for equity ownership, driving innovation and business growth. Working capital refers to the difference between a company's current assets and current liabilities, crucial for managing day-to-day operational expenses and maintaining liquidity. Understanding the distinction between venture capital and working capital helps businesses optimize funding strategies and ensure financial stability.
Defining Venture Capital: Purpose and Scope
Venture capital is a form of private equity financing provided by investors to startups and early-stage companies with high growth potential, aiming to accelerate innovation and market expansion. It involves exchanging capital for equity shares, giving investors ownership stakes and active roles in strategic decisions. This funding purpose contrasts with working capital, which represents a company's short-term assets used for daily operational expenses rather than long-term growth investments.
Understanding Working Capital: Key Components
Working capital represents the difference between a company's current assets and current liabilities, serving as a critical indicator of short-term financial health. Key components include cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, inventory, accounts payable, and other short-term obligations, which together determine liquidity and operational efficiency. Efficient management of working capital ensures a business can meet its short-term debts and continue day-to-day operations without financial strain.
Core Differences Between Venture Capital and Working Capital
Venture capital involves investment funds provided by investors to startups or early-stage companies with high growth potential, typically in exchange for equity ownership. Working capital represents the difference between a company's current assets and current liabilities, used to cover day-to-day operational expenses and maintain liquidity. The core difference lies in venture capital being a long-term funding source aimed at business expansion, whereas working capital ensures short-term financial health and operational efficiency.
Sources and Availability of Venture Capital vs Working Capital
Venture capital is sourced primarily from institutional investors, high-net-worth individuals, and venture capital firms targeting startups with high growth potential, whereas working capital typically derives from a company's internal cash flow, short-term loans, or credit lines to fund day-to-day operations. Availability of venture capital depends on market conditions, investor interest, and startup scalability, often requiring rigorous due diligence and equity negotiation. Working capital is usually more accessible and flexible, reflecting the company's operational efficiency and creditworthiness rather than external investor appetite.
Impact on Business Growth and Scalability
Venture capital provides substantial funding aimed at accelerating business growth and scaling operations rapidly by enabling product development, market expansion, and talent acquisition. Working capital, on the other hand, ensures smooth day-to-day operations by maintaining liquidity needed for inventory management, payroll, and operational expenses but has limited direct influence on long-term scalability. Businesses leveraging venture capital often experience faster scalability due to larger capital injection and strategic support, whereas those relying on working capital focus on operational stability and incremental growth.
Risk Factors and Financial Implications
Venture capital involves high risk due to funding startups with uncertain returns but offers potential for substantial equity growth, while working capital focuses on short-term liquidity to ensure operational stability and minimize insolvency risk. Venture capital financing impacts a company's ownership structure and long-term valuation, whereas managing working capital affects cash flow efficiency and day-to-day financial health. Understanding these distinctions helps businesses balance growth opportunities against maintaining sufficient liquidity to meet immediate obligations.
Decision-Making: When to Seek Venture Capital or Manage Working Capital
Decision-making regarding venture capital or working capital hinges on a company's growth stage and financial needs. Venture capital is optimal for startups or high-growth businesses requiring significant funds to scale operations or develop innovative products. Managing working capital is critical for established firms focused on maintaining liquidity, optimizing cash flow, and ensuring smooth day-to-day operations.
Industry Examples and Case Studies
Venture capital fuels startups like Airbnb and Uber, providing essential growth funding in exchange for equity, while working capital supports daily operations in established firms such as Walmart and General Electric, ensuring smooth cash flow management. Case studies reveal that Airbnb's venture capital rounds enabled rapid global expansion, whereas Walmart's focus on optimizing working capital ratios sustained its retail dominance. Industry examples highlight differences in financial strategy: tech startups rely on venture capital for innovation-driven scaling, whereas manufacturing firms prioritize working capital efficiency to maintain production and supply chain stability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Capital for Your Business
Selecting between venture capital and working capital depends on your business goals, growth stage, and financial needs. Venture capital suits startups seeking rapid expansion with equity financing, while working capital focuses on managing daily operations and maintaining liquidity. Understanding your company's priorities ensures the right capital type supports sustainable development and operational efficiency.
Venture Capital Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com