Hierarchical structures organize organizations, systems, or data into levels of authority or importance, streamlining decision-making and improving clarity. Understanding these layers helps You navigate complex environments, from corporate settings to computer science models. Explore the rest of this article to uncover how hierarchical structures impact efficiency and communication.
Table of Comparison
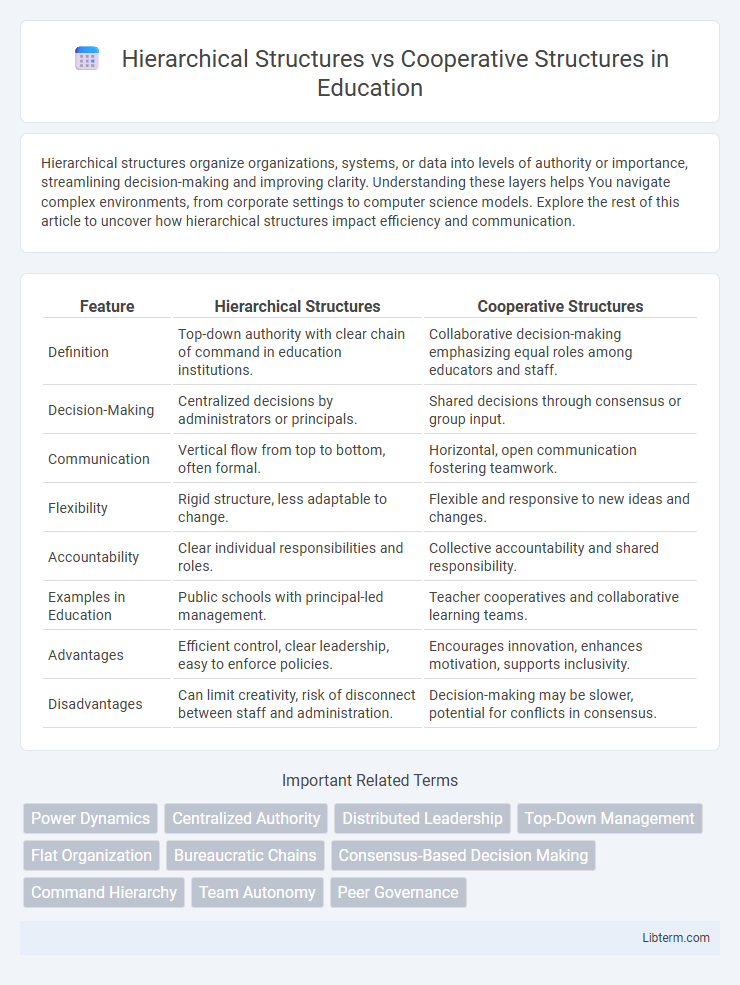
| Feature | Hierarchical Structures | Cooperative Structures |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Top-down authority with clear chain of command in education institutions. | Collaborative decision-making emphasizing equal roles among educators and staff. |
| Decision-Making | Centralized decisions by administrators or principals. | Shared decisions through consensus or group input. |
| Communication | Vertical flow from top to bottom, often formal. | Horizontal, open communication fostering teamwork. |
| Flexibility | Rigid structure, less adaptable to change. | Flexible and responsive to new ideas and changes. |
| Accountability | Clear individual responsibilities and roles. | Collective accountability and shared responsibility. |
| Examples in Education | Public schools with principal-led management. | Teacher cooperatives and collaborative learning teams. |
| Advantages | Efficient control, clear leadership, easy to enforce policies. | Encourages innovation, enhances motivation, supports inclusivity. |
| Disadvantages | Can limit creativity, risk of disconnect between staff and administration. | Decision-making may be slower, potential for conflicts in consensus. |
Introduction to Organizational Structures
Hierarchical structures organize organizations into clear, top-down layers of authority, promoting efficient decision-making and accountability. Cooperative structures emphasize collaboration and shared responsibilities among team members, fostering innovation and flexibility. Understanding these organizational structures helps businesses align their management style with strategic goals for optimal performance.
Defining Hierarchical Structures
Hierarchical structures are organizational frameworks where authority and decision-making flow from top-level management down through successive layers of subordinates, establishing clear lines of command. These structures emphasize a rigid chain of command, with each employee having a specific role and responsibility within defined levels. This system promotes order, accountability, and control but often limits flexibility and collaboration across departments.
Understanding Cooperative Structures
Cooperative structures emphasize collaborative decision-making where members share responsibilities and benefits, fostering equal participation and democratic control. These organizations rely on collective ownership, mutual support, and decentralized management to enhance accountability and transparency among stakeholders. Understanding cooperative structures involves recognizing their core principles of voluntary association, economic participation, and commitment to community development.
Key Differences Between Hierarchical and Cooperative Models
Hierarchical structures feature a clear chain of command with top-down decision-making, emphasizing control and authority within organizational layers. Cooperative structures prioritize collaboration and shared responsibilities, promoting decentralized decision-making and equal participation among members. Key differences lie in power distribution, communication flow, and adaptability, where hierarchical models are rigid and formal, while cooperative models foster flexibility and collective engagement.
Advantages of Hierarchical Structures
Hierarchical structures provide clear lines of authority and responsibility, allowing for efficient decision-making and streamlined communication within organizations. These structures facilitate accountability by defining specific roles and reporting relationships, which can enhance operational control and consistency. Furthermore, hierarchical frameworks support scalability and stability, making them ideal for large organizations requiring formal governance and standardized processes.
Benefits of Cooperative Structures
Cooperative structures promote enhanced innovation and creativity by encouraging collaboration and the free exchange of ideas among team members. They improve employee satisfaction and motivation through shared decision-making and collective responsibility, reducing turnover rates. These structures also increase adaptability and responsiveness to change, enabling organizations to react faster in dynamic markets.
Challenges Facing Hierarchical Organizations
Hierarchical structures often face challenges such as rigid communication channels, slower decision-making processes, and limited employee empowerment, which can stifle innovation and adaptability. These organizations struggle with top-down control that may lead to decreased transparency and employee dissatisfaction. Inefficiencies arise when lower-level employees lack autonomy, hindering responsiveness to dynamic market demands.
Obstacles in Cooperative Management
Cooperative management faces obstacles such as decision-making delays due to the need for consensus among members and conflicting interests that complicate unified action. Unlike hierarchical structures where authority flows top-down, cooperative structures often struggle with role ambiguity and accountability issues, impacting operational efficiency. Resolving these challenges requires well-defined governance mechanisms and effective communication strategies to balance democratic participation with timely execution.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Organization
Choosing the right organizational structure depends on your company's size, culture, and strategic goals. Hierarchical structures offer clear lines of authority and streamlined decision-making, ideal for large or established organizations requiring stability and control. Cooperative structures foster collaboration and flexibility, better suited for innovative or startup environments seeking agility and employee empowerment.
Future Trends: Hybrid Approaches and Evolving Structures
Future organizational trends emphasize hybrid structures combining hierarchical clarity with cooperative flexibility to enhance adaptability and innovation. Emerging models integrate decentralized decision-making while maintaining defined leadership layers, supporting dynamic team collaboration and rapid response to market changes. Technology-driven platforms enable seamless communication across these evolving structures, fostering transparency and agility in complex business environments.
Hierarchical Structures Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com