Orality refers to the transmission of knowledge, culture, and traditions through spoken language rather than written texts. It plays a crucial role in preserving histories, shaping identities, and fostering community connections across generations. Discover how orality influences communication and societal development in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
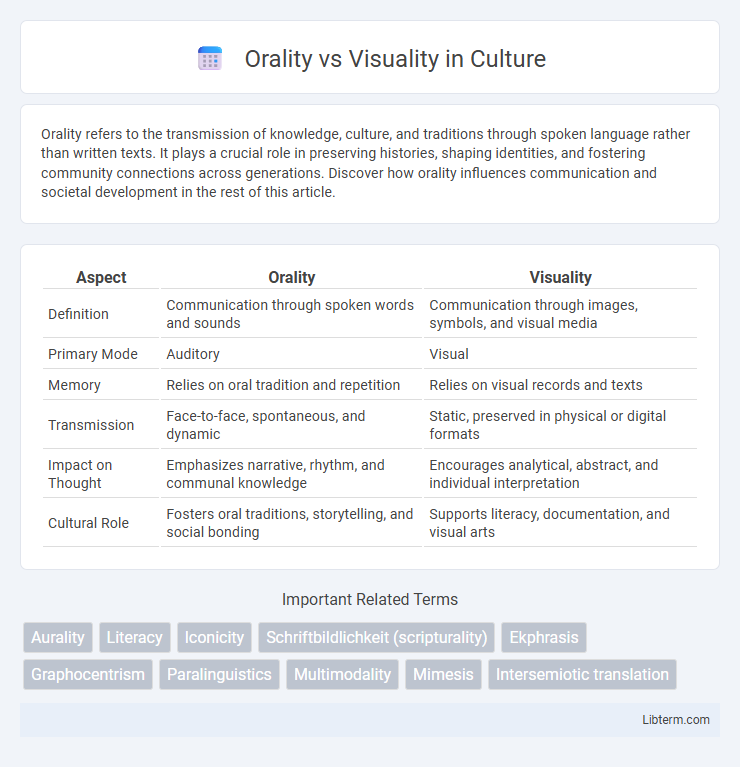
| Aspect | Orality | Visuality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Communication through spoken words and sounds | Communication through images, symbols, and visual media |
| Primary Mode | Auditory | Visual |
| Memory | Relies on oral tradition and repetition | Relies on visual records and texts |
| Transmission | Face-to-face, spontaneous, and dynamic | Static, preserved in physical or digital formats |
| Impact on Thought | Emphasizes narrative, rhythm, and communal knowledge | Encourages analytical, abstract, and individual interpretation |
| Cultural Role | Fosters oral traditions, storytelling, and social bonding | Supports literacy, documentation, and visual arts |
Introduction to Orality and Visuality
Orality refers to the transmission of knowledge and culture through spoken word, emphasizing memory, repetition, and communal participation, while visuality centers on the reception and interpretation of visual images and text as primary sources of information. The study of orality explores how oral traditions shape cognition and social interaction, contrasting with visuality's focus on the impact of written and pictorial representation in communication. Understanding these concepts is essential for analyzing how different modes of expression influence human perception and knowledge dissemination.
Historical Evolution of Communication Modes
The historical evolution of communication modes reveals a shift from orality, characterized by spoken language and memory-based transmission, to visuality, marked by the rise of writing, print, and digital media. Oral traditions dominated early human societies, relying on communal storytelling and verbal exchange, whereas visual communication emerged with the invention of writing systems like cuneiform and hieroglyphs, enabling record-keeping and knowledge preservation. The transition accelerated through printing technology and digital screens, embedding visuality as a primary mode for information dissemination and cultural expression in modern societies.
Key Characteristics of Orality
Orality is characterized by its reliance on spoken language, fostering immediate and interactive communication that emphasizes memory, repetition, and communal participation. Key traits include formulaic expressions, rhythmic patterns, and contextualized storytelling, which help preserve knowledge without written records. This oral tradition supports fluid, adaptive narratives shaped by the speaker-audience dynamic and situational context.
Defining Features of Visuality
Visuality centers on the dominance of sight as a mode of perception, emphasizing image-based communication and spatial awareness. It involves the processing of visual signals, prioritizing clarity, objectivity, and the externalization of knowledge through photography, film, and graphic representation. This sensory orientation shapes cognitive frameworks by privileging visual evidence and often marginalizing other sensory experiences.
Cognitive Impacts: Oral vs Visual Cultures
Oral cultures enhance memory retention and auditory processing through storytelling and verbal repetition, fostering strong communal bonds and active listening skills. Visual cultures emphasize spatial awareness, pattern recognition, and visual literacy, improving the brain's ability to interpret and analyze images and symbols rapidly. Cognitive impacts differ as oral traditions engage sequential and narrative cognition, while visual traditions stimulate holistic and simultaneous information processing.
Orality in Modern Digital Communication
Orality in modern digital communication emphasizes spoken language and interactive dialogue through voice messages, podcasts, and live video chats, fostering immediate, personal connection. The resurgence of oral traditions is supported by AI-driven speech recognition and synthesis technologies, which enhance accessibility and user engagement. This oral-centric communication style contrasts with text-based interaction, prioritizing tone, emotion, and spontaneity.
Visuality’s Influence on Media Consumption
Visuality shapes media consumption by prioritizing images and visual storytelling, enhancing immediate engagement and comprehension. Digital platforms leverage visual content such as videos, infographics, and memes to capture audience attention and convey complex information quickly. This shift influences cognitive processing, favoring visual literacy and reducing reliance on textual or oral narratives in media.
The Interplay between Orality and Visuality
The interplay between orality and visuality shapes how information is transmitted and interpreted across cultures, influencing cognitive processes and memory retention. Oral traditions rely on rhythmic patterns, storytelling, and vocal dynamics, while visuality employs imagery, symbols, and spatial arrangement to convey meaning. Understanding this dynamic interaction enhances communication strategies, particularly in education, media, and digital environments where blending auditory and visual stimuli improves engagement and comprehension.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Mode
Orality faces challenges such as the impermanence of spoken words and difficulties in preserving precise information over time, which limits accurate transmission across generations. Visuality struggles with interpretation bias, as images can be ambiguous and culturally specific, leading to misunderstandings or varied meanings. Both orality and visuality depend heavily on context, making it challenging to ensure consistent comprehension without supporting frameworks.
Future Prospects: Integrating Orality and Visuality
Future prospects for communication emphasize integrating orality and visuality to enhance cognitive engagement and information retention. Technological advancements in multimedia platforms enable seamless blending of spoken language and visual elements, fostering richer storytelling and educational experiences. This integration supports diverse learning styles and promotes accessibility, broadening the impact of digital communication globally.
Orality Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com