A Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) outlines strategies and supports designed to address challenging behaviors by identifying their root causes and teaching positive alternatives. This personalized approach helps improve your child's social and learning environment, fostering better outcomes in school and daily life. Explore this article to learn how an effective BIP can transform behavioral challenges into opportunities for growth.
Table of Comparison
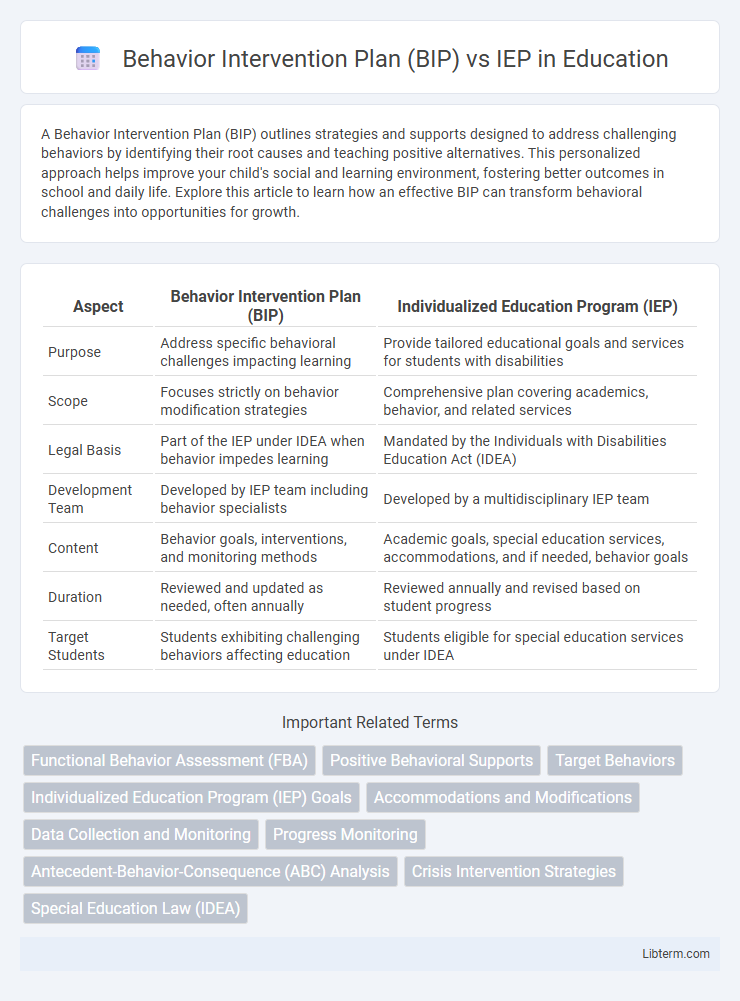
| Aspect | Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) | Individualized Education Program (IEP) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Address specific behavioral challenges impacting learning | Provide tailored educational goals and services for students with disabilities |
| Scope | Focuses strictly on behavior modification strategies | Comprehensive plan covering academics, behavior, and related services |
| Legal Basis | Part of the IEP under IDEA when behavior impedes learning | Mandated by the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) |
| Development Team | Developed by IEP team including behavior specialists | Developed by a multidisciplinary IEP team |
| Content | Behavior goals, interventions, and monitoring methods | Academic goals, special education services, accommodations, and if needed, behavior goals |
| Duration | Reviewed and updated as needed, often annually | Reviewed annually and revised based on student progress |
| Target Students | Students exhibiting challenging behaviors affecting education | Students eligible for special education services under IDEA |
Introduction to Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) and Individualized Education Program (IEP)
A Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) is a strategic approach designed to address specific behavioral challenges by outlining proactive interventions and supports tailored to a student's unique needs. An Individualized Education Program (IEP) is a comprehensive educational plan developed for students with disabilities, detailing personalized goals, accommodations, and services to support academic progress and overall development. While the BIP focuses primarily on modifying behavior, the IEP encompasses broader educational objectives, including both academic and behavioral components.
