The gig economy has revolutionized traditional employment by offering flexible work opportunities that cater to diverse skills and schedules. It empowers workers to take control of their income while presenting challenges such as income instability and lack of benefits. Explore the rest of this article to understand how the gig economy impacts your career and financial future.
Table of Comparison
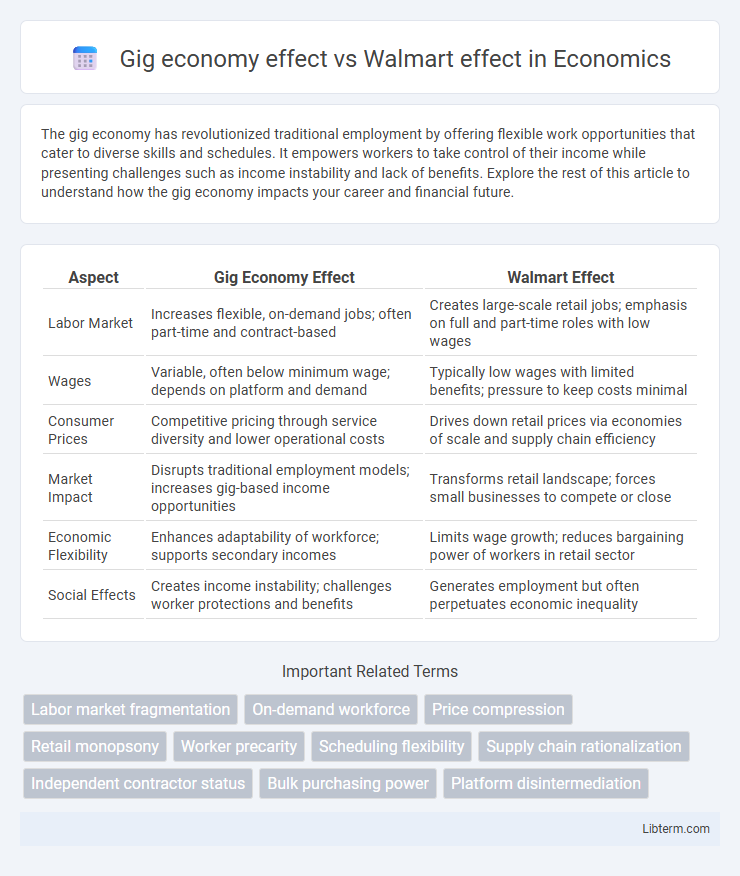
| Aspect | Gig Economy Effect | Walmart Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Market | Increases flexible, on-demand jobs; often part-time and contract-based | Creates large-scale retail jobs; emphasis on full and part-time roles with low wages |
| Wages | Variable, often below minimum wage; depends on platform and demand | Typically low wages with limited benefits; pressure to keep costs minimal |
| Consumer Prices | Competitive pricing through service diversity and lower operational costs | Drives down retail prices via economies of scale and supply chain efficiency |
| Market Impact | Disrupts traditional employment models; increases gig-based income opportunities | Transforms retail landscape; forces small businesses to compete or close |
| Economic Flexibility | Enhances adaptability of workforce; supports secondary incomes | Limits wage growth; reduces bargaining power of workers in retail sector |
| Social Effects | Creates income instability; challenges worker protections and benefits | Generates employment but often perpetuates economic inequality |
Introduction: Comparing the Gig Economy and Walmart Effects
The Gig Economy effect reshapes labor markets by promoting flexible, freelance job opportunities, increasing worker autonomy but often lacking traditional employment benefits. The Walmart effect influences local economies through large-scale retail dominance, driving down prices while impacting small businesses and wage standards. Both phenomena significantly alter economic landscapes, with the Gig Economy emphasizing decentralized work and the Walmart effect highlighting centralized retail power.
Historical Overview: Rise of the Gig Economy and Walmart
The gig economy emerged in the early 2000s with platforms like Uber and Airbnb, revolutionizing labor markets by promoting flexible, on-demand work and challenging traditional employment models. Walmart's rise in the mid-20th century reshaped retail by leveraging economies of scale, low prices, and extensive supply chains, driving widespread changes in consumer behavior and labor practices. Both phenomena highlight fundamental shifts in economic structures: Walmart catalyzed mass retail centralization, while the gig economy fosters decentralized, technology-driven labor participation.
