Cultural mediation bridges gaps between diverse communities, facilitating understanding and collaboration by resolving conflicts and promoting mutual respect. It plays a crucial role in education, healthcare, and social services to ensure inclusive communication and equitable access. Discover how cultural mediation can enhance your interactions and improve cross-cultural relationships throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
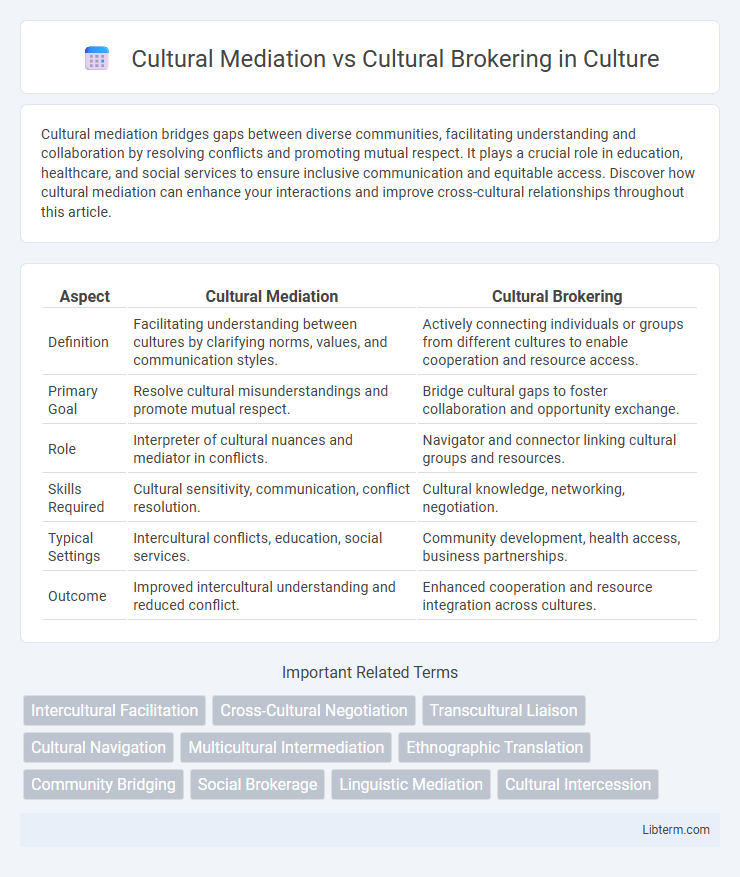
| Aspect | Cultural Mediation | Cultural Brokering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Facilitating understanding between cultures by clarifying norms, values, and communication styles. | Actively connecting individuals or groups from different cultures to enable cooperation and resource access. |
| Primary Goal | Resolve cultural misunderstandings and promote mutual respect. | Bridge cultural gaps to foster collaboration and opportunity exchange. |
| Role | Interpreter of cultural nuances and mediator in conflicts. | Navigator and connector linking cultural groups and resources. |
| Skills Required | Cultural sensitivity, communication, conflict resolution. | Cultural knowledge, networking, negotiation. |
| Typical Settings | Intercultural conflicts, education, social services. | Community development, health access, business partnerships. |
| Outcome | Improved intercultural understanding and reduced conflict. | Enhanced cooperation and resource integration across cultures. |
Introduction to Cultural Mediation and Cultural Brokering
Cultural mediation facilitates understanding and communication between individuals or groups from different cultural backgrounds by interpreting values, norms, and customs to reduce conflict. Cultural brokering involves actively negotiating and bridging cultural differences, often in institutional settings, to advocate and support marginalized communities. Both practices are essential in enhancing cross-cultural interactions, yet mediation emphasizes communication facilitation while brokering centers on negotiation and advocacy.