Defining Behavior Intervention Plans (BIP)
A Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) is a detailed strategy developed to address specific behavioral challenges exhibited by a student, designed to replace negative behaviors with positive ones through targeted interventions and supports. Unlike an Individualized Education Program (IEP), which outlines a student's overall educational goals, services, and accommodations, a BIP focuses specifically on modifying behavior that impedes learning. BIPs are typically created based on a functional behavioral assessment (FBA) and include proactive strategies, teaching new skills, and measures for preventing behavioral issues.
Understanding Individualized Education Programs (IEP)
An Individualized Education Program (IEP) is a legally binding document tailored to meet a student's unique educational needs, outlining specific goals, accommodations, and services to support academic success. In contrast, a Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) is a component often integrated within an IEP that addresses behavioral challenges by outlining strategies and interventions to improve student behavior. Understanding the IEP's comprehensive role highlights its broader scope, encompassing academic, behavioral, and developmental objectives for the student's overall progress.
Key Differences Between BIP and IEP
A Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) focuses specifically on addressing and modifying a student's challenging behaviors through targeted strategies and supports. In contrast, an Individualized Education Program (IEP) encompasses a comprehensive educational plan tailored to a student's unique learning needs, goals, and accommodations across all academic areas. While a BIP can be a component of an IEP, the IEP serves as the broader framework guiding the student's overall educational experience.
How BIPs Support Students with Behavioral Challenges
Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) provide targeted strategies to address specific behavioral challenges identified in students, supporting their emotional and social development within the educational environment. In contrast to Individualized Education Programs (IEPs), which outline broader academic and support goals for students with disabilities, BIPs offer detailed, data-driven interventions to modify and improve problematic behaviors. Implementing a BIP helps reduce disruptions, enhance classroom engagement, and promote positive behavior outcomes, ensuring students receive the necessary behavioral supports to succeed alongside their peers.
The Role of IEP in Academic and Behavioral Success
The Individualized Education Program (IEP) serves as a comprehensive framework that outlines tailored educational goals, services, and accommodations to support a student's academic and behavioral success. The Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) is a specialized component within the IEP designed to address specific behavioral challenges by implementing targeted strategies and interventions. By integrating the BIP into the IEP, educators ensure a holistic approach that promotes positive behavior while advancing academic achievement.
When Is a BIP Included in an IEP?
A Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) is included in an Individualized Education Program (IEP) when a student's behavior impedes their learning or that of others, as determined through a Functional Behavioral Assessment (FBA). The BIP outlines specific strategies and supports designed to address challenging behaviors and promote positive behavior changes within the educational setting. This integration ensures that behavioral goals align with the student's overall educational objectives and legal requirements under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA).
Developing Effective BIPs: Strategies and Best Practices
Developing effective Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) requires a thorough Functional Behavioral Assessment (FBA) to identify the root causes of challenging behaviors in students with Individualized Education Programs (IEPs). Incorporating data-driven strategies, such as positive reinforcement, clear behavioral goals, and consistent monitoring, enhances the success of BIPs in promoting adaptive behaviors. Collaboration among educators, parents, and specialists ensures that BIPs are tailored to meet the unique needs outlined in the student's IEP, facilitating improved academic and social outcomes.
Collaboration Among Educators and Families in Creating BIPs and IEPs
Collaboration among educators and families is crucial in creating effective Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) and Individualized Education Programs (IEPs), ensuring that student-specific behavioral and educational needs are met comprehensively. Educators, specialists, and family members contribute valuable insights and data during the development process, fostering communication that enhances the implementation and consistency of interventions. This collaborative approach helps to align behavioral objectives in BIPs with academic goals in IEPs, promoting a supportive learning environment tailored to the student's unique needs.
Legal Considerations and Compliance: BIP vs IEP
Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) are legally required under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) when a student's behavior impedes their own learning or that of others, ensuring tailored strategies within the educational framework. Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) encompass broader educational goals, including behavior goals, with strict compliance mandates for schools to provide Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE) as outlined in IDEA. Legal compliance for both BIPs and IEPs involves documenting interventions, parental consent, regular progress monitoring, and adherence to state and federal regulations to protect student rights and promote effective behavior and academic outcomes.
Behavior Intervention Plan (BIP) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com