Labor Market Transformation: Flexibility vs. Stability
The gig economy revolutionizes the labor market by offering unparalleled flexibility, enabling workers to choose when and how much they work, often at the expense of job security and consistent income. In contrast, Walmart's labor model emphasizes stability through predictable schedules, steady wages, and traditional employment benefits, supporting long-term workforce retention. This dichotomy shapes labor market transformation by highlighting the tension between adaptable, on-demand work structures and conventional, stable employment frameworks.
Wage Dynamics: Income Patterns in Both Models
The gig economy generates flexible income streams with fluctuating wages based on demand, often resulting in inconsistent earnings for workers, whereas Walmart's wage structure provides more stable, hourly wages with periodic raises and benefits tied to tenure. Gig workers typically face unpredictable income patterns and lack traditional employment protections, causing volatility in financial planning. In contrast, Walmart's model offers a more predictable income trajectory but with limited wage growth, influencing worker retention and economic security differently than the gig economy.
Worker Rights and Protections: Contrasts and Consequences
The gig economy often sidesteps traditional worker rights and protections, classifying workers as independent contractors without access to benefits like health insurance, paid leave, or collective bargaining rights. In contrast, Walmart's employment model typically provides a limited set of protections under established labor laws but faces criticism for low wages and minimal union presence, impacting worker stability and advocacy. These contrasting frameworks result in divergent consequences for job security, legal recourse, and economic equity among frontline workers.
Consumer Benefits: Accessibility and Affordability
The gig economy enhances consumer benefits by providing greater accessibility through flexible, on-demand services that cater to diverse needs and schedules. Walmart's effect drives affordability by leveraging large-scale operations and supply chain efficiencies to offer low prices and wide product availability. Together, these models improve consumer options by combining immediate access with competitive pricing in retail and service sectors.
Impact on Small Businesses: Disruption and Adaptation
The gig economy disrupts small businesses by increasing competition from flexible, low-overhead service providers that attract customers seeking convenience and lower prices. Walmart's effect forces small retailers to adapt through cost-cutting, niche marketing, or enhancing local customer experiences to survive the overwhelming pricing and supply chain advantages of the retail giant. Both phenomena drive small businesses to innovate rapidly, often reshaping local economies and employment structures.
Socioeconomic Implications: Inequality and Community Change
The gig economy fosters flexible work opportunities but often leads to income volatility and limited benefits, intensifying socioeconomic inequality. Walmart's presence in communities frequently results in job displacement among small businesses, altering local economic landscapes and exacerbating wealth disparities. Both models contribute to community transformation, with the gig economy promoting fragmented labor relations and Walmart influencing urban development patterns and consumption behaviors.
Technological Influence: Platforms vs. Supply Chains
The gig economy leverages digital platforms such as Uber and TaskRabbit to connect freelancers with customers, emphasizing flexible, on-demand labor through algorithm-driven matching and real-time data analytics. In contrast, Walmart's influence centers on advanced supply chain technologies, including automated inventory management and sophisticated logistics systems that optimize product flow and reduce costs at scale. Both models demonstrate how technological innovation reshapes economic structures--platforms prioritize decentralized labor coordination, while Walmart's supply chains focus on integrated, centralized resource distribution.
Future Outlook: Evolving Workforce and Economic Landscapes
The gig economy's future outlook reveals a dynamic workforce characterized by increased flexibility, technological integration, and decentralized job opportunities, contrasting with Walmart's traditional retail model that emphasizes large-scale employment and supply chain dominance. Economic landscapes are shifting as gig platforms promote entrepreneurship and adaptive skillsets, while Walmart's influence drives changes in local economies through automation and scalability. These evolving patterns suggest a transformative labor market where digital platforms and corporate giants coexist, shaping income distribution, job security, and economic resilience worldwide.
Gig economy effect Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com