Reshoring brings manufacturing jobs back to your home country, reducing reliance on overseas suppliers and cutting transportation costs. It enhances supply chain resilience and promotes local economic growth by revitalizing industries. Discover how reshoring can benefit your business and the broader economy in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
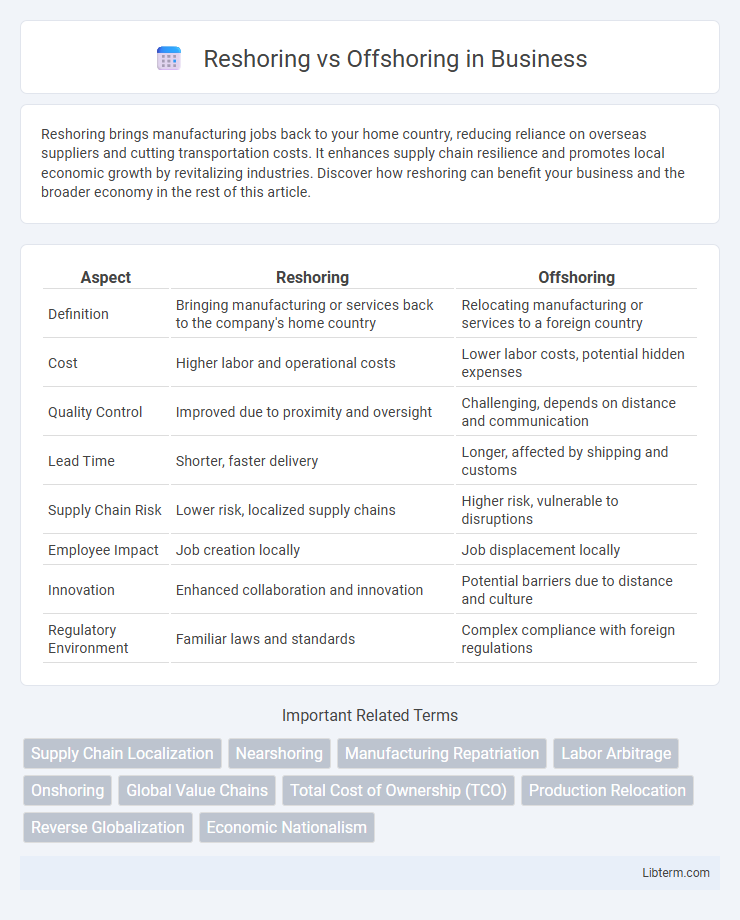
| Aspect | Reshoring | Offshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bringing manufacturing or services back to the company's home country | Relocating manufacturing or services to a foreign country |
| Cost | Higher labor and operational costs | Lower labor costs, potential hidden expenses |
| Quality Control | Improved due to proximity and oversight | Challenging, depends on distance and communication |
| Lead Time | Shorter, faster delivery | Longer, affected by shipping and customs |
| Supply Chain Risk | Lower risk, localized supply chains | Higher risk, vulnerable to disruptions |
| Employee Impact | Job creation locally | Job displacement locally |
| Innovation | Enhanced collaboration and innovation | Potential barriers due to distance and culture |
| Regulatory Environment | Familiar laws and standards | Complex compliance with foreign regulations |
Introduction to Reshoring and Offshoring
Reshoring involves relocating manufacturing or business operations back to the company's original country to enhance control, reduce supply chain risks, and support local economies. Offshoring refers to transferring business processes or production to foreign countries, often to leverage cost advantages, specialized skills, or market access. Both strategies play pivotal roles in global supply chain management, influencing economic, operational, and competitive dynamics.
Key Definitions and Concepts
Reshoring refers to the process of bringing manufacturing and services back to a company's original country, countering the offshoring strategy of relocating production to foreign locations to reduce costs. Key concepts in reshoring include cost-benefit analysis, supply chain resilience, and domestic job creation, while offshoring emphasizes labor arbitrage, operational efficiency, and global market access. Understanding these definitions helps businesses optimize sourcing strategies for competitive advantage and risk management.
Historical Overview of Manufacturing Trends
Manufacturing trends have fluctuated between offshoring and reshoring due to shifts in economic factors and global supply chain dynamics. Offshoring surged in the late 20th century as companies sought lower labor costs in countries like China and Mexico, driving mass relocation of production facilities. Recent decades have seen a resurgence in reshoring efforts, driven by rising overseas wages, trade uncertainties, and advancements in automation technology.
Primary Drivers Behind Offshoring
Cost reduction remains the primary driver behind offshoring, with companies seeking lower labor expenses and operational costs in emerging markets. Access to specialized skills and advanced manufacturing capabilities in countries like China and India also motivates businesses to offshore production. Furthermore, efforts to expand into global markets and leverage local supply chain efficiencies contribute significantly to offshoring decisions.
Emerging Motivations for Reshoring
Rising labor costs in traditional offshore locations and increasing supply chain risks have driven companies to reshore manufacturing operations closer to home markets. Technological advancements like automation and robotics reduce dependence on cheap labor, making reshoring more economically viable in developed countries. Growing consumer demand for locally made products and increased regulatory pressures on sustainability also motivate firms to prioritize reshoring strategies.
Cost Analysis: Reshoring vs Offshoring
Reshoring often reduces long-term costs by minimizing supply chain disruptions, lowering transportation expenses, and enhancing quality control, despite higher initial labor expenses compared to offshoring. Offshoring typically offers lower direct labor costs and access to large, skilled labor pools but incurs added costs in logistics, tariffs, and longer lead times that can impact overall profitability. A comprehensive cost analysis must consider total landed costs, including inventory carrying costs, risk management, and potential tariff impacts to determine the most cost-effective sourcing strategy.
Impact on Supply Chain Efficiency
Reshoring enhances supply chain efficiency by reducing lead times and minimizing transportation costs, leading to more responsive and flexible operations. Offshoring often introduces delays and complexity due to longer shipping routes and increased risk of disruption from geopolitical factors. Companies prioritizing resiliency increasingly favor reshoring to improve inventory management and streamline supply chain visibility.
Economic and Employment Implications
Reshoring manufacturing operations can boost domestic job creation by revitalizing local labor markets and increasing wage competitiveness, while offshoring often reduces production costs but may lead to job losses in the home country. Economic implications include reshoring driving investments in advanced manufacturing technologies and improving supply chain resilience, whereas offshoring lowers operational expenses but may increase exposure to geopolitical risks. Balancing reshoring and offshoring strategies impacts national economic growth, workforce skill development, and overall industrial competitiveness.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Reshoring reduces carbon emissions by minimizing long-distance transportation and promoting local supply chains, enhancing overall environmental sustainability. Offshoring often leads to higher environmental risks due to varying regulations, increased energy consumption, and waste management challenges in remote manufacturing sites. Companies prioritizing sustainability increasingly favor reshoring to align operations with stricter environmental standards and reduce their global carbon footprint.
Strategic Recommendations for Businesses
Businesses aiming for resiliency should prioritize reshoring to mitigate supply chain disruptions and reduce lead times. Investing in automation and local talent development enhances cost-efficiency and operational agility in reshoring initiatives. Leveraging advanced analytics to evaluate total cost of ownership between offshore and nearshore options informs strategic decisions aligned with market dynamics.
Reshoring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com