Geocentric models place Earth at the center of the universe, a concept that shaped ancient astronomy and influenced early scientific thought. This perspective was widely accepted until the heliocentric model provided a more accurate understanding of planetary motion. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how geocentric ideas evolved and impacted modern astronomy.
Table of Comparison
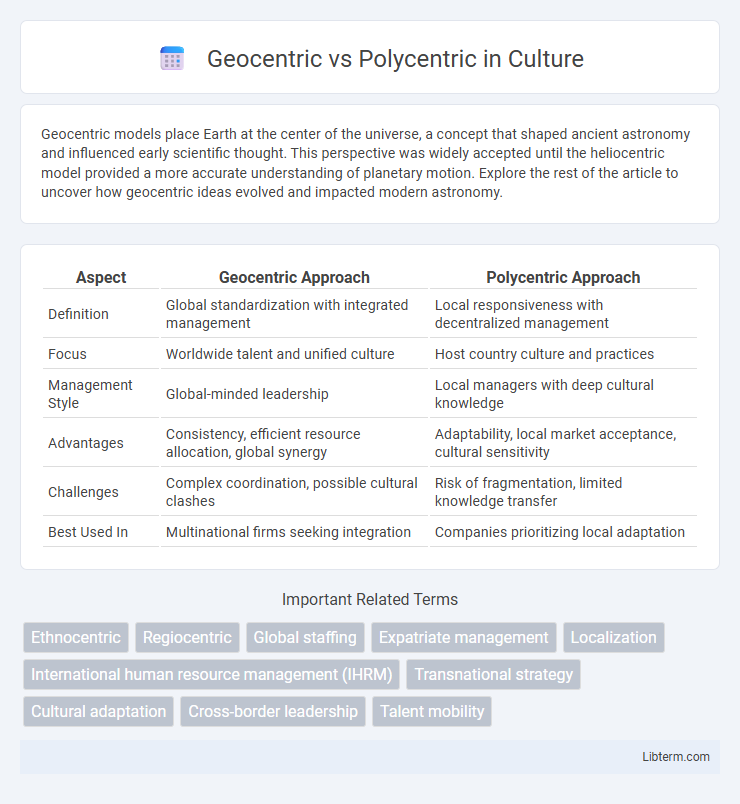
| Aspect | Geocentric Approach | Polycentric Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Global standardization with integrated management | Local responsiveness with decentralized management |
| Focus | Worldwide talent and unified culture | Host country culture and practices |
| Management Style | Global-minded leadership | Local managers with deep cultural knowledge |
| Advantages | Consistency, efficient resource allocation, global synergy | Adaptability, local market acceptance, cultural sensitivity |
| Challenges | Complex coordination, possible cultural clashes | Risk of fragmentation, limited knowledge transfer |
| Best Used In | Multinational firms seeking integration | Companies prioritizing local adaptation |
Understanding Geocentric and Polycentric Approaches
The geocentric approach integrates global and local business strategies, emphasizing a unified corporate culture that leverages the best talent worldwide for optimal decision-making. Conversely, the polycentric approach localizes management, allowing subsidiaries to operate independently with strategies tailored to their specific markets, enhancing cultural sensitivity and customer responsiveness. Understanding these approaches helps multinational corporations balance global efficiency and local adaptation for sustainable international growth.
Historical Background of Global Management Models
The geocentric model emerged during the mid-20th century as multinational corporations sought a unified global strategy to integrate diverse markets and optimize resource allocation across borders. In contrast, the polycentric approach developed as companies recognized the importance of adapting management practices to local cultures, legal systems, and consumer preferences to enhance responsiveness and competitive advantage. Historical shifts in global trade, technological advancements, and cultural awareness during the post-World War II era significantly influenced the evolution and application of these global management frameworks.
Key Characteristics of Geocentric Strategy
Geocentric strategy emphasizes a global approach where organizations integrate both global efficiencies and local responsiveness by valuing talent and ideas regardless of geographic location. It adopts a unified corporate culture, leveraging the best practices and personnel worldwide to optimize global performance and foster innovation. This approach balances the strengths of ethnocentric, polycentric, and regiocentric orientations, aiming for an inclusive and synergistic international business model.
Defining Features of Polycentric Approach
The polycentric approach in international business emphasizes local responsiveness by allowing subsidiaries to operate independently and adapt strategies to fit their host country's cultural, legal, and market conditions. This management style fosters decentralized decision-making, empowering local managers with autonomy to address specific market needs effectively. It contrasts with geocentric approaches by prioritizing regional and national differences, enhancing global competitiveness through tailored local expertise.
Comparative Analysis: Geocentric vs Polycentric
Geocentric approaches integrate global perspectives by balancing both headquarters and local subsidiary inputs, fostering unified strategies that optimize resource allocation across borders. Polycentric models prioritize local responsiveness, tailoring management and operations to specific regional markets, which enhances cultural adaptability but may increase complexity and costs. Comparing the two, geocentric frameworks promote global standardization and knowledge sharing, whereas polycentric frameworks emphasize decentralization and local autonomy to meet diverse market demands effectively.
Advantages of Geocentric Orientation
Geocentric orientation integrates global and local perspectives, allowing multinational companies to leverage the best talent worldwide while ensuring consistent corporate culture and strategy. This approach enhances cross-cultural collaboration and innovation, leading to improved competitive advantage in international markets. It reduces ethnocentric bias by promoting diversity and aligning organizational objectives with a truly global mindset.
Benefits of Polycentric Management
Polycentric management enhances local responsiveness by empowering subsidiaries to tailor strategies based on regional market dynamics, consumer behavior, and cultural nuances, leading to increased customer satisfaction and competitive advantage. It fosters stronger relationships with local stakeholders, improving adaptability and operational efficiency through decentralized decision-making. This approach also reduces the risk of cultural misunderstandings and enables faster problem-solving by relying on managers with in-depth knowledge of local environments.
Challenges in Implementing Geocentric and Polycentric Models
Implementing geocentric models faces challenges such as integrating diverse cultural perspectives into a unified corporate strategy while managing complex communication across global subsidiaries. Polycentric models struggle with inconsistent global policies and difficulties in maintaining a coherent brand image due to strong localization efforts by regional branches. Both models require balancing global efficiency with local responsiveness, demanding robust coordination and adaptive leadership to overcome operational conflicts.
Real-World Examples: Geocentric and Polycentric in Practice
Geocentric strategies are evident in companies like Unilever, which integrates global consistency with local responsiveness by employing managers worldwide to balance headquarters' control and local insights. Polycentric approaches are employed by multinational corporations such as Nestle, allowing subsidiaries in countries like Brazil and India to operate independently and tailor products to local markets. These real-world examples demonstrate how businesses leverage geocentric and polycentric models to optimize international management and market adaptation.
Choosing the Right Approach for International Expansion
Selecting between geocentric and polycentric approaches for international expansion hinges on balancing global integration with local responsiveness. A geocentric strategy leverages a unified corporate culture and standardized processes, fostering operational efficiency and consistent brand identity across markets. In contrast, the polycentric approach empowers local subsidiaries with autonomy to adapt products and marketing to country-specific preferences, enhancing customer relevance and regulatory compliance.
Geocentric Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com