A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) outlines the terms and details of a mutual agreement between parties before formal contracts are finalized. It serves as a clear framework to ensure that all parties are aligned on expectations, responsibilities, and objectives. Explore the full article to understand how an MOU can protect your interests and facilitate effective collaboration.
Table of Comparison
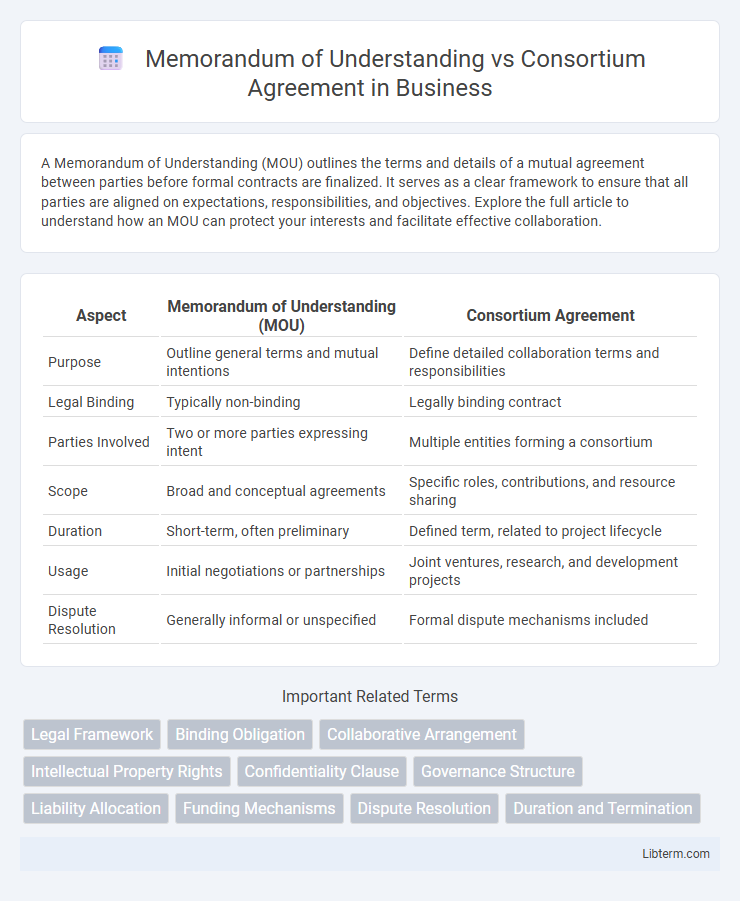
| Aspect | Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) | Consortium Agreement |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Outline general terms and mutual intentions | Define detailed collaboration terms and responsibilities |
| Legal Binding | Typically non-binding | Legally binding contract |
| Parties Involved | Two or more parties expressing intent | Multiple entities forming a consortium |
| Scope | Broad and conceptual agreements | Specific roles, contributions, and resource sharing |
| Duration | Short-term, often preliminary | Defined term, related to project lifecycle |
| Usage | Initial negotiations or partnerships | Joint ventures, research, and development projects |
| Dispute Resolution | Generally informal or unspecified | Formal dispute mechanisms included |
Introduction to Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) and Consortium Agreement
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) is a formal but non-binding document outlining the intentions and preliminary terms agreed upon by parties entering a collaboration, often used to establish a framework before detailed agreements are drafted. A Consortium Agreement is a legally binding contract that defines the roles, responsibilities, and financial arrangements among multiple organizations working together on a specific project, commonly seen in research and development initiatives. The MoU serves as an initial step to clarify mutual objectives, while the Consortium Agreement governs the operational execution and legal obligations within the partnership.
