A mixed economy combines elements of both private enterprise and government intervention, balancing free market principles with regulatory policies to promote economic stability and growth. This system allows for private businesses to operate competitively while the government provides essential services and addresses market failures. Discover how a mixed economy can impact your financial future and societal well-being in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
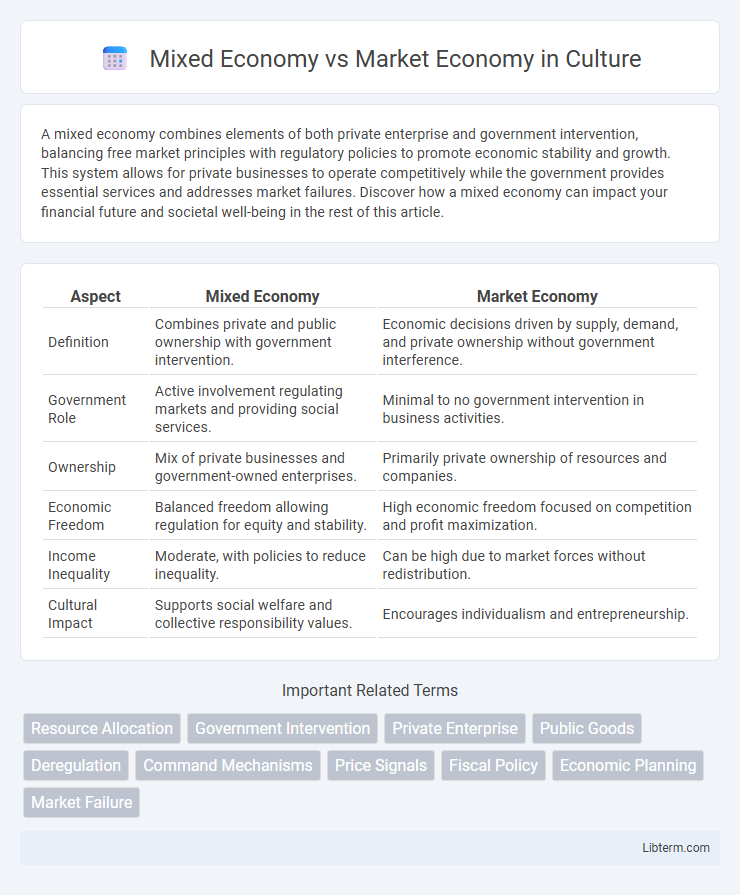
| Aspect | Mixed Economy | Market Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines private and public ownership with government intervention. | Economic decisions driven by supply, demand, and private ownership without government interference. |
| Government Role | Active involvement regulating markets and providing social services. | Minimal to no government intervention in business activities. |
| Ownership | Mix of private businesses and government-owned enterprises. | Primarily private ownership of resources and companies. |
| Economic Freedom | Balanced freedom allowing regulation for equity and stability. | High economic freedom focused on competition and profit maximization. |
| Income Inequality | Moderate, with policies to reduce inequality. | Can be high due to market forces without redistribution. |
| Cultural Impact | Supports social welfare and collective responsibility values. | Encourages individualism and entrepreneurship. |
Introduction to Economic Systems
A mixed economy blends elements of both market and planned economic systems, allowing government intervention alongside private enterprise to balance efficiency and social welfare. In contrast, a market economy operates primarily on supply and demand with minimal government interference, emphasizing free competition and consumer choice. Understanding these economic systems is crucial for analyzing how resources are allocated and economic policies are formulated globally.
Defining Mixed Economy
A mixed economy combines elements of both market and command economies, blending private enterprise with government intervention to regulate economic activities. This system allows market forces to drive supply and demand while enabling public policies to address market failures, promote social welfare, and ensure economic stability. Countries like the United States and Sweden exemplify mixed economies by balancing free-market dynamics with government programs and regulations.
Understanding Market Economy
A market economy operates primarily on the principles of supply and demand, where prices and production are determined by unrestricted competition among private businesses. It fosters innovation and efficiency through minimal government intervention, allowing consumers and producers to make independent economic decisions. Understanding market economies involves recognizing the role of decentralized decision-making and the importance of property rights in promoting economic growth.
Key Features of Mixed Economy
A mixed economy combines elements of both market and planned economies, blending private enterprise with government intervention to regulate production, distribution, and resource allocation. Key features include coexisting public and private sectors, government regulations to correct market failures, and social welfare programs to ensure economic stability and equitable wealth distribution. This hybrid system aims to balance economic efficiency with social equity, fostering sustainable growth while protecting public interests.
Core Principles of Market Economy
Market economies operate on the core principles of supply and demand, where prices are determined by voluntary exchanges between consumers and producers, ensuring efficient allocation of resources. Private ownership and minimal government intervention promote competition, innovation, and consumer choice. Profit motives drive businesses to optimize production and respond dynamically to market signals, differentiating market economies from mixed economies that incorporate varying degrees of government regulation.
Government Role in Mixed and Market Economies
In a mixed economy, the government plays a crucial role by regulating industries, providing public goods, and intervening to correct market failures while allowing private enterprise to operate freely. In contrast, a market economy relies predominantly on supply and demand forces with minimal government interference, where private businesses and consumers drive economic decisions. Government involvement in mixed economies aims to balance economic efficiency with social welfare, ensuring equitable distribution and stability.
Advantages of Mixed Economy
A mixed economy combines the efficiency of market economies with government intervention to ensure social welfare, addressing market failures and reducing income inequality. It promotes economic stability through regulatory policies while encouraging private enterprise and innovation. This balance enables sustainable growth, improved public services, and protection of consumers and workers.
Benefits of Market Economy
Market economy promotes efficient resource allocation by relying on supply and demand dynamics, encouraging innovation and competition. It fosters individual entrepreneurship, leading to diverse product offerings and economic growth. Consumer preferences directly influence production, enhancing responsiveness and market adaptability.
Challenges and Critiques of Each System
Mixed economies face challenges in balancing government intervention with free market forces, often leading to inefficiencies, regulatory overreach, and bureaucratic delays. Market economies frequently encounter critiques related to income inequality, market failures, and the lack of social safety nets, which can result in economic instability and social unrest. Both systems must address trade-offs between economic freedom and government control to achieve sustainable growth and equitable resource distribution.
Mixed Economy vs Market Economy: Comparative Analysis
Mixed economy blends private enterprise with government intervention, ensuring regulation in key sectors to balance economic growth and social welfare. Market economy relies primarily on supply and demand with minimal state interference, promoting competition and efficiency but risking inequality and market failures. Comparative analysis reveals mixed economies mitigate market risks through state policies, while market economies emphasize innovation and consumer choice driven by free market forces.
Mixed Economy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com