Detention refers to the act of holding someone in custody, typically by legal or institutional authorities, to prevent freedom of movement for a specified period. It can occur in various contexts such as criminal justice, immigration, or school disciplinary settings, with each having distinct procedures and rights involved. Explore the full article to understand how detention impacts your rights and the legal processes involved.
Table of Comparison
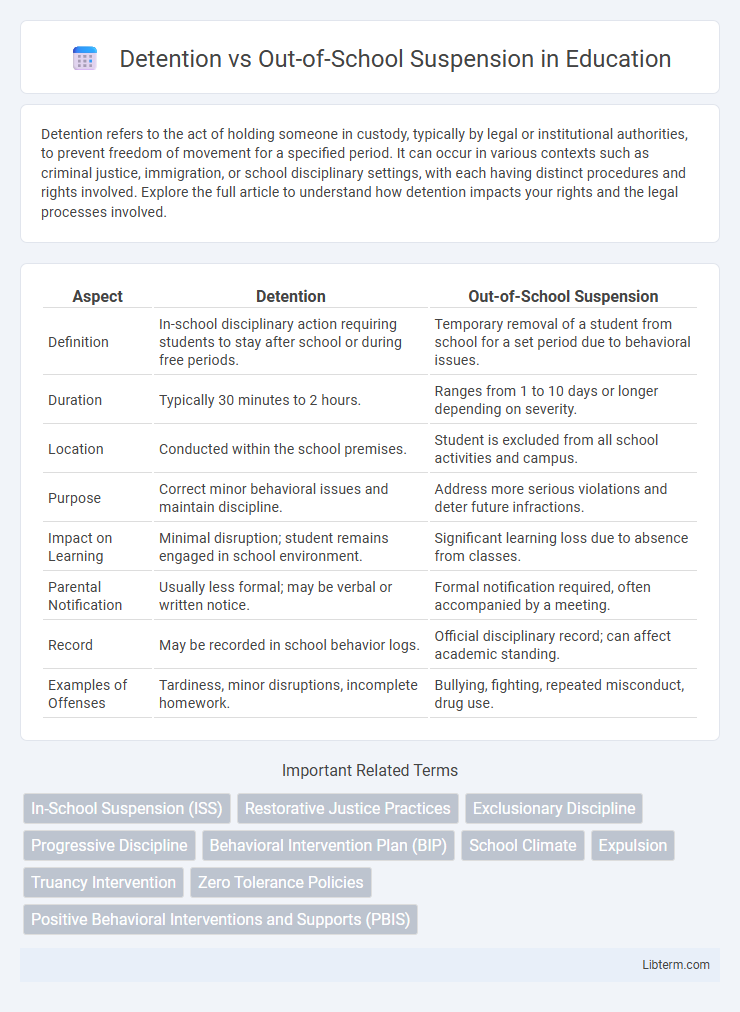
| Aspect | Detention | Out-of-School Suspension |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | In-school disciplinary action requiring students to stay after school or during free periods. | Temporary removal of a student from school for a set period due to behavioral issues. |
| Duration | Typically 30 minutes to 2 hours. | Ranges from 1 to 10 days or longer depending on severity. |
| Location | Conducted within the school premises. | Student is excluded from all school activities and campus. |
| Purpose | Correct minor behavioral issues and maintain discipline. | Address more serious violations and deter future infractions. |
| Impact on Learning | Minimal disruption; student remains engaged in school environment. | Significant learning loss due to absence from classes. |
| Parental Notification | Usually less formal; may be verbal or written notice. | Formal notification required, often accompanied by a meeting. |
| Record | May be recorded in school behavior logs. | Official disciplinary record; can affect academic standing. |
| Examples of Offenses | Tardiness, minor disruptions, incomplete homework. | Bullying, fighting, repeated misconduct, drug use. |
Understanding Detention and Out-of-School Suspension
Detention serves as a disciplinary action requiring students to remain in school outside regular hours, promoting accountability and behavior correction within the educational environment. Out-of-school suspension involves temporarily removing students from school premises to address severe misconduct, aiming to ensure safety and provide a period for reflection. Understanding the distinct purposes and impacts of these consequences is essential for effective student discipline management and fostering a positive learning atmosphere.
