Postmodernism challenges traditional narratives and embraces fragmented perspectives, questioning the idea of objective truth and absolute meaning. It influences various fields including art, literature, philosophy, and architecture by promoting skepticism toward grand theories and highlighting diversity and pluralism. Discover how postmodernism reshapes your understanding of culture and knowledge throughout this article.
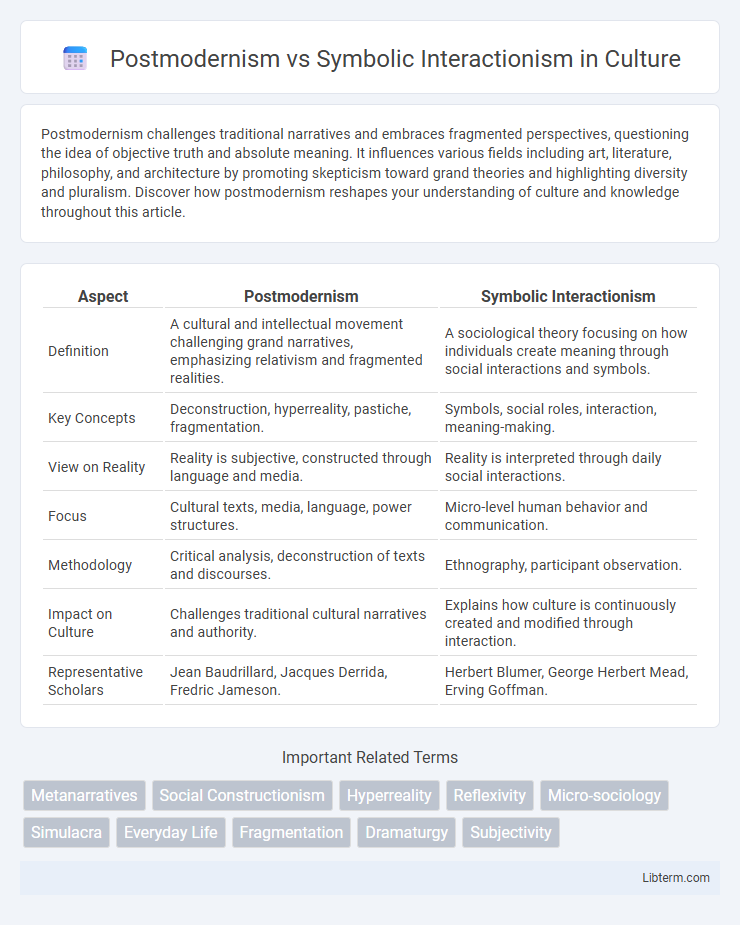
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Postmodernism | Symbolic Interactionism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A cultural and intellectual movement challenging grand narratives, emphasizing relativism and fragmented realities. | A sociological theory focusing on how individuals create meaning through social interactions and symbols. |
| Key Concepts | Deconstruction, hyperreality, pastiche, fragmentation. | Symbols, social roles, interaction, meaning-making. |
| View on Reality | Reality is subjective, constructed through language and media. | Reality is interpreted through daily social interactions. |
| Focus | Cultural texts, media, language, power structures. | Micro-level human behavior and communication. |
| Methodology | Critical analysis, deconstruction of texts and discourses. | Ethnography, participant observation. |
| Impact on Culture | Challenges traditional cultural narratives and authority. | Explains how culture is continuously created and modified through interaction. |
| Representative Scholars | Jean Baudrillard, Jacques Derrida, Fredric Jameson. | Herbert Blumer, George Herbert Mead, Erving Goffman. |
Defining Postmodernism: Key Concepts
Postmodernism challenges grand narratives and objective truths by emphasizing fragmented identities, multiple realities, and the fluidity of meaning. It critiques modernist assumptions of progress and fixed structures, highlighting the role of language and power in shaping knowledge and social practices. Central concepts include relativism, deconstruction, and the rejection of universal metanarratives, which contrast sharply with the more structured focus of symbolic interactionism on social interactions and meaning-making processes.
