The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) ensures that children with disabilities receive free appropriate public education tailored to their unique needs. It mandates individualized education programs (IEPs), emphasizing specialized instruction and related services to support academic success. Explore the rest of the article to understand how IDEA impacts your child's educational journey and rights.
Table of Comparison
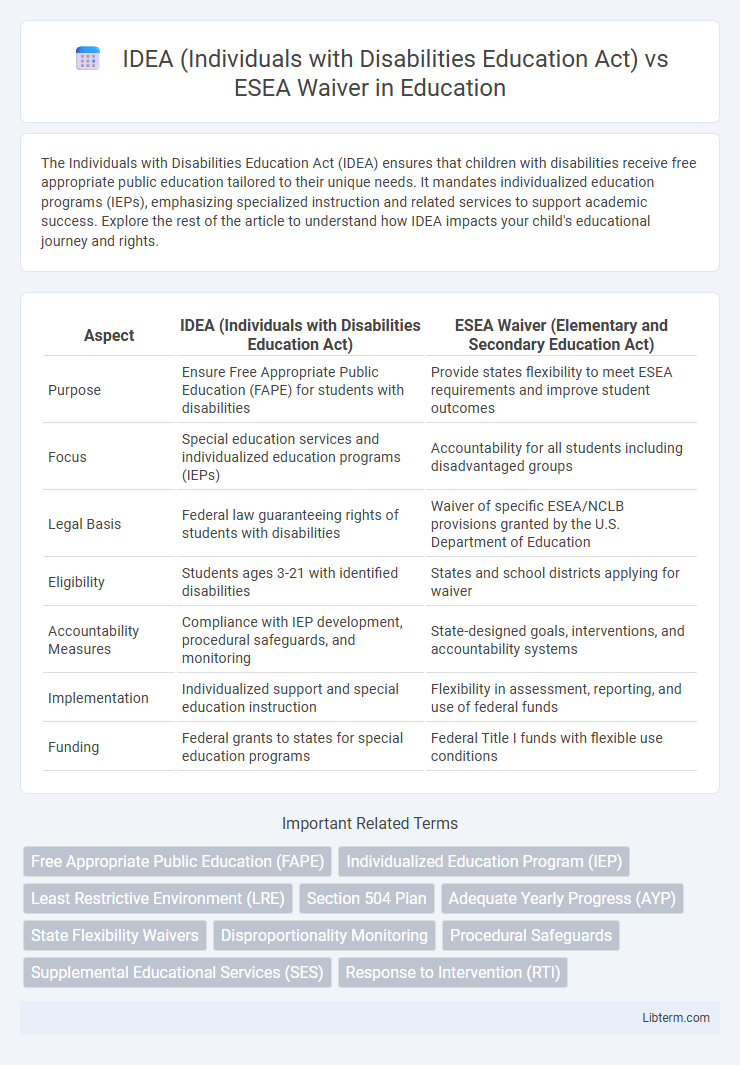
| Aspect | IDEA (Individuals with Disabilities Education Act) | ESEA Waiver (Elementary and Secondary Education Act) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Ensure Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE) for students with disabilities | Provide states flexibility to meet ESEA requirements and improve student outcomes |
| Focus | Special education services and individualized education programs (IEPs) | Accountability for all students including disadvantaged groups |
| Legal Basis | Federal law guaranteeing rights of students with disabilities | Waiver of specific ESEA/NCLB provisions granted by the U.S. Department of Education |
| Eligibility | Students ages 3-21 with identified disabilities | States and school districts applying for waiver |
| Accountability Measures | Compliance with IEP development, procedural safeguards, and monitoring | State-designed goals, interventions, and accountability systems |
| Implementation | Individualized support and special education instruction | Flexibility in assessment, reporting, and use of federal funds |
| Funding | Federal grants to states for special education programs | Federal Title I funds with flexible use conditions |
Overview: IDEA and ESEA Waiver Explained
The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) mandates special education services for students with disabilities, ensuring access to free appropriate public education tailored to individual needs. The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) Waiver allows states flexibility to modify federal accountability and funding requirements, promoting innovation in educational programs. While IDEA focuses on special education rights and services, ESEA Waivers emphasize state-driven reforms to improve overall school performance and student outcomes.
Historical Context: Origins and Evolution
The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), enacted in 1975, originated to ensure free appropriate public education for children with disabilities, mandating individualized education programs and least restrictive environments. The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) Waiver, introduced in the early 2010s under the Obama administration, marked an evolution from strict federal testing mandates toward granting states flexibility in accountability and educational standards. Both IDEA and the ESEA Waiver reflect evolving federal commitments to inclusive education, with IDEA focusing on special education rights and ESEA Waiver emphasizing tailored school improvement strategies.
