Renewable resources, such as solar, wind, and hydro energy, provide sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels by naturally replenishing over time and reducing environmental impact. Utilizing these resources helps mitigate climate change and promotes energy independence. Discover how embracing renewable resources can transform Your energy future by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
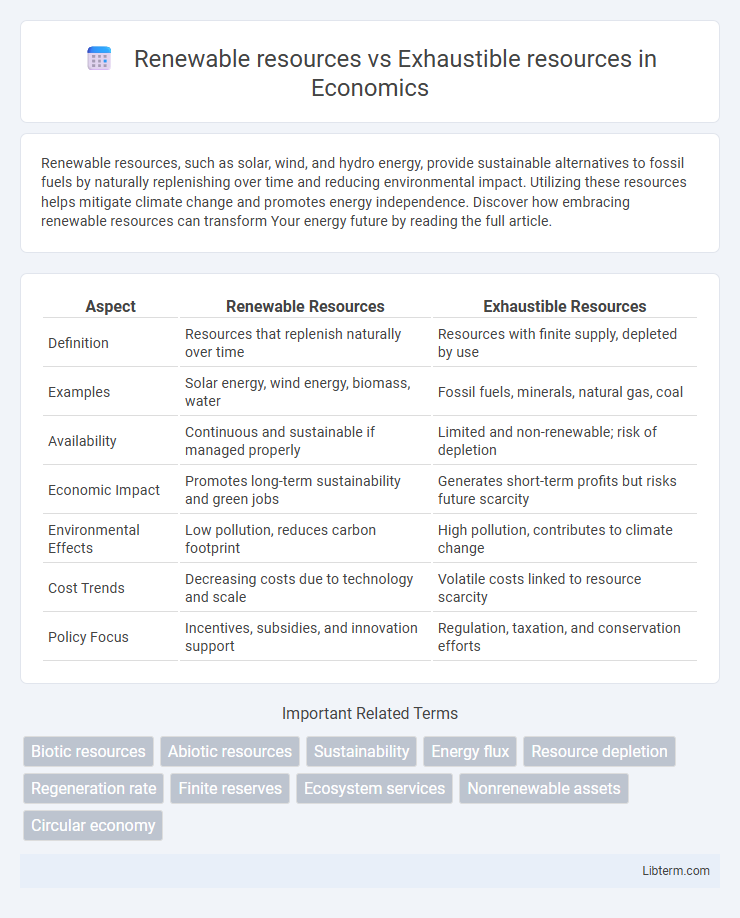
| Aspect | Renewable Resources | Exhaustible Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Resources that replenish naturally over time | Resources with finite supply, depleted by use |
| Examples | Solar energy, wind energy, biomass, water | Fossil fuels, minerals, natural gas, coal |
| Availability | Continuous and sustainable if managed properly | Limited and non-renewable; risk of depletion |
| Economic Impact | Promotes long-term sustainability and green jobs | Generates short-term profits but risks future scarcity |
| Environmental Effects | Low pollution, reduces carbon footprint | High pollution, contributes to climate change |
| Cost Trends | Decreasing costs due to technology and scale | Volatile costs linked to resource scarcity |
| Policy Focus | Incentives, subsidies, and innovation support | Regulation, taxation, and conservation efforts |
Introduction to Renewable and Exhaustible Resources
Renewable resources, such as solar energy, wind, and biomass, are naturally replenished over short periods and provide sustainable energy solutions with minimal environmental impact. Exhaustible resources, including fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, are finite, depleting as they are consumed and causing significant ecological harm through greenhouse gas emissions. Understanding the distinction between renewable and exhaustible resources is essential for promoting sustainable development and addressing global energy challenges.
Defining Renewable Resources
Renewable resources are natural assets that replenish at a rate equal to or faster than their consumption, such as solar energy, wind power, and biomass. These resources provide sustainable energy solutions by continuously regenerating through natural processes, making them essential for reducing environmental impact and conserving ecosystems. Unlike exhaustible resources like fossil fuels and minerals, renewable resources offer long-term availability without depleting the Earth's reserves.
Defining Exhaustible Resources
Exhaustible resources are natural resources that exist in finite quantities and cannot be replenished within a human lifespan, such as fossil fuels, minerals, and certain metals. Unlike renewable resources like solar and wind energy, exhaustible resources deplete over time due to continuous extraction and consumption. Their scarcity drives the need for efficient management and the development of sustainable alternatives to mitigate environmental impact.
Key Differences Between Renewable and Exhaustible Resources
Renewable resources such as solar energy, wind, and biomass replenish naturally over short periods, ensuring sustainable availability, whereas exhaustible resources like fossil fuels and minerals form over millions of years and cannot be quickly replaced once depleted. Renewable resources support continuous energy production without significant environmental degradation, while exhaustible resources involve finite reserves that lead to resource scarcity and ecological harm with excessive extraction. The key difference lies in renewability and environmental impact, with renewable resources promoting long-term sustainability compared to the finite and polluting nature of exhaustible resources.
Examples of Renewable Resources
Renewable resources include solar energy, wind power, hydropower, geothermal energy, and biomass, all naturally replenished on a human timescale. These resources provide sustainable alternatives to exhaustible resources like coal, oil, natural gas, and minerals, which deplete with continued use. Utilizing renewable resources reduces dependence on finite reserves and minimizes environmental impacts associated with fossil fuel extraction and consumption.
Examples of Exhaustible Resources
Exhaustible resources, also known as non-renewable resources, include fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, which form over millions of years and are depleted faster than they regenerate. Minerals like gold, silver, and uranium are other examples of exhaustible resources that exist in limited quantities within the Earth's crust. Dependence on these finite materials poses significant challenges for sustainable development and environmental conservation.
Environmental Impact of Resource Consumption
Renewable resources such as solar, wind, and biomass provide energy with minimal greenhouse gas emissions, significantly reducing pollution and habitat destruction compared to exhaustible resources like coal, oil, and natural gas. The consumption of exhaustible resources contributes to air and water pollution, soil degradation, and increases carbon footprints, accelerating climate change and biodiversity loss. Utilizing renewable resources promotes sustainable environmental management by preserving ecosystems and supporting long-term ecological balance.
Sustainability Challenges and Solutions
Renewable resources such as solar, wind, and biomass face sustainability challenges related to intermittent supply and land use conflicts, requiring advanced storage technologies and efficient resource management for optimization. Exhaustible resources like fossil fuels and minerals pose critical sustainability issues including depletion rates, environmental degradation, and carbon emissions, emphasizing the urgent need for transitioning to alternative energy sources and circular economy practices. Implementing integrated policies that promote renewable energy adoption, resource recycling, and technological innovation is essential to mitigate the sustainability risks associated with both resource types.
The Role of Technology in Resource Management
Advanced technology enhances the efficiency of harnessing renewable resources such as solar, wind, and bioenergy by optimizing energy capture and storage systems, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Innovations in resource management, including improved monitoring and predictive analytics, help mitigate the depletion of exhaustible resources like oil, coal, and natural gas by enabling better extraction techniques and promoting sustainable consumption patterns. Integrating digital tools and smart infrastructure supports a balanced approach to utilizing both renewable and exhaustible resources, minimizing environmental impact while boosting economic viability.
Future Prospects for Global Resource Use
Renewable resources like solar, wind, and biomass offer sustainable energy solutions vital for reducing global carbon emissions and supporting long-term economic growth. Exhaustible resources such as fossil fuels and minerals face depletion risks, driving innovation in resource efficiency and alternative technologies. Future global resource use increasingly depends on advancing renewable technologies and implementing circular economy models to balance environmental preservation with economic development.
Renewable resources Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com