Profit sharing boosts employee motivation by directly linking their efforts to company success, creating a sense of ownership and teamwork. This strategy enhances productivity, reduces turnover, and aligns individual goals with organizational objectives. Discover how implementing profit sharing can transform your business culture and financial growth by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
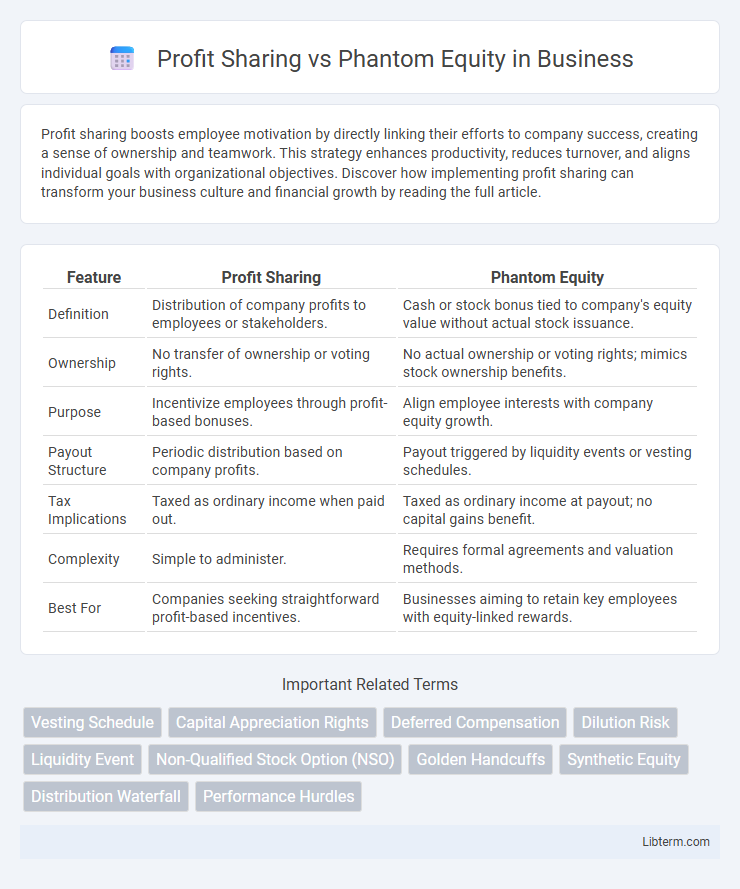
| Feature | Profit Sharing | Phantom Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distribution of company profits to employees or stakeholders. | Cash or stock bonus tied to company's equity value without actual stock issuance. |
| Ownership | No transfer of ownership or voting rights. | No actual ownership or voting rights; mimics stock ownership benefits. |
| Purpose | Incentivize employees through profit-based bonuses. | Align employee interests with company equity growth. |
| Payout Structure | Periodic distribution based on company profits. | Payout triggered by liquidity events or vesting schedules. |
| Tax Implications | Taxed as ordinary income when paid out. | Taxed as ordinary income at payout; no capital gains benefit. |
| Complexity | Simple to administer. | Requires formal agreements and valuation methods. |
| Best For | Companies seeking straightforward profit-based incentives. | Businesses aiming to retain key employees with equity-linked rewards. |
Introduction to Profit Sharing and Phantom Equity
Profit sharing is a compensation strategy where a company distributes a portion of its profits directly to employees, aligning their interests with business performance and fostering motivation. Phantom equity offers a similar incentive by granting employees the benefits of stock ownership through cash bonuses tied to the company's valuation, without transferring actual equity or voting rights. Both mechanisms aim to enhance employee engagement and retention by linking rewards to the company's financial success.
Key Differences Between Profit Sharing and Phantom Equity
Profit sharing distributes actual company profits directly to employees as cash or contributions to retirement plans, aligning compensation with company performance. Phantom equity grants employees the right to receive cash bonuses equivalent to stock value appreciation without conferring actual ownership or voting rights, simulating equity benefits. Key differences include profit sharing's reliance on current profits versus phantom equity's focus on long-term value growth, and phantom equity's ability to motivate retention through deferred payouts tied to company valuation.
How Profit Sharing Plans Work
Profit sharing plans distribute a portion of company profits to employees based on predetermined formulas, aligning their interests with overall business success. Contributions to these plans are typically discretionary, allowing employers flexibility in determining payout amounts and timing, often based on annual net income. Unlike phantom equity, profit sharing does not confer ownership, but provides direct financial incentives tied to the company's profitability.
Understanding Phantom Equity Arrangements
Phantom equity arrangements grant employees the financial benefits of stock ownership without actual equity transfer, creating a cash bonus tied to company valuation or performance milestones. Unlike profit sharing, which distributes a portion of company profits regularly, phantom equity mimics stock ownership, aligning employee incentives with long-term company growth. These arrangements often include vesting schedules and payout triggered by liquidity events, enhancing retention and motivation within privately held firms.
Advantages of Profit Sharing
Profit sharing offers employees a direct stake in company earnings, enhancing motivation and aligning individual goals with business success. It provides immediate financial rewards based on actual profits, which can improve employee retention and foster a culture of teamwork. Unlike phantom equity, profit sharing does not dilute ownership, allowing founders to maintain full control while still incentivizing staff.
Benefits of Phantom Equity
Phantom equity offers employees the benefits of equity ownership without diluting company shares or requiring actual stock issuance, aligning employee incentives with long-term company performance. This structure provides cash bonuses tied to company valuation, which motivates retention and enhances employee loyalty without transferring voting rights or ownership risks. Phantom equity plans are flexible, customizable, and simpler to administer compared to traditional stock options or profit sharing, making them attractive for privately-held companies seeking to reward key talent.
Drawbacks and Risks of Profit Sharing
Profit sharing can create dependency among employees on business fluctuations, potentially leading to income instability and reduced motivation during unprofitable periods. This approach may also dilute individual performance incentives, as rewards are tied to overall company profits rather than personal contributions. Furthermore, profit sharing schemes can cause internal conflicts if transparency is lacking or if employees perceive the distribution as unfair.
Potential Downsides of Phantom Equity
Phantom equity plans can create complex tax implications for both employees and employers, as payouts are typically taxed as ordinary income without the benefit of capital gains treatment. These arrangements may also expose companies to long-term financial liabilities due to the obligation to pay out cash or stock equivalents at a future date, potentially impacting cash flow. Moreover, phantom equity lacks shareholder voting rights and actual ownership, which might reduce employee motivation compared to traditional profit-sharing or equity grants.
Choosing the Right Incentive Plan for Your Business
Selecting the right incentive plan for your business depends on your goals, company structure, and employee motivation strategies. Profit sharing distributes actual profits, directly rewarding employees with a tangible share of company success, ideal for fostering a performance-driven culture. Phantom equity offers stock value benefits without diluting ownership, providing long-term incentives aligned with company growth without formal equity issuance.
Legal and Tax Considerations for Profit Sharing and Phantom Equity
Profit sharing plans are subject to specific IRS regulations under Section 401(k) and ERISA, often requiring formal plan documentation and adherence to nondiscrimination rules to maintain tax-qualified status. Phantom equity, treated as a form of deferred compensation under Section 409A, mandates careful structuring to avoid adverse tax implications, with payouts typically taxed as ordinary income upon vesting or exercise. Legal compliance for profit sharing entails fiduciary responsibilities and regular reporting requirements, whereas phantom equity agreements must clearly define valuation methods and trigger events to mitigate disputes and ensure enforceability.
Profit Sharing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com