The Dodd-Frank Act introduced significant regulatory reforms aimed at increasing transparency and reducing risks within the financial system. It established new agencies and oversight mechanisms to prevent another financial crisis and protect consumers. Explore the rest of the article to understand how this legislation impacts your financial rights and responsibilities.
Table of Comparison
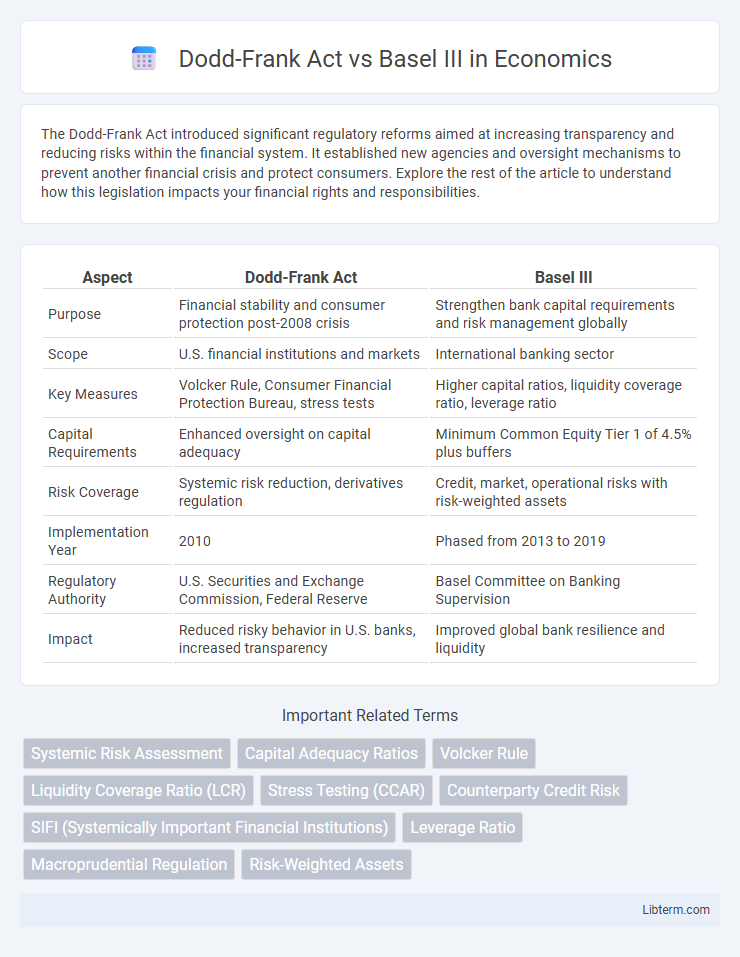
| Aspect | Dodd-Frank Act | Basel III |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Financial stability and consumer protection post-2008 crisis | Strengthen bank capital requirements and risk management globally |
| Scope | U.S. financial institutions and markets | International banking sector |
| Key Measures | Volcker Rule, Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, stress tests | Higher capital ratios, liquidity coverage ratio, leverage ratio |
| Capital Requirements | Enhanced oversight on capital adequacy | Minimum Common Equity Tier 1 of 4.5% plus buffers |
| Risk Coverage | Systemic risk reduction, derivatives regulation | Credit, market, operational risks with risk-weighted assets |
| Implementation Year | 2010 | Phased from 2013 to 2019 |
| Regulatory Authority | U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, Federal Reserve | Basel Committee on Banking Supervision |
| Impact | Reduced risky behavior in U.S. banks, increased transparency | Improved global bank resilience and liquidity |
Overview of the Dodd-Frank Act and Basel III
The Dodd-Frank Act, enacted in 2010, is a comprehensive U.S. federal law aimed at reducing risks in the financial system through increased regulation of banks, consumer protection, and creation of oversight bodies like the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB). Basel III, developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision, establishes international regulatory standards on bank capital adequacy, stress testing, and market liquidity risk to strengthen global banking resilience post-2008 financial crisis. Both frameworks emphasize risk management and financial stability but differ in scope, with Dodd-Frank focused on U.S. financial institutions and consumer safeguards, and Basel III addressing global banking capital and liquidity requirements.
Historical Context and Development
The Dodd-Frank Act, enacted in 2010 in response to the 2008 financial crisis, aimed to increase regulatory oversight of the U.S. financial system and prevent systemic risk through measures like the Volcker Rule and enhanced capital requirements. Basel III, developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision between 2010 and 2017, followed the global financial crisis to strengthen international banking regulations by improving capital adequacy, liquidity, and risk management standards. Both regulatory frameworks emerged from the necessity to address weaknesses exposed by the 2007-2008 crisis, shaping the modern regulatory landscape with complementary but distinct scopes--Dodd-Frank focusing on U.S. financial institutions and consumer protections, while Basel III established global banking standards.
