Microculture refers to a small group within a larger culture that shares distinct values, behaviors, and beliefs, often shaped by specific social, geographic, or organizational factors. Understanding microcultures can help you navigate diverse environments more effectively and foster better communication and collaboration. Explore the rest of this article to discover how microcultures impact social dynamics and influence your everyday interactions.
Table of Comparison
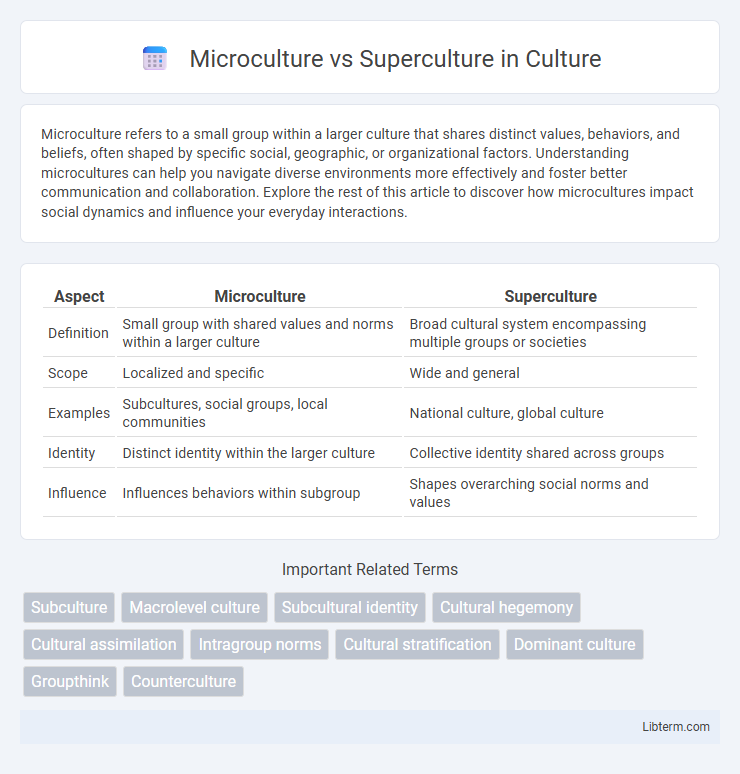
| Aspect | Microculture | Superculture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Small group with shared values and norms within a larger culture | Broad cultural system encompassing multiple groups or societies |
| Scope | Localized and specific | Wide and general |
| Examples | Subcultures, social groups, local communities | National culture, global culture |
| Identity | Distinct identity within the larger culture | Collective identity shared across groups |
| Influence | Influences behaviors within subgroup | Shapes overarching social norms and values |
Defining Microculture and Superculture
Microculture refers to a smaller cultural group within a larger society that shares its own distinct values, norms, language, and customs, often based on ethnicity, age, or social interests. Superculture encompasses the overarching cultural framework that integrates multiple microcultures, providing common beliefs, practices, and institutions that create social cohesion across diverse groups. Understanding the dynamic interaction between microcultures and superculture is essential for analyzing cultural identity and social structure in multicultural societies.
Key Characteristics of Microcultures
Microcultures are distinct groups within a larger culture defined by unique values, behaviors, customs, and language that differentiate them from the dominant culture. They often form around shared interests, ethnicity, religion, or geographic regions, maintaining specific traditions and social norms. These characteristics enable microcultures to sustain close-knit identities and influence individual socialization and communication patterns within the broader society.
Essential Traits of Supercultures
Supercultures exhibit essential traits such as extensive spatial reach, encompassing diverse microcultures within broad geographic regions or populations. They maintain a high degree of stability and continuity over long periods, enabling the transmission of shared values, norms, and institutional frameworks across generations. Centralized symbols, collective identities, and integrated political or economic structures further distinguish supercultures from localized microcultures.
Origins and Evolution of Microcultures
Microcultures originate from specific social groups or communities that share distinct customs, languages, or interests within a broader cultural context, evolving through unique environmental, economic, or technological influences. The development of microcultures is driven by interactions, adaptations, and innovations that differentiate them from the dominant superculture while maintaining some overarching cultural elements. Over time, microcultures contribute to cultural diversity and can influence or merge with supercultures, reflecting dynamic processes of identity formation and social cohesion.
Formation and Influence of Supercultures
Supercultures form through the amalgamation of diverse microcultures, driven by shared language, values, and institutions that establish broad societal norms. These large-scale cultures influence individual behaviors and microcultural identities by providing overarching frameworks for social interaction and collective meaning. The dynamic interplay between supercultures and microcultures shapes cultural continuity and change within complex societies.
Microculture vs Superculture: Core Differences
Microculture refers to the distinct cultural patterns, beliefs, and behaviors shared by a small group within a larger society, often defined by factors such as ethnicity, religion, or social interests. Superculture encompasses the overarching cultural framework that unites multiple microcultures within a broad society, providing common norms, values, and institutions. The core difference lies in scale and influence: microcultures maintain unique identities within the superculture, while the superculture sets the dominant societal context shaping the microcultures.
Social Impact of Microcultures
Microcultures shape social identity and community cohesion by fostering unique values, norms, and behaviors within a larger society. These distinct groups influence social dynamics through niche communication styles, traditions, and shared experiences, enabling members to find belonging and collective support. The social impact of microcultures contributes to cultural diversity, challenges mainstream norms, and drives social innovation by introducing alternative perspectives.
Superculture’s Role in Shaping Society
Superculture acts as the overarching framework guiding societal norms, values, and collective identity, integrating diverse microcultures into a cohesive social fabric. It influences legislation, education systems, and mass media, ensuring uniformity while allowing microcultures room for distinct expressions. This dominant cultural system fosters social cohesion and stability by providing shared meanings and expectations essential for societal functioning.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Case studies of microculture vs superculture reveal how localized subgroups, such as the Amish community in the United States, maintain distinct customs and resist mainstream cultural norms, highlighting microculture resilience. In contrast, superculture examples like global corporate culture demonstrate widespread influence and integration across diverse regions, promoting uniform business practices. These real-world cases illustrate the dynamic interplay between localized identities and overarching cultural frameworks within societal structures.
Navigating Interactions Between Microculture and Superculture
Navigating interactions between microculture and superculture requires understanding the specific values, norms, and communication styles unique to each microculture within the broader societal superculture. Effective intercultural communication involves recognizing both the diversity of microcultures and the unifying elements of the superculture to foster mutual respect and collaboration. Adapting strategies that respect microcultural identities while aligning with overarching supercultural expectations enhances social cohesion and reduces conflict.
Microculture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com