Disciplinary actions are essential for maintaining order and enforcing rules within organizations or institutions. Proper understanding of disciplinary procedures helps ensure fairness and consistency while protecting both the organization and individual rights. Explore the rest of the article to learn how effective disciplinary practices can improve your environment.
Table of Comparison
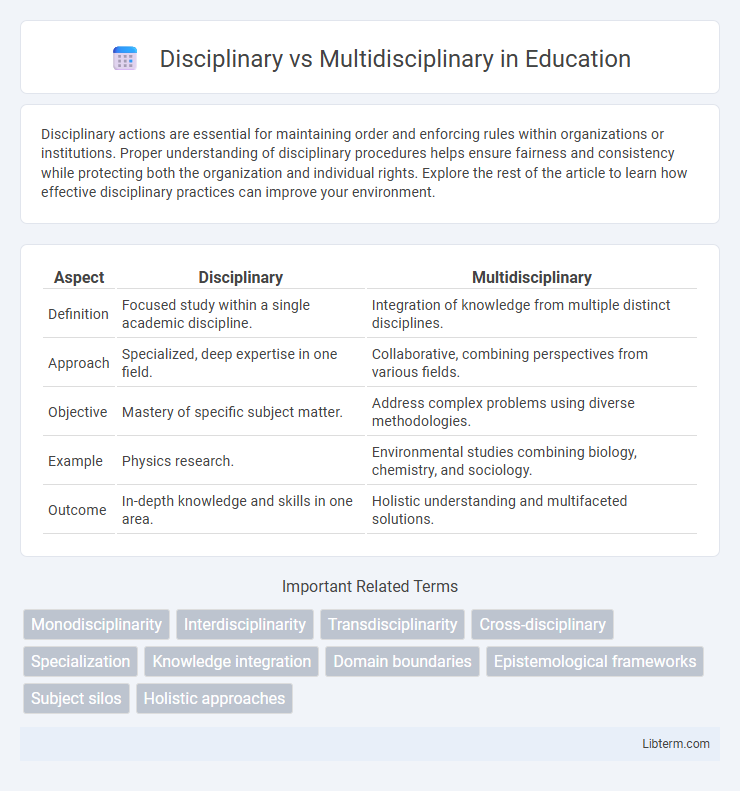
| Aspect | Disciplinary | Multidisciplinary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focused study within a single academic discipline. | Integration of knowledge from multiple distinct disciplines. |
| Approach | Specialized, deep expertise in one field. | Collaborative, combining perspectives from various fields. |
| Objective | Mastery of specific subject matter. | Address complex problems using diverse methodologies. |
| Example | Physics research. | Environmental studies combining biology, chemistry, and sociology. |
| Outcome | In-depth knowledge and skills in one area. | Holistic understanding and multifaceted solutions. |
Understanding Disciplinary Approaches
Disciplinary approaches focus on deep expertise within a single field, emphasizing specialized knowledge, methods, and perspectives unique to that domain. This approach fosters rigorous analysis and problem-solving grounded in the foundational theories and practices of one discipline. Understanding disciplinary approaches is crucial for developing in-depth skills and generating precise insights before integrating multiple fields.
Defining Multidisciplinary Methods
Multidisciplinary methods integrate knowledge and techniques from various disciplines without merging their perspectives into a single framework, allowing each field to maintain its distinct approach while contributing to a common goal. These methods facilitate collaboration among experts from diverse domains such as biology, engineering, and sociology to address complex problems with complementary insights. Unlike disciplinary approaches, multidisciplinary strategies emphasize parallel contributions rather than synthesis, promoting comprehensive analysis through varied specialized lenses.
Key Differences Between Disciplinary and Multidisciplinary
Disciplinary approaches concentrate on a single field of study, emphasizing depth and specialized knowledge within that specific domain. Multidisciplinary methods integrate insights and techniques from multiple distinct disciplines to address complex problems without necessarily synthesizing these perspectives into a unified framework. The key difference lies in the scope and interaction: disciplinary work is narrowly focused and depth-oriented, whereas multidisciplinary work spans diverse fields, facilitating broader but sometimes parallel analyses.
Advantages of Disciplinary Study
Disciplinary study offers deep expertise within a specific field, enabling rigorous analysis and mastery of core methodologies and theories. This approach supports the development of specialized skills and a strong foundational knowledge base, which are critical for advancing innovation and research. Concentrated focus in one discipline also facilitates clearer communication and standards within professional communities.
Benefits of Multidisciplinary Collaboration
Multidisciplinary collaboration integrates expertise from diverse disciplines, fostering innovative problem-solving and comprehensive approaches that single-discipline efforts may lack. This synergy enhances creativity, accelerates knowledge exchange, and improves the effectiveness of complex projects by combining varied perspectives and methodologies. Organizations benefit from increased adaptability and superior outcomes through the enriched insights derived from multidisciplinary teamwork.
Challenges in Disciplinary Research
Disciplinary research often faces challenges such as limited scope, which can hinder the ability to address complex, real-world problems requiring diverse perspectives. Researchers may encounter difficulties in integrating knowledge from other fields, leading to potential gaps in understanding and innovation. Additionally, strict adherence to disciplinary boundaries can restrict collaboration opportunities and reduce the overall impact of findings.
Obstacles in Multidisciplinary Projects
Multidisciplinary projects often face communication barriers due to differing terminologies and methodologies across disciplines, which can hinder effective collaboration. Conflicting priorities and goals among team members from varied specialties create challenges in aligning project objectives and decision-making processes. Resource allocation and management become complicated as disciplines compete for time, funding, and attention, slowing project progress and innovation.
Examples of Disciplinary Applications
Disciplinary applications focus on specialized knowledge within a single field, such as a surgeon applying advanced medical techniques to perform complex operations or a chemist researching molecular interactions in a laboratory. Engineers designing bridges rely on civil engineering principles, while economists use statistical models to analyze market trends. These examples illustrate deep expertise confined to one domain, contrasting with multidisciplinary approaches that integrate multiple fields.
Real-World Multidisciplinary Case Studies
Real-world multidisciplinary case studies demonstrate the integration of diverse disciplinary perspectives to solve complex problems, often involving collaboration across fields such as engineering, healthcare, and social sciences. This approach contrasts with disciplinary methods that focus narrowly within a single field, limiting the scope and applicability of solutions. Examples include urban sustainability projects combining environmental science, economics, and public policy to address climate resilience effectively.
Choosing Between Disciplinary and Multidisciplinary Approaches
Choosing between disciplinary and multidisciplinary approaches depends on the complexity and scope of the problem being addressed. Disciplinary approaches focus deeply on a single field, such as biology or economics, offering specialized expertise and detailed knowledge essential for in-depth analysis. Multidisciplinary methods integrate insights from multiple disciplines, promoting comprehensive understanding and innovative solutions by combining perspectives from fields like engineering, sociology, and environmental science.
Disciplinary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com