Understanding Symbolic Interactionism
Symbolic Interactionism centers on the micro-level analysis of human interactions where individuals create and interpret symbols to construct social reality. It emphasizes how meanings are negotiated through communication and social interaction, shaping identity and behavior in everyday life. Unlike Postmodernism's skepticism of grand narratives, Symbolic Interactionism focuses on the fluid, dynamic process of meaning-making within interpersonal relationships.
Historical Origins of Each Perspective
Postmodernism emerged in the mid-20th century as a reaction against the grand narratives and objective truths espoused by modernism, rooted in philosophical skepticism and influenced by thinkers like Michel Foucault and Jean-Francois Lyotard. Symbolic Interactionism originated in the early 20th century, primarily through the works of George Herbert Mead and Herbert Blumer, focusing on the social construction of meaning through human interactions and symbols. These historical origins highlight Postmodernism's critique of universal truths and Symbolic Interactionism's emphasis on micro-level social processes.
Foundational Theorists Compared
Postmodernism, with foundational theorists like Jean-Francois Lyotard and Michel Foucault, challenges grand narratives and emphasizes power dynamics and fragmented identities. Symbolic Interactionism, rooted in the works of George Herbert Mead and Herbert Blumer, focuses on micro-level social interactions and the construction of meaning through symbols. While Postmodernism critiques overarching structures and embraces relativism, Symbolic Interactionism centers on everyday communication and the interpretive process in social contexts.
Reality and Truth: Contrasting Epistemologies
Postmodernism challenges the existence of an absolute reality or truth, emphasizing that knowledge is subjective, fragmented, and constructed through language, power relations, and cultural contexts. Symbolic Interactionism centers on reality as a social construct created through interpersonal interactions and the use of shared symbols, focusing on how individuals interpret and negotiate meanings in everyday life. Both epistemologies reject fixed, objective truths but differ in scope, with postmodernism questioning grand narratives at a macro level, while symbolic interactionism examines micro-level processes of meaning-making.
Social Construction of Meaning
Postmodernism challenges fixed meanings and emphasizes the fluidity and multiple interpretations of social realities, while Symbolic Interactionism focuses on how individuals actively create and negotiate meaning through social interactions. Both perspectives highlight the social construction of meaning, but Postmodernism underscores the instability of these meanings in broader cultural narratives. Symbolic Interactionism, meanwhile, grounds meaning-making in everyday communication and shared symbols within social groups.
The Role of Language and Symbols
Postmodernism emphasizes the fluidity and fragmentation of language, viewing symbols as tools that construct multiple, often conflicting realities rather than fixed meanings. Symbolic Interactionism focuses on how individuals use language and symbols in everyday interactions to create shared meanings and social reality. Both perspectives highlight the central role of language and symbols in shaping human experience but differ in their views on the stability and coherence of meaning.
Power Dynamics and Social Structures
Postmodernism critiques traditional power structures by emphasizing the fluidity of social identities and the instability of meaning, challenging grand narratives that legitimize authority. Symbolic Interactionism examines power dynamics through face-to-face interactions and the construction of social reality via symbols, highlighting how individuals negotiate status and influence within social structures. Both perspectives offer insights into power relations, with Postmodernism problematizing overarching hierarchies and Symbolic Interactionism revealing micro-level processes shaping social order.
Critiques and Limitations of Both Theories
Postmodernism faces critiques for its skepticism toward objective truth and tendency to promote relativism, which can undermine the possibility of definitive knowledge and social progress. Symbolic Interactionism is limited by its micro-level focus, often neglecting broader structural and power dynamics that shape social interactions. Both theories are criticized for insufficiently addressing material conditions and institutional influences that impact social identities and behaviors.
Contemporary Applications in Sociology
Postmodernism in sociology challenges grand narratives and emphasizes fragmented, fluid identities, influencing contemporary research on cultural diversity and media representation. Symbolic interactionism focuses on face-to-face interactions and the construction of meaning, shaping studies on social identity, everyday communication, and group dynamics. Both frameworks are applied in examining social realities, with postmodernism critiquing established power structures while symbolic interactionism offers granular insights into individual agency within social contexts.
Postmodernism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com