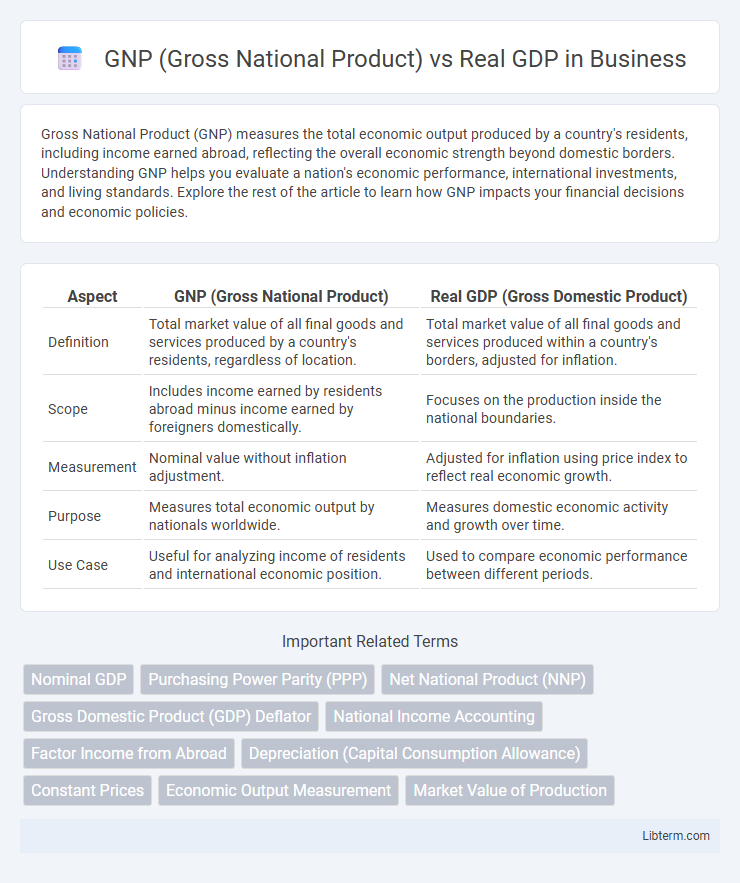
Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total economic output produced by a country's residents, including income earned abroad, reflecting the overall economic strength beyond domestic borders. Understanding GNP helps you evaluate a nation's economic performance, international investments, and living standards. Explore the rest of the article to learn how GNP impacts your financial decisions and economic policies.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | GNP (Gross National Product) | Real GDP (Gross Domestic Product) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total market value of all final goods and services produced by a country's residents, regardless of location. | Total market value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders, adjusted for inflation. |
| Scope | Includes income earned by residents abroad minus income earned by foreigners domestically. | Focuses on the production inside the national boundaries. |
| Measurement | Nominal value without inflation adjustment. | Adjusted for inflation using price index to reflect real economic growth. |
| Purpose | Measures total economic output by nationals worldwide. | Measures domestic economic activity and growth over time. |
| Use Case | Useful for analyzing income of residents and international economic position. | Used to compare economic performance between different periods. |
Introduction to GNP and Real GDP
Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total market value of all goods and services produced by a country's residents, both domestically and abroad, within a specific time period. Real GDP, on the other hand, calculates the value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders, adjusted for inflation to reflect actual economic growth. Understanding the distinction between GNP and Real GDP is essential for analyzing national economic performance and international income flows.
Defining Gross National Product (GNP)
Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total market value of all final goods and services produced by the residents of a country, regardless of whether the production occurs domestically or abroad, distinguishing it from Gross Domestic Product (GDP) which limits to domestic production. GNP includes net income earned from abroad, capturing the economic output generated by a nation's citizens and businesses internationally. This metric helps evaluate the overall economic performance including overseas investments and income from foreign operations owned by residents.
Understanding Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP)
Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP) measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country's borders, adjusted for inflation to reflect true economic growth. Unlike GNP, which includes income earned by a nation's residents abroad, Real GDP focuses solely on domestic production, providing a clearer picture of a country's economic performance over time. Tracking Real GDP enables accurate comparisons across different periods by removing the effects of price changes.
Key Differences Between GNP and Real GDP
Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total market value of all goods and services produced by a country's residents, both domestically and abroad, whereas Real GDP calculates the value of goods and services produced within a country's borders adjusted for inflation. Key differences include GNP accounting for income earned by citizens overseas and excluding foreign residents' income, while Real GDP focuses strictly on domestic production regardless of ownership. Real GDP provides a precise gauge of domestic economic activity, making it essential for analyzing economic growth, whereas GNP reflects the overall economic strength and income of a nation's residents globally.
Components Included in GNP vs Real GDP
Gross National Product (GNP) includes the total market value of all final goods and services produced by a country's residents, regardless of location, encompassing income earned by citizens abroad and excluding income earned by foreigners domestically. Real GDP measures the value of goods and services produced within a country's borders, adjusted for inflation, focusing solely on domestic economic activity. Key components of GNP consist of consumption, investment, government spending, and net income from abroad, while Real GDP comprises consumption, investment, government expenditure, and net exports confined to domestic production.
Calculation Methods for GNP and Real GDP
GNP (Gross National Product) is calculated by adding the total market value of all final goods and services produced by a nation's residents, both domestically and abroad, and subtracting the income earned by foreign residents within the country. Real GDP measures the value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders, adjusted for inflation, using constant base-year prices to reflect true economic growth. The primary difference in calculation lies in GNP accounting for net income from abroad, while Real GDP focuses solely on domestic production adjusted for price level changes.
Importance of GNP and Real GDP in Economic Analysis
GNP (Gross National Product) measures the total income earned by a country's residents and businesses, including international income, providing insights into national economic strength and global economic influence. Real GDP adjusts for inflation to reflect the true value of goods and services produced domestically, enabling accurate comparisons of economic performance over time. Analyzing both GNP and Real GDP is crucial for policymakers to assess economic health, guide fiscal policy, and formulate strategies for sustainable economic growth.
Advantages and Limitations of GNP
Gross National Product (GNP) measures the total market value of all final goods and services produced by a country's residents, including income from abroad, whereas Real GDP accounts for the value of goods and services produced within a country's borders adjusted for inflation. GNP's advantage lies in capturing the economic activities of citizens and businesses internationally, providing a broader perspective on national income and economic strength. However, GNP's limitations include its failure to reflect domestic economic conditions accurately and potential distortion from fluctuating foreign income flows, which can complicate comparative economic analysis.
Advantages and Limitations of Real GDP
Real GDP measures the value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders adjusted for inflation, providing a more accurate reflection of economic performance over time compared to nominal figures. It excludes income earned by nationals abroad, unlike GNP, which can be advantageous for analyzing domestic economic activity and living standards. However, Real GDP does not account for non-market transactions, income distribution, or environmental degradation, limiting its ability to fully capture economic well-being.
Choosing the Right Economic Indicator: GNP or Real GDP
GNP measures the total economic output produced by a country's residents, including income from abroad, while Real GDP calculates the value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders, adjusted for inflation. Choosing between GNP and Real GDP depends on the focus of economic analysis: GNP is ideal for assessing national income and international economic activity, whereas Real GDP provides a precise measure of domestic economic performance and growth. Policymakers use Real GDP to track economic health over time, but GNP offers insights into a nation's total economic strength, especially for countries with significant income from or to foreign investments.
GNP (Gross National Product) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com