Compliance ensures that your business adheres to legal regulations and industry standards, reducing the risk of penalties and enhancing reputation. Staying informed about compliance requirements helps maintain operational integrity and fosters trust among stakeholders. Explore the rest of this article to understand key compliance strategies and how they benefit your organization.
Table of Comparison
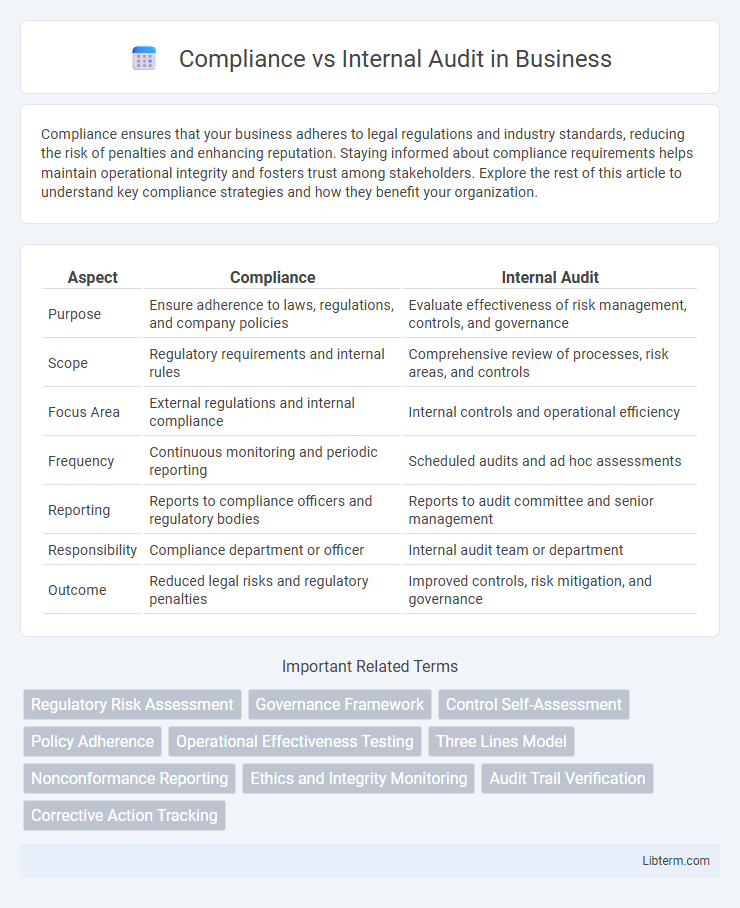
| Aspect | Compliance | Internal Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Ensure adherence to laws, regulations, and company policies | Evaluate effectiveness of risk management, controls, and governance |
| Scope | Regulatory requirements and internal rules | Comprehensive review of processes, risk areas, and controls |
| Focus Area | External regulations and internal compliance | Internal controls and operational efficiency |
| Frequency | Continuous monitoring and periodic reporting | Scheduled audits and ad hoc assessments |
| Reporting | Reports to compliance officers and regulatory bodies | Reports to audit committee and senior management |
| Responsibility | Compliance department or officer | Internal audit team or department |
| Outcome | Reduced legal risks and regulatory penalties | Improved controls, risk mitigation, and governance |
Introduction to Compliance and Internal Audit
Compliance ensures that organizations adhere to laws, regulations, and internal policies to mitigate risks and avoid penalties. Internal Audit evaluates the effectiveness of governance, risk management, and control processes, providing independent assurance to management and the board. Both functions collaborate to enhance organizational accountability and operational efficiency, but Compliance focuses on regulatory adherence while Internal Audit emphasizes comprehensive risk assessment and control validation.
Defining Compliance: Scope and Objectives
Compliance encompasses adhering to laws, regulations, and internal policies to mitigate legal and financial risks within an organization. Its scope includes regulatory requirements, industry standards, and corporate governance, aiming to ensure that business operations align with mandated rules and ethical practices. The primary objectives of compliance are to prevent violations, protect organizational integrity, and maintain stakeholder trust through systematic monitoring and enforcement.
Understanding Internal Audit: Purpose and Functions
Internal audit serves as an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization's operations by evaluating the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governance processes. It systematically examines financial, operational, and compliance activities to ensure policies are properly implemented and identifies areas for improvement while mitigating risks. The internal audit function supports management by providing insights that enhance organizational performance and uphold regulatory accountability.
Key Differences Between Compliance and Internal Audit
Compliance focuses on ensuring an organization adheres to external laws, regulations, and internal policies, while internal audit evaluates and improves the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governance processes. Compliance activities are typically ongoing, monitoring specific regulatory requirements, whereas internal audit operates on a periodic basis, providing independent assessments and recommendations. The key difference lies in compliance's role as a rule enforcer and internal audit's function as an objective evaluator of overall organizational controls.
Roles and Responsibilities in Organizations
Compliance teams ensure organizations adhere to legal regulations, industry standards, and internal policies to mitigate risks and avoid penalties. Internal audit functions evaluate the effectiveness of governance, risk management, and control processes by providing independent assurance to the board and senior management. While compliance focuses on operational adherence, internal audit provides objective assessments to enhance organizational controls and promote continuous improvement.
Regulatory Requirements: Compliance vs Internal Audit
Compliance ensures that an organization adheres to external regulatory requirements, laws, and industry standards to prevent legal penalties and reputational damage. Internal audit evaluates the effectiveness of compliance programs and internal controls, providing independent assurance that regulatory obligations are met and risks are managed efficiently. Regulatory frameworks such as Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX), GDPR, and HIPAA are key benchmarks monitored by both compliance and internal audit functions.
Risk Management Approaches
Compliance focuses on ensuring adherence to laws, regulations, and internal policies, acting as a preventative risk management tool by identifying and mitigating regulatory risks. Internal audit provides an independent assessment of risk management processes, evaluating the effectiveness of controls and governance frameworks across operational, financial, and compliance risks. Both functions collaborate to enhance an organization's risk culture, with compliance implementing controls and internal audit verifying their adequacy and operational efficiency.
Collaboration and Communication Between Teams
Collaboration between Compliance and Internal Audit teams enhances risk mitigation by ensuring comprehensive review of regulatory adherence and operational controls. Clear communication channels facilitate timely sharing of insights and findings, promoting proactive issue resolution and alignment of objectives. Integrated reporting and joint risk assessments optimize resource utilization and strengthen organizational governance frameworks.
Impact on Organizational Governance
Compliance functions establish frameworks and ensure adherence to laws, regulations, and internal policies, reinforcing organizational governance by minimizing legal risks and promoting ethical behavior. Internal audit provides independent assessments of governance processes, risk management, and control effectiveness, enabling timely identification of vulnerabilities and enhancing transparency. Together, these roles strengthen decision-making, accountability, and strategic alignment within corporate governance structures.
Best Practices for Integrating Compliance and Internal Audit
Integrating compliance and internal audit functions enhances organizational governance by aligning risk management strategies with regulatory requirements. Best practices include establishing clear roles and responsibilities, fostering open communication channels, and leveraging data analytics to identify gaps and track remediation efforts. Collaborative frameworks ensure timely issue resolution, reduce duplication of efforts, and improve compliance monitoring effectiveness.
Compliance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com