Definition and Core Purpose of MoU
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) is a formal, non-binding agreement that outlines the intentions, roles, and responsibilities of parties collaborating on a project, serving as a foundation for mutual understanding. The core purpose of an MoU is to establish a clear framework and common goals before formal contracts are negotiated, enabling parties to align expectations and cooperation parameters. Unlike a Consortium Agreement, which is legally binding and governs detailed operational aspects of joint ventures or partnerships, the MoU focuses primarily on setting preliminary terms and fostering collaboration goodwill.
Definition and Core Purpose of Consortium Agreement
A Consortium Agreement is a legal contract between multiple parties aiming to collaborate on a specific project or business objective, outlining each member's roles, responsibilities, and financial contributions. Unlike a Memorandum of Understanding, which serves as a non-binding agreement to express general intent, a Consortium Agreement establishes binding terms and procedures for joint decision-making, intellectual property rights, and risk management. The core purpose of a Consortium Agreement is to formalize cooperation among partners, ensuring clear governance and accountability throughout the project's lifecycle.
Key Differences Between MoU and Consortium Agreement
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) outlines a non-binding agreement that establishes the general intentions and cooperative framework between parties without creating legal obligations. In contrast, a Consortium Agreement is a legally binding contract that specifies the roles, responsibilities, financial contributions, intellectual property rights, and governance structure among consortium members for executing a joint project. Key differences include the MoU's function as a preliminary understanding, while the Consortium Agreement formalizes detailed operational and management terms essential for collaborative project implementation.
Legal Binding Nature: MoU vs Consortium Agreement
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) typically serves as a non-binding agreement outlining the intentions and general terms between parties, lacking enforceable legal obligations. In contrast, a Consortium Agreement is a legally binding contract that establishes specific rights, responsibilities, and liabilities among consortium members, enforceable in courts. The legal binding nature of a Consortium Agreement provides greater certainty and clarity in collaborative projects compared to the generally non-binding MoU.
Typical Use Cases of MoU and Consortium Agreements
Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) are typically used for preliminary collaborations where parties outline general intentions without binding commitments, often in diplomatic, educational, or research partnerships. Consortium Agreements are commonly employed in complex joint ventures or multi-organization projects, particularly in R&D and innovation sectors, to define detailed roles, responsibilities, financial arrangements, and intellectual property rights. MoUs facilitate initial cooperation frameworks, while Consortium Agreements govern formal, legally-binding collaboration among multiple entities.
Essential Elements in a Memorandum of Understanding
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) includes essential elements such as the purpose of the agreement, detailed roles and responsibilities of each party, and clear terms of collaboration. It often specifies the duration, confidentiality clauses, and dispute resolution mechanisms to ensure mutual understanding without creating legally binding obligations. Unlike a Consortium Agreement, which governs joint ventures for specific projects with legal enforceability, an MoU primarily outlines intentions and fosters cooperation among stakeholders.
Essential Elements in a Consortium Agreement
A Consortium Agreement essential elements include clear definitions of roles and responsibilities, detailed governance structures, and comprehensive resource allocation terms. It specifies decision-making processes, intellectual property rights, and liability distribution among participating entities. These elements ensure effective collaboration and legal clarity beyond the preliminary nature of a Memorandum of Understanding.
Pros and Cons of MoU vs Consortium Agreement
A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) offers flexibility and simplicity, making it ideal for preliminary agreements without binding commitments, but it lacks enforceability and detailed terms. In contrast, a Consortium Agreement provides a comprehensive, legally binding framework that clearly defines roles, responsibilities, and dispute resolution, enhancing collaboration security while requiring more complex negotiation and formalization. Choosing between an MoU and a Consortium Agreement depends on the project's scope, need for formal obligations, and the partners' trust level.
Choosing the Right Agreement for Your Collaboration
Selecting the appropriate agreement depends on the collaboration's purpose and legal complexity. A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) outlines non-binding intentions, ideal for initial partnerships and mutual understanding without legal obligations. Consortium Agreements define binding terms, roles, responsibilities, and intellectual property rights, suited for joint projects requiring formal governance and risk management.
Memorandum of Understanding Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com