The income effect describes how changes in a consumer's income influence their purchasing decisions, often altering the quantity demanded for goods and services. Understanding this concept helps explain variations in consumer behavior as income rises or falls. Discover how the income effect shapes your spending patterns and impacts market dynamics by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
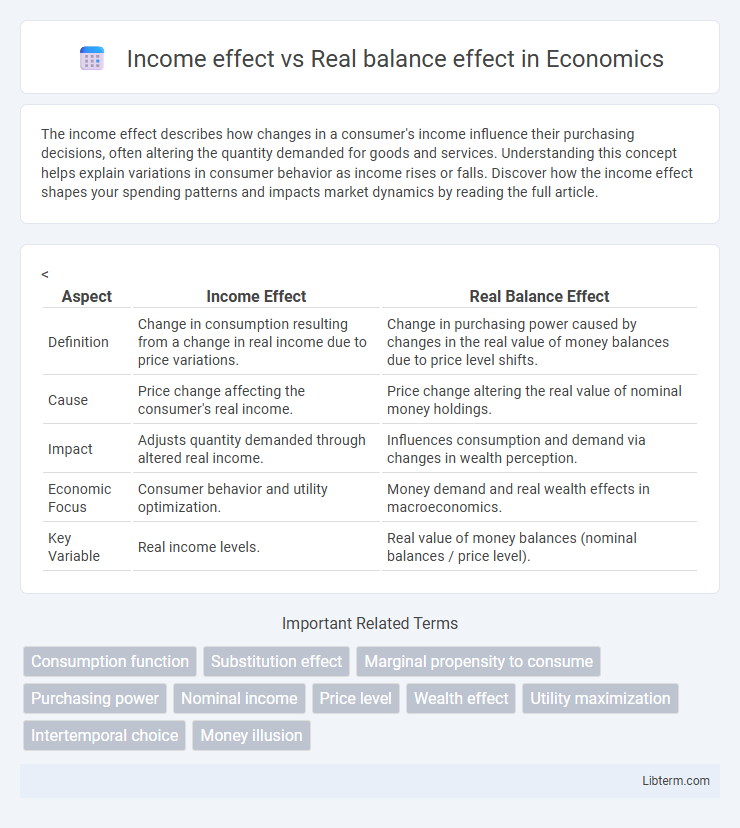
| Aspect | Income Effect | Real Balance Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Change in consumption resulting from a change in real income due to price variations. | Change in purchasing power caused by changes in the real value of money balances due to price level shifts. |
| Cause | Price change affecting the consumer's real income. | Price change altering the real value of nominal money holdings. |
| Impact | Adjusts quantity demanded through altered real income. | Influences consumption and demand via changes in wealth perception. |
| Economic Focus | Consumer behavior and utility optimization. | Money demand and real wealth effects in macroeconomics. |
| Key Variable | Real income levels. | Real value of money balances (nominal balances / price level). |
Introduction to Income Effect and Real Balance Effect
The income effect describes how changes in a consumer's real income influence their purchasing behavior, often leading to increased demand when income rises. The real balance effect, also known as the Pigou effect, explains how a change in the real value of money balances impacts consumption and aggregate demand. Both effects highlight the relationship between changes in price levels, consumer wealth, and spending patterns in the economy.
Definitions: Income Effect Explained
Income effect refers to the change in consumer purchasing power resulting from a change in real income, influencing demand for goods and services. When prices decrease, the consumer's real income effectively rises, allowing increased consumption due to higher purchasing power. This contrasts with the real balance effect, which emphasizes changes in the value of money holdings and their impact on spending behavior.
Understanding the Real Balance Effect
The real balance effect explains how changes in the price level influence consumer purchasing power by altering the value of money holdings, leading to shifts in consumption and aggregate demand. When the price level falls, the real value of money balances rises, increasing consumers' ability to buy goods and services without additional income. This mechanism highlights the direct impact of price changes on consumption through wealth effects, distinct from the income effect, which stems from changes in actual income or wages.
Key Differences Between Income Effect and Real Balance Effect
The income effect describes how changes in consumers' real income impact demand for goods, typically caused by price shifts affecting purchasing power. The real balance effect refers to how variations in the price level alter the real value of money holdings, influencing overall consumption and aggregate demand. Unlike the income effect, which operates at the individual consumer level, the real balance effect primarily affects aggregate economic activity through changes in real wealth.
How Income Effect Influences Consumer Behavior
The income effect influences consumer behavior by altering purchasing power when prices change, causing consumers to buy more or less of a good depending on their real income variation. A price decrease effectively increases real income, enabling consumers to afford higher quantities or more expensive items, while a price increase reduces real income and limits consumption. This change in consumption patterns due to shifts in real purchasing power differentiates the income effect from the real balance effect, which emphasizes changes in the value of money holdings.
The Role of Real Balance Effect in Economic Theory
The real balance effect plays a crucial role in economic theory by explaining how changes in the price level influence consumer spending through variations in the real value of money holdings. When the price level falls, the purchasing power of nominal money balances increases, effectively making consumers wealthier and prompting higher demand for goods and services. This mechanism helps to stabilize the economy by linking price level changes to shifts in aggregate demand, complementing the income effect but emphasizing real purchasing power adjustments.
Income Effect in the Context of Inflation
The income effect in the context of inflation describes how rising prices erode consumers' real purchasing power, causing a decrease in the quantity of goods and services demanded. As inflation reduces the real value of income, households may feel poorer and cut back on spending, directly impacting consumer demand and overall economic activity. Understanding the income effect is crucial for policymakers to address inflation's impact on consumption and to design effective monetary and fiscal interventions.
Real Balance Effect and Monetary Policy
The Real Balance Effect describes how changes in the price level influence consumers' purchasing power, with lower prices increasing real wealth and thus boosting consumption. This effect directly impacts monetary policy, as central banks monitor price stability to maintain real balances that support economic growth. By adjusting interest rates and controlling inflation, monetary policy helps preserve consumers' real balances, stabilizing demand and promoting overall economic equilibrium.
Practical Examples: Income Effect vs Real Balance Effect
The income effect occurs when a change in the price of goods impacts consumers' purchasing power, such as a drop in gasoline prices increasing disposable income and enabling more spending on other items. The real balance effect, also known as the wealth effect, happens when a decline in the price level raises the real value of money holdings, encouraging higher consumption, like lower inflation boosting the real value of savings accounts. For example, if food prices fall, consumers feel effectively richer due to increased real balances, while the direct increase in their budget from price savings illustrates the income effect.
Conclusion: Comparing Economic Impacts
The income effect primarily influences consumer purchasing power by altering real income when prices change, leading to shifts in demand. The real balance effect emphasizes the impact of price level changes on the value of money holdings, affecting overall consumption and aggregate demand. Comparing their economic impacts reveals that while both affect consumption, the income effect directly alters individual demand patterns, whereas the real balance effect modifies aggregate economic activity through changes in wealth perception.
Income effect Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com