Key Differences Between Detention and Suspension
Detention requires students to stay after school or during lunch as a consequence for minor behavioral issues, promoting reflection and continued engagement in school activities. Out-of-school suspension removes the student entirely from the school environment for a set period, typically for more serious infractions, impacting attendance and academic progress. The key differences lie in the severity of the behavior addressed, duration of the discipline, and the student's presence on campus during the disciplinary period.
Impact on Student Behavior and Learning
Detention often serves as a corrective measure that allows students to reflect on misbehavior without significant disruption to their academic progress, promoting accountability while maintaining classroom engagement. Out-of-school suspension, however, removes students from the educational environment entirely, increasing the risk of academic decline, disengagement, and negative behavioral outcomes. Research shows that frequent suspensions correlate with higher dropout rates and lower graduation probabilities, highlighting the importance of alternative disciplinary strategies that support learning and behavior improvement.
When Is Detention Appropriate?
Detention is appropriate for minor behavioral issues such as tardiness, incomplete homework, or classroom disruptions that do not warrant removal from school. It serves as an immediate corrective measure to reinforce accountability and encourage positive behavior without interrupting the student's academic progress. Schools often use detention to address first-time or low-risk infractions, promoting discipline while maintaining student engagement in daily learning activities.
When Is Out-of-School Suspension Justified?
Out-of-school suspension is justified when a student's behavior poses a significant threat to the safety or well-being of others, such as violence, possession of weapons, or severe drug infractions. It is reserved for serious offenses that disrupt the educational environment and cannot be effectively addressed through less severe disciplinary measures like detention. School policies typically mandate suspension only after thorough investigation and consideration of the incident's impact on the school community.
Pros and Cons of Detention
Detention allows students to remain in a supervised environment within school, promoting accountability while maintaining consistent access to educational resources. This disciplinary approach can reinforce behavioral expectations without removing students entirely from the learning process, minimizing academic disruption. However, detention may not effectively address underlying behavioral issues and can strain staff resources due to increased supervision requirements.
Pros and Cons of Out-of-School Suspension
Out-of-school suspension removes students from the school environment, which can reduce immediate behavioral disruptions and provide a clear consequence for serious infractions. However, it often results in missed instructional time, increased risk of academic decline, and potential negative social impacts due to isolation from peers and school support systems. This disciplinary method may also contribute to higher dropout rates and does not address underlying behavioral issues effectively.
Effects on Student Well-being and Future Outcomes
Detention and out-of-school suspension differ significantly in their effects on student well-being and future outcomes, with out-of-school suspension linked to higher risks of academic decline, increased dropout rates, and negative impacts on mental health due to isolation from peers and school support systems. Detention, while restrictive, allows continued engagement with the educational environment, promoting accountability without severing the student's connection to daily learning and social interaction. Research consistently shows that alternative disciplinary measures focused on in-school consequences foster better long-term academic success and emotional resilience compared to exclusionary practices like suspension.
Parental and Community Perspectives
Parental concerns about detention often center on its perceived lower impact compared to out-of-school suspension, which may disrupt academic progress and increase dropout risks. Community members emphasize that detentions can maintain school engagement while addressing behavioral issues without removing students from the educational environment. Both groups advocate for interventions that balance accountability with support, highlighting the need for clear communication and restorative practices to foster positive student outcomes.
Best Practices for Schools: Choosing the Right Disciplinary Approach
Effective disciplinary practices prioritize restorative methods over punitive measures, emphasizing student growth and accountability in school settings. Implementing detention allows for structured reflection without removing students from the learning environment, whereas out-of-school suspension often leads to academic disruption and increased dropout risks. Schools should assess behavioral incidents contextually, applying detention for minor infractions and reserving out-of-school suspension for severe cases, thereby promoting equity and reducing negative educational outcomes.
Detention Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com