Utopianism explores the vision of an ideal society where harmony, justice, and equality prevail, inspiring efforts to create better social, political, and economic systems. This concept has influenced literature, philosophy, and social movements by challenging the status quo and imagining progressive futures. Discover how utopian ideas can shape Your perspective on societal improvement in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
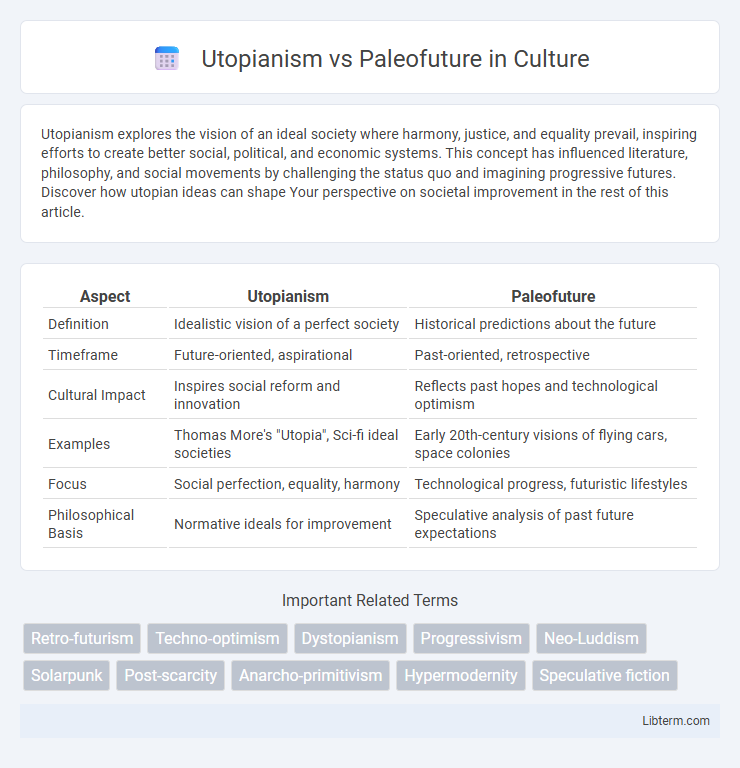
| Aspect | Utopianism | Paleofuture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Idealistic vision of a perfect society | Historical predictions about the future |
| Timeframe | Future-oriented, aspirational | Past-oriented, retrospective |
| Cultural Impact | Inspires social reform and innovation | Reflects past hopes and technological optimism |
| Examples | Thomas More's "Utopia", Sci-fi ideal societies | Early 20th-century visions of flying cars, space colonies |
| Focus | Social perfection, equality, harmony | Technological progress, futuristic lifestyles |
| Philosophical Basis | Normative ideals for improvement | Speculative analysis of past future expectations |
Understanding Utopianism: Origins and Ideals
Utopianism originated in the early 16th century with Thomas More's seminal work "Utopia," envisioning an ideal society based on justice, equality, and rational governance. This philosophical ideal contrasts sharply with Paleofuture, which explores historical predictions about the future, often highlighting technological optimism and socio-political expectations rooted in past cultural contexts. Understanding Utopianism involves examining its foundational ideals of perfectibility and social harmony as responses to contemporary societal flaws, influencing modern political and social theory.
Defining Paleofuture: Looking Back at Yesterday’s Tomorrow
Paleofuture explores how past generations envisioned the future, analyzing outdated predictions, technologies, and societal expectations that once shaped tomorrow's vision. This study contrasts sharply with utopianism, which imagines ideal futures without the constraints of historical inaccuracies or disillusionments. By examining artifacts, literature, and media from previous eras, paleofuture reveals the evolving hopes and fears that influenced technological and cultural aspirations.
Key Philosophical Differences Between Utopianism and Paleofuture
Utopianism envisions an idealized future society characterized by perfect social, political, and economic conditions, emphasizing human progress and moral improvement. Paleofuture approaches future predictions critically, analyzing historical visions of the future while highlighting the limitations and socio-cultural biases embedded in past futuristic ideologies. Key philosophical differences center on Utopianism's normative goals of achieving perfection versus Paleofuture's descriptive and analytical focus on how past futures were imagined and why those visions succeeded or failed.
Historical Visions: Utopias Through the Ages
Historical visions of utopia have evolved from classical ideal societies like Plato's Republic to Renaissance humanist sketches, emphasizing ideal governance and social harmony. Paleofuture perspectives reveal how early 20th-century technological optimism shaped futuristic predictions, blending utopian aspirations with emerging innovations such as flying cars and automated homes. These shifts illustrate the dynamic interplay between cultural ideals and technological advancements influencing utopian narratives across different eras.
Retro-Futurism: The Essence of Paleofuture Aesthetics
Retro-futurism embodies the core of paleofuture aesthetics by blending past visions of the future with nostalgic design elements, reflecting how earlier eras imagined technological and social advancements. This aesthetic often features chrome finishes, streamlined shapes, and vibrant, optimistic color schemes that symbolize mid-20th-century futurism. Utopianism contrasts with retro-futurism's nostalgic lens by emphasizing idealized, forward-looking societal models free from past constraints.
Social Impacts: How Utopianism Shaped Modern Society
Utopianism profoundly influenced modern society by inspiring reform movements that sought ideal social, economic, and political structures, leading to advancements in education, human rights, and urban planning. Its visionary narratives encouraged collective progress, fostering inclusive policies aimed at reducing inequality and promoting social welfare. In contrast, paleofuture perspectives often highlight the cautionary potential of technological and societal forecasts, emphasizing realistic assessments rather than idealistic aspirations.
Paleofuturism in Art, Literature, and Popular Culture
Paleofuturism in art, literature, and popular culture explores past predictions of the future, often highlighting retro-futuristic aesthetics and outdated technological visions. This movement captures nostalgic imaginations of progress, blending vintage design elements such as flying cars and robot assistants with mid-20th-century optimism. Influential works include films like "Metropolis" and graphic novels like "The Jetsons," reflecting a cultural fascination with how past societies envisioned tomorrow's world.
Criticisms and Limitations of Utopian Thinking
Utopianism often faces criticism for its impractical idealism and failure to account for complex socio-economic and political realities, leading to unrealistic expectations and potential disenfranchisement. Paleofuture perspectives highlight how many utopian visions from the past failed to materialize due to technological constraints and human unpredictability. The limitations of utopian thinking include its tendency to oversimplify human nature and ignore unintended consequences, which can result in rigid or authoritarian implementations.
Lessons from Paleofuture: Misplaced Hopes and Timeless Dreams
Paleofuture reveals how past visions of utopian technologies often underestimated complexities, teaching that technological optimism must be tempered with pragmatic foresight. Analyzing historical predictions exposes recurring patterns of misplaced hopes, emphasizing that progress depends on adaptable, realistic planning rather than idealized futures. These lessons underscore the importance of balancing innovation with ethical considerations and social impact when envisioning utopian futures.
Utopian Futures vs. Nostalgic Tomorrows: Relevance in Today’s World
Utopian futures envision idealized societies driven by progressive innovation, social equality, and sustainable development, reflecting humanity's aspirations for a better tomorrow. Paleofuture, or nostalgic tomorrows, romanticizes past predictions of the future, highlighting how earlier generations imagined technology and society's evolution, often revealing optimism and anxieties specific to their eras. In today's world, the tension between utopian futures and nostalgic tomorrows underscores the importance of balancing visionary goals with lessons from historical perspectives to guide realistic and inclusive development strategies.
Utopianism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com