User innovation drives product development by allowing individuals to create and modify solutions tailored to their unique needs. This process empowers users to contribute valuable insights, leading to more effective and customized innovations. Discover how embracing user innovation can enhance your creativity and problem-solving by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
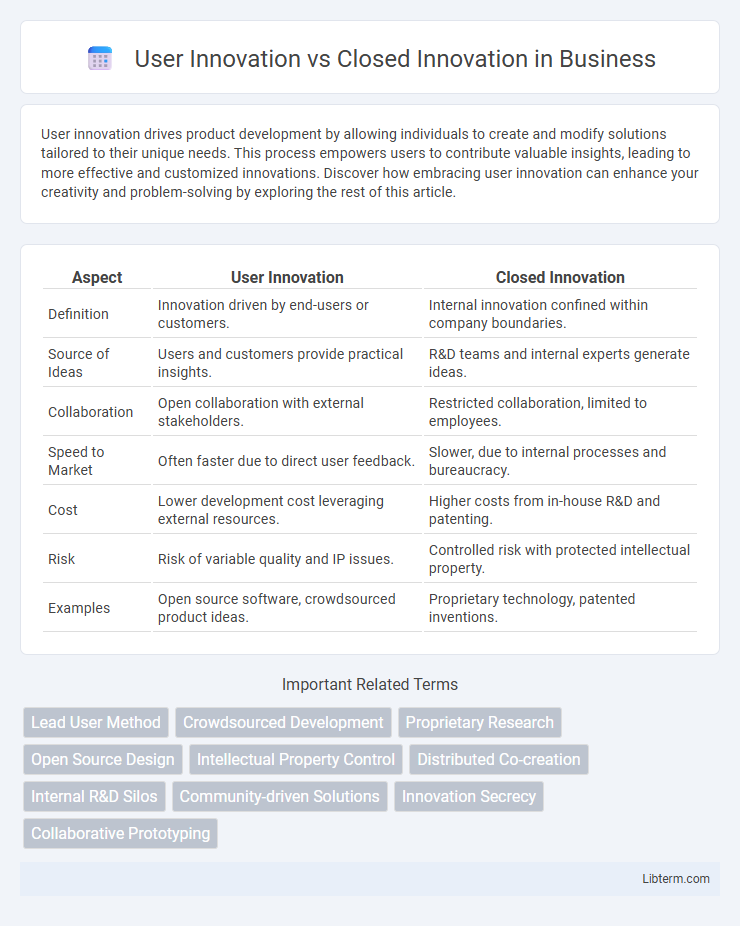
| Aspect | User Innovation | Closed Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Innovation driven by end-users or customers. | Internal innovation confined within company boundaries. |
| Source of Ideas | Users and customers provide practical insights. | R&D teams and internal experts generate ideas. |
| Collaboration | Open collaboration with external stakeholders. | Restricted collaboration, limited to employees. |
| Speed to Market | Often faster due to direct user feedback. | Slower, due to internal processes and bureaucracy. |
| Cost | Lower development cost leveraging external resources. | Higher costs from in-house R&D and patenting. |
| Risk | Risk of variable quality and IP issues. | Controlled risk with protected intellectual property. |
| Examples | Open source software, crowdsourced product ideas. | Proprietary technology, patented inventions. |
Understanding User Innovation: A Modern Approach
User innovation emphasizes the active role of consumers and end-users in developing new products or improving existing ones, leveraging their firsthand experience and specific needs. This modern approach contrasts with closed innovation, where research and development are restricted within company boundaries, limiting external contributions and insights. Embracing user innovation accelerates creativity, reduces market risks, and fosters collaborative ecosystems that drive sustainable competitive advantages.
Defining Closed Innovation: Traditional Boundaries
Closed Innovation is defined by its reliance on internal resources and strict control over intellectual property, limiting collaboration to within the company's established boundaries. This traditional approach prioritizes secrecy and proprietary development processes, ensuring that innovations are carefully managed and protected from external influence. Corporations practicing Closed Innovation often restrict access to research and development, maintaining competitive advantages through exclusive knowledge and internal expertise.
Historical Evolution of Innovation Models
User innovation emerged prominently in the late 20th century as users began actively modifying and creating products to meet personal needs, contrasting with closed innovation models that dominated the early industrial era where firms relied solely on internal R&D. The closed innovation paradigm, prevalent until the 1980s, emphasized proprietary development within organizational boundaries, restricting knowledge flow and market feedback. With the advent of digital technologies and the internet, open collaboration gained traction, highlighting the shift towards user-driven innovation ecosystems and collaborative networks that challenge traditional closed innovation frameworks.
Key Differences: User Innovation vs Closed Innovation
User Innovation leverages ideas and solutions generated by end-users, promoting collaborative development and faster adaptation to market needs. Closed Innovation relies on internal R&D processes within a company, focusing on proprietary knowledge and controlled innovation pipelines to protect competitive advantage. The key difference lies in openness and source of innovation: User Innovation taps external creativity while Closed Innovation emphasizes internal expertise and secrecy.
Advantages of User Innovation for Businesses
User innovation empowers businesses by harnessing creative solutions directly from end-users, leading to products that better meet market needs and increase customer satisfaction. This approach reduces R&D costs and accelerates the innovation cycle by leveraging external insights and real-world feedback. Embracing user innovation enhances competitive advantage through continuous product improvement and fosters stronger customer loyalty.
Limitations of Closed Innovation in Today’s Market
Closed innovation restricts idea generation to internal R&D teams, limiting access to diverse perspectives and expertise that drive breakthrough solutions. This approach often leads to slower innovation cycles and higher costs due to redundant efforts and lack of external feedback. In today's fast-paced markets, relying solely on closed innovation results in missed opportunities for collaboration and adaptation to rapidly changing consumer demands.
Case Studies: Success Stories from Both Models
User innovation thrives in cases like LEGO Ideas, where community-driven designs generate popular products, demonstrating how user insights fuel creativity and market success. Closed innovation exemplified by Apple's secretive development of the iPhone highlights disciplined R&D, preserving competitive advantage and delivering groundbreaking technology. Both models showcase distinct pathways to innovation success, emphasizing user engagement or proprietary control as key strategic elements.
Impact on Product Development and Speed to Market
User innovation accelerates product development by integrating direct feedback from end-users, enabling rapid iteration and highly tailored solutions that meet market demands more effectively. In contrast, closed innovation relies on internal R&D processes, which can slow down speed to market due to longer development cycles and limited external input. Companies leveraging user innovation often achieve faster market entry and increased product relevance, driving competitive advantage in dynamic industries.
Facilitating Transition: From Closed to User Innovation
Facilitating the transition from closed innovation to user innovation requires establishing open collaboration platforms that empower users to contribute ideas, prototypes, and feedback directly. Integrating user-generated insights with internal R&D processes accelerates product development and enhances customization, driving competitive advantage. Leveraging digital tools such as crowdsourcing portals and community forums ensures continuous user engagement and effective knowledge exchange.
Future Trends in Innovation Management
User innovation increasingly drives future trends by empowering customers and communities to co-create products, resulting in faster adaptation and personalized solutions. Closed innovation models, traditionally reliant on internal R&D and proprietary knowledge, face challenges in agility and scalability within rapidly changing markets. Hybrid approaches integrating open user contributions with secure internal processes are emerging as a strategic trend in innovation management to balance creativity with control.
User Innovation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com