Pluralism promotes the coexistence of diverse beliefs, values, and cultures within a society, encouraging mutual respect and open dialogue. It enhances social harmony by recognizing and validating multiple perspectives without demanding conformity. Discover how understanding pluralism can transform Your approach to community and governance in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
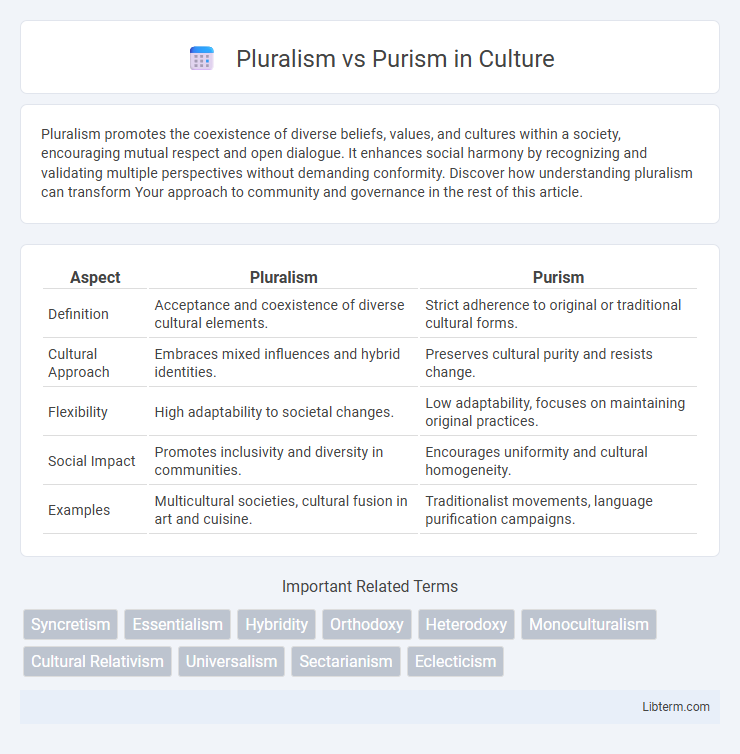
| Aspect | Pluralism | Purism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acceptance and coexistence of diverse cultural elements. | Strict adherence to original or traditional cultural forms. |
| Cultural Approach | Embraces mixed influences and hybrid identities. | Preserves cultural purity and resists change. |
| Flexibility | High adaptability to societal changes. | Low adaptability, focuses on maintaining original practices. |
| Social Impact | Promotes inclusivity and diversity in communities. | Encourages uniformity and cultural homogeneity. |
| Examples | Multicultural societies, cultural fusion in art and cuisine. | Traditionalist movements, language purification campaigns. |
Understanding Pluralism: Embracing Diversity
Embracing diversity through pluralism fosters a society where multiple cultural, religious, and ideological perspectives coexist and contribute to social harmony. Pluralism encourages open dialogue and mutual respect, allowing individuals and groups to express their unique identities without suppression or assimilation pressures. This approach contrasts with purism, which seeks homogeneity and often inhibits social integration by rejecting difference.
Defining Purism: Pursuit of the Ideal
Purism in linguistics emphasizes the pursuit of an ideal language standard, advocating for the preservation of linguistic purity by rejecting foreign influences, neologisms, and colloquialisms. This ideology seeks to maintain the language's original form and structure, often aligning with nationalistic or cultural identity preservation efforts. Purism contrasts with pluralism by prioritizing uniformity and historical authenticity over linguistic diversity and natural language evolution.
Historical Origins of Pluralism and Purism
Pluralism emerged historically during the Enlightenment as a response to increasing cultural interactions and the need for societal cohesion amid diversity, emphasizing acceptance and coexistence of multiple identities. Purism, rooted in nationalist and often reactionary movements of the 19th and 20th centuries, advocates for the preservation of a singular, "pure" cultural or linguistic identity to maintain social homogeneity. These contrasting origins reflect broader socio-political dynamics, where pluralism aligns with liberal democratic values, and purism often correlates with exclusionary and protectionist ideologies.
Core Principles and Philosophies
Pluralism emphasizes diversity and coexistence of multiple cultural, religious, or ideological perspectives within a society, promoting tolerance and mutual respect. It upholds the core principle that truth and values are context-dependent and multifaceted, encouraging open dialogue among differing views. Purism advocates for maintaining a singular, often traditional, set of cultural or ideological standards, prioritizing uniformity and purity to preserve perceived authenticity or original identity.
Pluralism in Modern Society
Pluralism in modern society promotes the coexistence of diverse cultural, religious, and ideological perspectives, fostering social harmony and mutual respect. It encourages open dialogue, inclusivity, and adaptability, enabling societies to navigate complexities and conflicts constructively. Embracing pluralism contributes to democratic governance, innovation, and resilience in increasingly globalized and interconnected communities.
Purism’s Influence on Culture and Art
Purism's influence on culture and art emphasizes clarity, order, and the reduction of complexity, promoting minimalist aesthetics that reject ornamental excess and embrace functional design. This movement inspired artists and designers to focus on geometric forms, smooth surfaces, and a restricted color palette, shaping modernist architecture, visual arts, and graphic design throughout the 20th century. Purism's principles continue to impact contemporary creative fields by advocating for simplicity and coherence, fostering environments where visual communication is precise and unambiguous.
Strengths and Limitations of Pluralism
Pluralism promotes inclusivity and diversity by encouraging multiple viewpoints and cultural expressions, fostering innovation and adaptability in social and political systems. Its strength lies in creating a dynamic environment where minority perspectives gain representation, preventing dominance by any single ideology. However, pluralism can lead to fragmentation and conflict due to competing interests and values, sometimes resulting in inefficiency or paralysis in decision-making processes.
Critiques and Challenges of Purism
Purism faces critiques for its rigid adherence to linguistic purity, often overlooking language evolution and regional variations. This approach can alienate speakers by dismissing colloquial, hybrid, or borrowed expressions, thereby limiting natural language growth and adaptability. Challenges of purism include resistance from diverse linguistic communities and difficulty in enforcing prescriptive norms in dynamic, multicultural societies.
Real-World Examples: Pluralism vs Purism
Pluralism in language is evident in the acceptance of diverse dialects and mixed-language usage, such as the widespread incorporation of English loanwords in Japanese business communication. Purism, by contrast, is exemplified by efforts like the Icelandic Language Council's initiatives to replace foreign terms with native neologisms, preserving linguistic heritage. These real-world cases demonstrate the tension between embracing linguistic evolution and maintaining language purity.
Bridging the Gap: Toward a Balanced Perspective
Bridging the gap between pluralism and purism involves recognizing the value of linguistic diversity while maintaining clarity and coherence in communication. Embracing pluralism promotes inclusivity and adaptability in language use, reflecting cultural and contextual variations. Balancing purism ensures standardized norms that facilitate mutual understanding and preserve linguistic heritage.
Pluralism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com