A licensing agreement is a legal contract that grants permission to use intellectual property, such as patents, trademarks, or copyrights, under specified conditions. This agreement protects the rights of the licensor while allowing the licensee to leverage the intellectual property for business or creative purposes. Discover how a well-drafted licensing agreement can safeguard your interests and maximize your opportunities by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
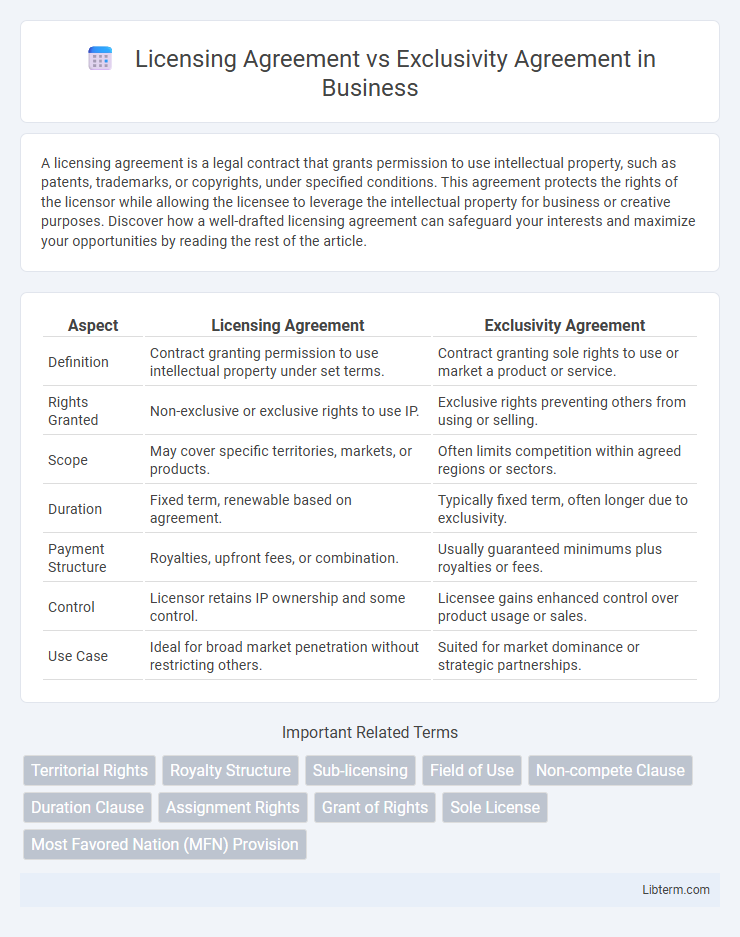
| Aspect | Licensing Agreement | Exclusivity Agreement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contract granting permission to use intellectual property under set terms. | Contract granting sole rights to use or market a product or service. |
| Rights Granted | Non-exclusive or exclusive rights to use IP. | Exclusive rights preventing others from using or selling. |
| Scope | May cover specific territories, markets, or products. | Often limits competition within agreed regions or sectors. |
| Duration | Fixed term, renewable based on agreement. | Typically fixed term, often longer due to exclusivity. |
| Payment Structure | Royalties, upfront fees, or combination. | Usually guaranteed minimums plus royalties or fees. |
| Control | Licensor retains IP ownership and some control. | Licensee gains enhanced control over product usage or sales. |
| Use Case | Ideal for broad market penetration without restricting others. | Suited for market dominance or strategic partnerships. |
Introduction to Licensing and Exclusivity Agreements
Licensing agreements grant permission to use intellectual property, such as patents, trademarks, or copyrights, under defined terms without transferring ownership. Exclusivity agreements restrict the licensee's ability to use or grant rights to third parties, often providing a competitive advantage in a specific market or territory. Understanding the differences between these contracts is essential for businesses seeking to protect their assets while optimizing market opportunities.
Definitions: What is a Licensing Agreement?
