Remedial curriculum is designed to help students who struggle with foundational skills, ensuring they catch up with their peers in subjects like math, reading, and writing. It focuses on personalized instruction that targets specific gaps in knowledge, boosting confidence and academic performance. Explore the rest of this article to learn how remedial programs can transform Your learning experience.
Table of Comparison
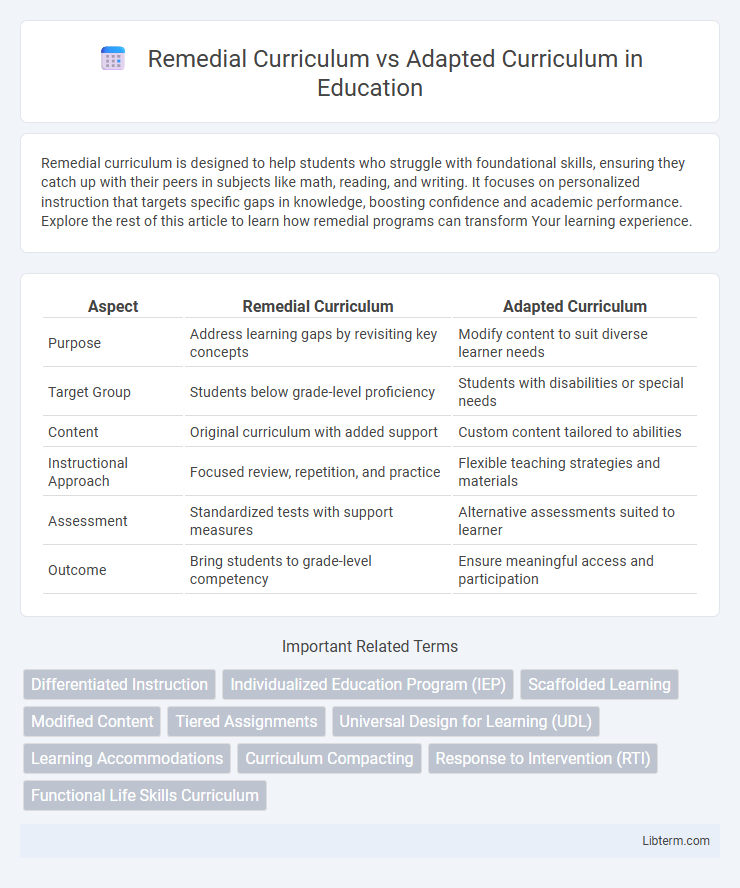
| Aspect | Remedial Curriculum | Adapted Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Address learning gaps by revisiting key concepts | Modify content to suit diverse learner needs |
| Target Group | Students below grade-level proficiency | Students with disabilities or special needs |
| Content | Original curriculum with added support | Custom content tailored to abilities |
| Instructional Approach | Focused review, repetition, and practice | Flexible teaching strategies and materials |
| Assessment | Standardized tests with support measures | Alternative assessments suited to learner |
| Outcome | Bring students to grade-level competency | Ensure meaningful access and participation |
Understanding Remedial Curriculum
Remedial curriculum is designed to help students master foundational skills they have not yet acquired, targeting gaps in knowledge often identified through assessments. It emphasizes repetition, targeted practice, and individualized instruction in core subjects such as reading, math, and writing to bring students up to grade-level proficiency. This approach contrasts with adapted curriculum, which modifies content or delivery methods to meet the needs of students with disabilities or learning differences without necessarily focusing solely on skill deficits.
Defining Adapted Curriculum
Adapted curriculum refers to instructional modifications tailored to meet the diverse needs of students with disabilities, ensuring equitable access to content aligned with general education standards. It involves changes in teaching strategies, materials, and assessment methods to accommodate individual learning profiles without altering the core educational objectives. This approach emphasizes personalized support within the mainstream curriculum framework, contrasting with remedial curriculum that focuses primarily on reteaching foundational skills for struggling learners.
Core Objectives: Remediation vs Adaptation
Remedial curriculum targets core objectives by reinforcing foundational skills in students who have fallen behind, emphasizing skill recovery through repetitive practice and targeted instruction. Adapted curriculum modifies core objectives to accommodate diverse learner needs, ensuring accessibility by altering content complexity, delivery methods, or assessment criteria. The primary distinction lies in remediation aiming to bring students up to standard proficiency, while adaptation customizes learning goals to reflect individual capabilities.
Target Learners for Each Curriculum
Remedial curriculum targets students who struggle to meet standard academic benchmarks, offering focused instruction to address specific skill gaps and improve foundational knowledge. Adapted curriculum is designed for learners with diverse needs, including students with disabilities, by modifying content, delivery, and assessment to match individual abilities and learning styles. Both curricula aim to support learner achievement but differ in scope, with remedial focusing on skill reinforcement and adapted emphasizing personalized access to the general education framework.
Instructional Strategies Compared
Remedial curriculum instruction prioritizes skill reinforcement through repetitive practice and structured drills aimed at closing learning gaps, often emphasizing foundational competencies like reading or math. Adapted curriculum employs differentiated instructional strategies tailored to individual student needs, incorporating flexible materials, personalized pacing, and alternative assessments to accommodate diverse learning abilities. Effective implementation of both approaches relies on ongoing assessment and responsive adjustments to teaching methods to optimize student engagement and achievement.
Assessment Methods in Both Curricula
Remedial curriculum assessment methods primarily focus on diagnostic tests and skill-based evaluations to identify and target specific learning gaps in foundational knowledge. Adapted curriculum assessments emphasize individualized performance measures, often utilizing formative assessments and portfolio reviews to track progress aligned with each student's unique learning needs and accommodations. Both approaches rely on continuous monitoring but differ in the granularity and purpose of the assessments to optimize educational outcomes.
Curriculum Design and Content Modifications
Remedial Curriculum focuses on reinforcing foundational skills through standardized content and structured practice to address learning gaps, often following a fixed scope and sequence aligned with grade-level standards. Adapted Curriculum involves significant content modifications tailored to individual student needs, including simplifying objectives, integrating alternative resources, and emphasizing functional or life skills beyond typical grade expectations. Curriculum design for remedial emphasizes repetition and skill mastery, while adapted curriculum prioritizes personalized learning goals and flexible pathways to accommodate diverse abilities.
Teacher Roles and Responsibilities
Teachers in remedial curriculum focus on identifying learning gaps and providing targeted instruction to help students achieve grade-level competencies through structured, skill-based interventions. In adapted curriculum, educators modify content, teaching methods, and assessment strategies to meet diverse learner needs, often collaborating with specialists to support students with disabilities. Both roles require ongoing assessment, individualized planning, and fostering a supportive learning environment to maximize student progress.
Classroom Implementation Challenges
Remedial curriculum often faces challenges in classroom implementation due to its focus on reinforcing foundational skills, which can lead to repetitive and disengaging lessons for students struggling with core content. Adapted curriculum requires significant teacher training and resource allocation to differentiate instruction effectively for diverse learning needs, which can strain classroom management and instructional time. Both approaches demand careful balancing of individualized support without isolating students from the general education environment.
Selecting the Right Curriculum for Student Needs
Selecting the right curriculum for student needs involves evaluating the specific academic gaps and learning abilities of each learner. A remedial curriculum targets students needing instruction to catch up to grade-level competencies, emphasizing skill reinforcement and foundational knowledge. Conversely, an adapted curriculum modifies content and teaching methods to accommodate diverse learning styles and disabilities, ensuring accessibility and meaningful engagement for all students.
Remedial Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com