Defining Cultural Mediation
Cultural mediation involves facilitating understanding and communication between individuals or groups from different cultural backgrounds to resolve conflicts and foster mutual respect. It emphasizes interpreting cultural norms, values, and practices to bridge gaps and enhance intercultural dialogue. This process often requires skilled negotiators who can sensitively address cultural differences without imposing one culture over another.
Understanding Cultural Brokering
Cultural brokering involves acting as an intermediary between individuals or groups from different cultural backgrounds to facilitate communication, understanding, and conflict resolution. Unlike cultural mediation, which often focuses on resolving disputes through dialogue, cultural brokering encompasses a broader role that includes interpreting cultural norms, negotiating differences, and fostering trust in diverse settings such as healthcare, education, and social services. Effective cultural brokers possess deep cultural knowledge, linguistic skills, and the ability to navigate complex social systems to bridge gaps and promote inclusion.
Historical Origins of Both Concepts
Cultural mediation originated in the fields of anthropology and intercultural communication during the mid-20th century, emphasizing the role of mediators in facilitating mutual understanding between diverse cultural groups. Cultural brokering has roots in social work and community organization, particularly emerging in the 1980s as a strategy to help immigrants and marginalized populations navigate institutional systems and access resources. Both concepts address cross-cultural interactions but differ historically in their primary focus and application contexts.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Cultural mediation involves facilitating understanding and communication between individuals from different cultural backgrounds, emphasizing conflict resolution and mutual respect. Cultural brokers actively bridge gaps by translating cultural norms, values, and practices to enable access to services or resources, often advocating for marginalized groups. Both roles require deep cultural competence, effective communication skills, and the ability to navigate complex social systems to promote inclusion and equity.
Skills Required for Each Approach
Cultural mediation requires advanced intercultural communication skills, empathy, and the ability to facilitate mutual understanding between parties from diverse cultural backgrounds. Cultural brokering demands negotiation skills, conflict resolution abilities, and a strong knowledge of both cultures' social norms and values to effectively bridge gaps between communities and institutions. Both approaches emphasize cultural competence but differ in their practical applications and the specific skills needed to navigate and reconcile cultural differences.
Comparative Analysis: Similarities and Differences
Cultural mediation and cultural brokering both serve to bridge gaps between diverse cultural groups by facilitating communication and understanding, yet cultural mediation emphasizes resolving conflicts through dialogue and negotiation, while cultural brokering involves actively navigating and translating cultural norms and systems to enable access to services or resources. Both roles require deep cultural competence and interpersonal skills, but mediators often work in formal dispute resolution settings, whereas brokers typically function within community engagement or institutional contexts. Understanding these nuanced distinctions enhances effective cross-cultural interaction and promotes equitable outcomes in multicultural environments.
Practical Applications in Diverse Settings
Cultural mediation involves facilitating understanding and resolving conflicts between differing cultural groups by interpreting social norms and values, commonly applied in healthcare, education, and immigration services to improve communication and trust. Cultural brokering emphasizes negotiating and bridging cultural gaps by actively advocating for marginalized communities, often utilized in social work, legal aid, and community development to ensure equitable access to resources. Both approaches enhance cross-cultural interactions by addressing cultural barriers and promoting inclusion in diverse settings.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Cultural mediation and cultural brokering both address cross-cultural communication but present distinct challenges, such as navigating differing cultural norms and managing expectations between parties. Ethical considerations include maintaining impartiality, respecting confidentiality, and avoiding cultural imposition or bias that can undermine trust and authenticity. Practitioners must balance advocacy with neutrality to ensure equitable representation without compromising professional integrity.
Choosing the Right Approach: Mediation vs Brokering
Choosing the right approach between cultural mediation and cultural brokering depends on the context and goals of the interaction. Cultural mediation emphasizes facilitating understanding and communication between parties by interpreting cultural meaning, while cultural brokering involves actively negotiating and bridging gaps to create mutual agreements or solutions. Selecting mediation suits situations focused on dialogue and awareness, whereas brokering is ideal for resolving conflicts or establishing partnerships across cultural divides.
Cultural Mediation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com