A Licensing Agreement is a legal contract where the owner of intellectual property (licensor) grants permission to another party (licensee) to use, produce, or sell the licensed asset under specified terms without transferring ownership. This agreement typically outlines the scope, duration, territory, and financial arrangements such as royalties or fees. It enables businesses to monetize intangible assets like patents, trademarks, copyrights, or technology while retaining control over their use.
Definitions: What is an Exclusivity Agreement?
An Exclusivity Agreement is a contract where one party agrees to grant exclusive rights to another party, preventing the licensor from engaging with competitors regarding the same product or service within a defined territory or market. Unlike a general Licensing Agreement, which permits multiple licensees, exclusivity ensures sole access or distribution rights to the licensee, often enhancing competitive advantage and market control. This type of agreement is crucial for businesses seeking to protect proprietary technology, brand identity, or market share by limiting competition.
Key Differences Between Licensing and Exclusivity Agreements
Licensing agreements grant permission to use intellectual property under defined terms, allowing multiple licensees, while exclusivity agreements restrict use to a single licensee, ensuring exclusive rights within a market or territory. Licensing enables broader distribution and royalty-based revenue from multiple partners, whereas exclusivity limits competition by granting sole access, often in exchange for higher fees or stricter obligations. The core difference lies in the scope of rights: licensing permits shared usage, exclusivity guarantees sole usage.
Legal Framework Governing Each Agreement
Licensing agreements typically operate under intellectual property law, defining the rights to use, produce, or sell a product or technology without transferring ownership, while specifying terms such as duration, territory, and royalty payments. Exclusivity agreements, governed by contract law, establish conditions under which one party gains exclusive rights to sell or distribute a product or service within a defined market or geographic area, often limiting the licensor's ability to engage with other parties. Both agreements require precise legal drafting to address enforcement mechanisms, breach consequences, and compliance with antitrust regulations.
Benefits of Licensing Agreements
Licensing agreements allow companies to expand their market reach by granting rights to use intellectual property without relinquishing ownership, enabling multiple licensees to generate revenue streams simultaneously. This flexibility encourages innovation and collaboration while reducing the licensor's risk and investment in product development and distribution. Licensing agreements also foster brand recognition and customer access without the constraints of exclusivity, making them ideal for scalable growth strategies in competitive markets.
Advantages of Exclusivity Agreements
Exclusivity agreements offer a strategic advantage by granting one party sole rights to a product or service within a specific market or territory, eliminating competition and strengthening market presence. These agreements foster deeper collaboration and investment between parties, leading to enhanced product development and consistent branding. By restricting access to others, exclusivity agreements can increase the licensor's leverage in negotiations and potentially command higher financial returns.
Potential Risks and Drawbacks
Licensing agreements risk loss of control over intellectual property and potential revenue dilution if the licensee underperforms or breaches terms. Exclusivity agreements may limit market opportunities and create dependency on a single partner, increasing vulnerability if that partner fails to meet expectations. Both agreements can lead to legal disputes due to unclear terms or misuse of licensed rights, emphasizing the need for precise contract drafting and risk assessment.
How to Choose the Right Agreement for Your Business
When selecting between a Licensing Agreement and an Exclusivity Agreement for your business, evaluate the scope of rights granted, including territorial, product, and duration limitations. Consider your strategic goals: Licensing Agreements allow broader market reach by permitting multiple licensees, while Exclusivity Agreements restrict rights to a single party, often enhancing market control and brand consistency. Analyze factors like risk tolerance, revenue models, and competitive advantage to determine which agreement aligns best with your business objectives and growth plans.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision
Choosing between a Licensing Agreement and an Exclusivity Agreement depends on the desired level of control and market reach; licensing typically allows broader distribution with less control, while exclusivity grants sole rights but limits potential partners. Evaluating business objectives, market conditions, and the importance of brand control helps determine the most strategic contract. Thorough legal review and clear terms are essential to ensure alignment with long-term goals and risk management.
Licensing Agreement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com