Core Objectives: Comparing IDEA and ESEA Waiver
IDEA (Individuals with Disabilities Education Act) ensures free appropriate public education tailored to meet the unique needs of students with disabilities, emphasizing individualized education programs (IEPs) and inclusion. The ESEA Waiver, tied to the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) framework, grants states flexibility in accountability, focusing on improving educational outcomes for all students, including historically underserved populations. While IDEA targets specialized support and legal protections for disabled students, the ESEA Waiver centers on broad academic achievement and school accountability, balancing federal oversight with state-driven educational reforms.
Eligibility Criteria: Who Qualifies under Each
IDEA eligibility requires that a child have a recognized disability impacting educational performance, including categories such as specific learning disabilities, autism, or emotional disturbances. ESEA Waiver eligibility focuses on schools and districts rather than individual students, targeting those that fail to meet federal academic standards or demonstrate low performance. While IDEA supports individualized assessments for special education services, ESEA Waiver eligibility is determined by overall school accountability metrics and state-set criteria.
Key Provisions: Services and Support Differences
IDEA mandates specialized educational services, individualized education programs (IEPs), and related support such as therapy and assistive technology to ensure free appropriate public education (FAPE) for students with disabilities. In contrast, ESEA Waivers primarily focus on broad accountability measures, flexible funding uses, and enhanced access to quality instruction, with less emphasis on individualized services. IDEA's provisions require procedural safeguards and parent involvement, while ESEA Waivers support systemic school improvement and interventions without specific mandates for special education services.
Accountability Measures: Monitoring and Compliance
The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) mandates robust accountability measures ensuring states adhere to specific monitoring and compliance standards for special education services, focusing on individualized education programs (IEPs) and timely evaluations. In contrast, the Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) waiver emphasizes flexibility in accountability by allowing states to implement tailored improvement strategies and report on school performance metrics such as student growth and achievement gaps. IDEA's compliance monitoring involves rigorous state performance plans and annual performance reports, while ESEA waivers prioritize state-designed accountability systems including differentiated support for low-performing schools and interventions based on data-driven outcomes.
Funding Structures: Financial Implications
The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) provides dedicated federal funding specifically allocated to support special education and related services for students with disabilities, ensuring schools receive targeted resources for these needs. In contrast, the Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) waivers offer states increased flexibility to reallocate Title I funds aimed at improving educational outcomes for disadvantaged students, sometimes allowing blending or shifting of funds across programs. The financial implications highlight IDEA's role in guaranteeing specialized funding stability while ESEA waivers promote adaptable funding structures that can address broader educational priorities within states.
Impact on Schools: Implementation and Outcomes
The IDEA mandates specialized education services tailored to individual students with disabilities, ensuring access to free appropriate public education and compliance with strict evaluation and individualized education program (IEP) requirements, which require schools to allocate substantial resources for effective implementation. The ESEA Waiver allowed states flexibility in meeting federal accountability standards, often emphasizing broader student achievement goals and standardized testing, which led schools to shift focus toward overall academic performance and closing achievement gaps. Together, these federal policies influence school priorities and resource distribution, with IDEA focusing on individualized support and ESEA Waiver driving systemic accountability and school improvement efforts.
Student Rights and Protections: A Comparative Analysis
IDEA (Individuals with Disabilities Education Act) guarantees specific rights and protections for students with disabilities, including individualized education programs (IEPs), free appropriate public education (FAPE), and procedural safeguards to ensure parental involvement. In contrast, the ESEA Waiver primarily focuses on accountability and flexibility for states in meeting academic standards, offering fewer explicit protections for individual student rights. While IDEA mandates tailored services and legal protections for students with disabilities, the ESEA Waiver emphasizes overall student achievement and system-wide reforms without the same level of individualized rights.
Future Outlook: Policy Trends and Implications
The future outlook for IDEA emphasizes strengthening individualized support by increasing funding and integrating advanced assistive technologies to improve educational outcomes for students with disabilities. ESEA Waiver trends suggest a shift towards greater flexibility in state accountability systems, promoting data-driven decision-making to address achievement gaps more effectively. Policymakers are expected to align IDEA and ESEA initiatives, fostering inclusive education environments while ensuring equitable access to quality resources and services.
IDEA (Individuals with Disabilities Education Act) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com