Core Objectives of Dodd-Frank and Basel III
The Dodd-Frank Act primarily aims to enhance financial stability by reducing systemic risk, increasing transparency, and protecting consumers through regulations like the Volcker Rule and the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau. Basel III focuses on strengthening bank capital requirements, improving risk management, and increasing liquidity standards to prevent bank failures and financial crises. Both frameworks seek to mitigate risks in the financial system but emphasize different mechanisms: Dodd-Frank through regulatory oversight and consumer protections, Basel III through quantitative capital and liquidity measures.
Regulatory Scope and Applicability
The Dodd-Frank Act primarily targets the U.S. financial sector, focusing on reducing systemic risk by regulating banks, investment firms, and derivatives markets within the United States. Basel III is a global regulatory framework established by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision, aimed at strengthening bank capital requirements and enhancing liquidity standards across internationally active banks. While Dodd-Frank enforces broad financial reforms with an emphasis on consumer protection and transparency, Basel III concentrates on capital adequacy, stress testing, and market discipline for banks worldwide.
Key Provisions: Risk Management and Capital Requirements
The Dodd-Frank Act enforces stringent risk management through enhanced oversight of large financial institutions, including stress testing and living wills to prevent systemic collapse. Basel III establishes global capital requirements by imposing higher minimum capital ratios, leverage limits, and liquidity coverage ratios to strengthen banks' resilience against financial shocks. Both frameworks emphasize robust capital buffers and risk controls but differ in scope: Dodd-Frank targets U.S. institutions with regulatory supervision, while Basel III offers an international standard promoting financial stability.
Approaches to Liquidity and Leverage
The Dodd-Frank Act enforces strict regulations on liquidity risk management through tools like the Liquidity Coverage Ratio and mandates leverage caps to limit excessive borrowing by financial institutions. Basel III introduces standardized liquidity standards including the Net Stable Funding Ratio and sets a maximum leverage ratio to ensure banks maintain adequate capital buffers. Both frameworks aim to enhance financial stability by controlling leverage and strengthening liquidity resilience, yet Dodd-Frank emphasizes regulatory oversight specific to U.S. markets while Basel III provides a global regulatory baseline.
Impact on Financial Institutions
The Dodd-Frank Act significantly increased regulatory requirements for U.S. financial institutions by imposing stricter capital, leverage, and risk management standards to enhance transparency and reduce systemic risk. Basel III complements these efforts globally by enforcing higher capital adequacy ratios, liquidity coverage ratios, and enhanced supervisory review processes, which collectively strengthen banks' resilience against financial shocks. Both frameworks have driven financial institutions to improve risk governance, increase compliance costs, and adopt more rigorous stress testing and reporting mechanisms.
Implications for Global Banking Operations
The Dodd-Frank Act enhances U.S. financial stability by imposing stringent capital requirements, stress testing, and oversight on banks, directly influencing global banking risk management and compliance practices. Basel III establishes comprehensive international regulatory standards for capital adequacy, leverage ratios, and liquidity, promoting uniform risk mitigation and financial resilience across global banking institutions. The convergence of these frameworks compels multinational banks to harmonize risk management strategies and regulatory reporting, resulting in increased operational complexity and elevated compliance costs worldwide.
Strengths and Criticisms of Each Framework
The Dodd-Frank Act strengthens U.S. financial stability by imposing stricter regulatory oversight and enhancing consumer protection but faces criticism for increasing compliance costs and potential restrictions on credit availability. Basel III improves global banking resilience through higher capital requirements and liquidity standards, yet it is often criticized for complexity and uneven implementation across jurisdictions. Both frameworks aim to mitigate systemic risk but differ in scope, with Dodd-Frank focusing on domestic reform and Basel III promoting international harmonization.
Future Trends and Regulatory Evolution
Future trends in financial regulation indicate increased integration of Basel III's global capital and liquidity standards with Dodd-Frank's U.S.-specific systemic risk controls to enhance resilience against market disruptions. Regulatory evolution emphasizes advanced stress testing, improved transparency, and stricter oversight of systemically important financial institutions (SIFIs) to mitigate systemic risks. Ongoing reforms aim at harmonizing international and domestic frameworks to address emerging risks from fintech innovations and climate-related financial vulnerabilities.
Dodd-Frank Act Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com