Subculture represents a distinct group within a larger society that differentiates itself through unique values, norms, styles, or interests. These groups often influence fashion, language, and behavior, shaping identity and community among their members. Discover how understanding subcultures can enrich your perspective by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
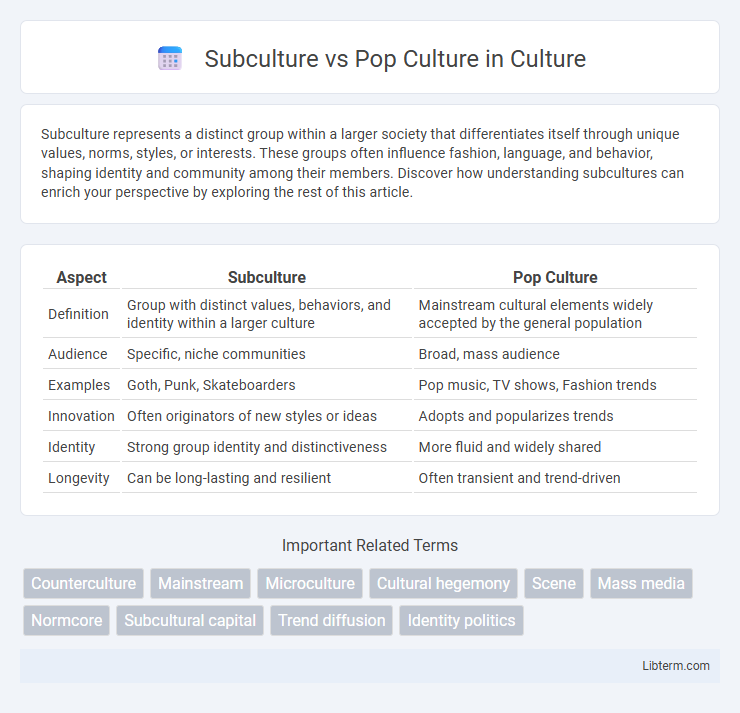
| Aspect | Subculture | Pop Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Group with distinct values, behaviors, and identity within a larger culture | Mainstream cultural elements widely accepted by the general population |
| Audience | Specific, niche communities | Broad, mass audience |
| Examples | Goth, Punk, Skateboarders | Pop music, TV shows, Fashion trends |
| Innovation | Often originators of new styles or ideas | Adopts and popularizes trends |
| Identity | Strong group identity and distinctiveness | More fluid and widely shared |
| Longevity | Can be long-lasting and resilient | Often transient and trend-driven |
Introduction to Subculture and Pop Culture
Subculture refers to a distinct group within society that shares unique values, norms, and behaviors that differentiate them from the mainstream culture. Pop culture, or popular culture, encompasses widespread trends, entertainment, and lifestyle elements embraced by the majority, often driven by media, music, fashion, and technology. Understanding the dynamics between subcultures and pop culture reveals how alternative identities influence mainstream tastes and societal norms.
Defining Subculture: Characteristics and Examples
Subculture is defined by distinctive values, norms, and styles that differentiate a group from the dominant mainstream culture, often rooted in shared interests or identities. Key characteristics include unique language, fashion, music preferences, and social behaviors that foster a sense of community and resistance to mainstream cultural norms. Examples of prominent subcultures include punk, goth, hip-hop, and gaming communities, each showcasing specific symbols, rituals, and collective identity markers.
Understanding Pop Culture: Features and Influence
Pop culture encompasses mainstream ideas, trends, and entertainment that shape societal norms and collective behavior through widespread media and consumer engagement. It features rapidly evolving fashion, music, and digital content that influence identity and social interactions across diverse demographics. The pervasive reach of pop culture impacts advertising, politics, and global communication, making it a powerful force in shaping public opinion and lifestyle choices.
Historical Evolution: Subculture vs Pop Culture
Subculture emerged as distinctive groups in the mid-20th century, often forming in opposition to mainstream norms, characterized by unique styles, values, and behaviors evident in music genres like punk and hip-hop. Pop culture, evolving concurrently, has roots in mass media and consumerism, reflecting dominant societal trends and rapidly adapting through television, film, and digital platforms since the early 1900s. The historical evolution highlights subcultures as niche, countercultural identities, while pop culture maintains widespread appeal and commercial influence.
The Role of Media in Shaping Cultures
Media plays a pivotal role in shaping both subculture and pop culture by disseminating ideas, values, and trends to vast audiences. Pop culture is often propelled by mass media platforms such as television, social media, and mainstream music channels that amplify widely accepted norms and styles. Conversely, subcultures utilize niche media outlets, underground publications, and online communities to maintain distinct identities and resist homogenization by dominant cultural narratives.
Key Differences Between Subculture and Pop Culture
Subculture represents a distinct group with unique values, behaviors, and symbols that differentiate it from the mainstream, often resisting predominant cultural norms. Pop culture encompasses widespread trends, media, and practices that dominate the mainstream, appealing to a broad audience through mass consumption. Key differences include the scope of influence--subcultures are niche and localized, while pop culture is extensive and widely accessible--and the depth of identity, with subcultures fostering strong community bonds versus pop culture's transient, commercial nature.
How Subcultures Influence Mainstream Trends
Subcultures shape mainstream trends by introducing unique fashion, music, and language that are gradually adopted by wider audiences. These niche groups act as innovation hubs, where new styles and ideas originate before being commercialized by pop culture. The continuous exchange between subcultures and mainstream media drives cultural evolution and diversifies popular expressions.
Cultural Identity and Community Belonging
Subculture fosters a strong cultural identity by emphasizing distinctive values, styles, and beliefs that set members apart from mainstream society. Pop culture, conversely, promotes widespread community belonging through shared symbols, trends, and entertainment embraced across diverse demographics. Both influence social cohesion, but subculture cultivates niche identities while pop culture drives collective cultural participation.
Challenges and Conflicts Between Subculture and Pop Culture
Subcultures often face challenges maintaining authenticity as mainstream pop culture frequently commercializes and dilutes their unique symbols and values. This conflict arises when pop culture appropriates subcultural elements, leading to tensions over cultural ownership and identity preservation. Additionally, subcultures may resist assimilation, fostering a sense of rebellion that highlights the ongoing struggle between individuality and mass appeal.
The Future of Cultural Dynamics: Blending and Divergence
Subcultures and pop culture shape the future of cultural dynamics through both blending and divergence, as emerging technologies enable niche communities to influence mainstream trends while preserving unique identities. Social media platforms accelerate cultural exchange, fostering hybrid expressions that challenge traditional boundaries between subculture and pop culture. This interplay promotes a dynamic cultural landscape where innovation thrives amid ongoing negotiations of authenticity and mass appeal.
Subculture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com