Ideology shapes the way individuals and groups perceive the world, influencing political beliefs, social behaviors, and cultural values. Understanding various ideologies helps you critically evaluate information and recognize underlying motivations in public discourse. Explore the rest of the article to gain deeper insights into how ideology impacts society and your daily life.
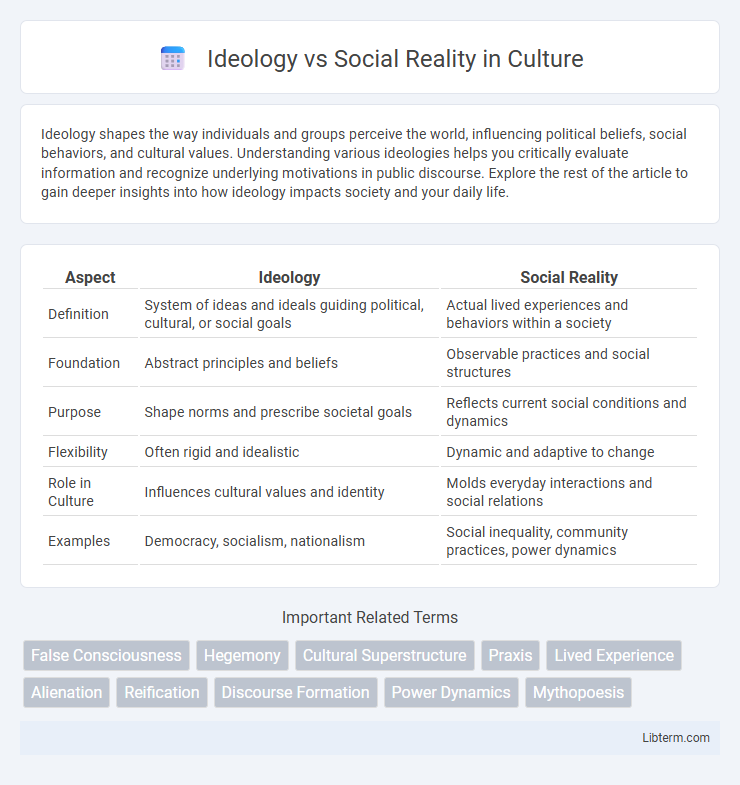
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Ideology | Social Reality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | System of ideas and ideals guiding political, cultural, or social goals | Actual lived experiences and behaviors within a society |
| Foundation | Abstract principles and beliefs | Observable practices and social structures |
| Purpose | Shape norms and prescribe societal goals | Reflects current social conditions and dynamics |
| Flexibility | Often rigid and idealistic | Dynamic and adaptive to change |
| Role in Culture | Influences cultural values and identity | Molds everyday interactions and social relations |
| Examples | Democracy, socialism, nationalism | Social inequality, community practices, power dynamics |
Defining Ideology: Concepts and Origins
Ideology consists of a coherent set of ideas and beliefs that shape individuals' perceptions of social, political, and economic structures, originating from historical, cultural, and philosophical foundations. It functions as a framework that influences collective behavior and justifies power relations within societies. Understanding ideology requires analyzing its roots in class relations, economic interests, and institutional power dynamics that inform social reality.
Understanding Social Reality: What Shapes Our World
Social reality is shaped by a complex interplay of cultural norms, economic structures, and political power that influence individual and collective behavior. Ideologies provide frameworks that interpret and sometimes distort these social dynamics to justify or challenge existing power relations. Understanding social reality requires analyzing the material conditions and subjective beliefs that coexist and drive societal change.
The Interaction Between Ideology and Social Reality
The interaction between ideology and social reality shapes collective behavior and societal norms by influencing how individuals perceive and respond to their environment. Ideologies provide frameworks that interpret social realities, guiding political, economic, and cultural practices while social realities, in turn, challenge or reinforce these ideological constructs through lived experiences and material conditions. This dynamic interplay drives social change, stability, or conflict by continuously negotiating the alignment or divergence between belief systems and empirical social conditions.
Historical Shifts: When Ideology Confronts Reality
Historical shifts demonstrate that ideology often clashes with social reality when entrenched beliefs meet evolving societal conditions. For example, Marxist ideology faced challenges as industrial societies transitioned into complex capitalist economies with varied class structures. These moments reveal how rigid ideological frameworks must adapt or transform in response to changing economic, cultural, and political realities.
Political Power and the Shaping of Social Narratives
Political power plays a crucial role in shaping social narratives by controlling discourse and influencing public perception through media and education systems. Ideology serves as a framework for legitimizing existing power structures while social reality reflects the complex interactions and lived experiences of individuals within those structures. The dynamic tension between ideology and social reality determines how political authority is maintained and challenged within society.
Media’s Role: Constructing or Reflecting Reality?
Media plays a pivotal role in shaping social reality by selecting, framing, and emphasizing certain narratives that align with dominant ideologies, thereby constructing a version of reality that influences public perception. This construction often reinforces power structures by promoting specific ideological viewpoints, while simultaneously appearing to reflect an objective social reality. Examining media content reveals how ideological biases and interests are embedded within representations, demonstrating that media is as much a constructor of social reality as it is a reflector.
Education Systems: Transmitting Ideology or Facts?
Education systems serve as crucial platforms where ideology and social reality intersect, often shaping curricula to reflect dominant societal values and power structures. While schools aim to transmit factual knowledge, they simultaneously perpetuate ideological narratives that influence students' worldviews and social roles. This dual function highlights the complex role of education in reinforcing or challenging prevailing social inequalities and cultural norms.
Ideological Conflicts in Contemporary Society
Ideological conflicts in contemporary society often stem from deeply rooted beliefs clashing with the evolving social realities shaped by globalization, technology, and cultural diversity. These disputes manifest in political polarization, debates over social justice, and struggles for identity recognition, reflecting how ideology can both resist and influence social change. Understanding the dynamic tension between ideology and social reality is crucial for addressing societal divisions and fostering inclusive dialogue.
Bridging the Gap: Reconciling Ideas with Experience
Bridging the gap between ideology and social reality requires aligning theoretical frameworks with empirical evidence to ensure policies reflect lived experiences. Effective reconciliation involves continuous dialogue between intellectual concepts and community perspectives, fostering adaptive solutions that address real-world challenges. This process enhances social cohesion by validating diverse experiences within ideological constructs, creating a dynamic interplay between ideas and practice.
The Future of Ideology in a Changing Social Landscape
The future of ideology is increasingly shaped by rapid technological advancements and shifting demographic trends that challenge traditional belief systems. As social realities evolve through globalization and digital interconnectedness, ideological frameworks must adapt to address complex issues such as climate change, social justice, and economic inequality. Emerging ideologies are likely to blend pragmatic solutions with ethical considerations, reflecting a dynamic interplay between enduring values and contemporary social demands.
Ideology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com