Public schools provide accessible education funded by local, state, and federal governments to ensure equal learning opportunities for all students. They offer diverse curricula and extracurricular activities designed to support academic and social development. Discover how public schools can benefit your child's educational journey by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
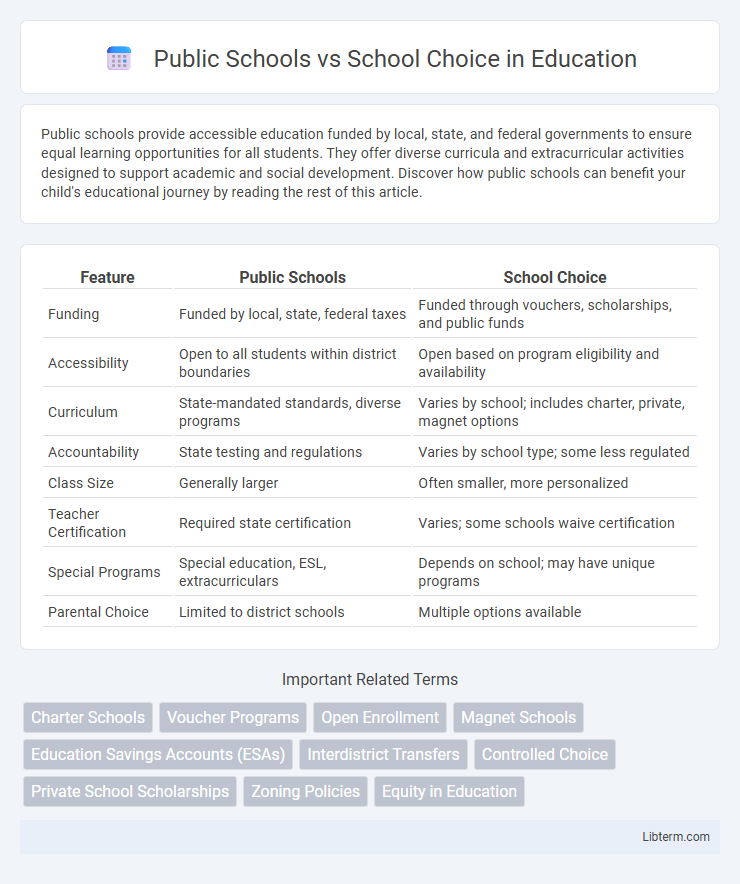
| Feature | Public Schools | School Choice |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Funded by local, state, federal taxes | Funded through vouchers, scholarships, and public funds |
| Accessibility | Open to all students within district boundaries | Open based on program eligibility and availability |
| Curriculum | State-mandated standards, diverse programs | Varies by school; includes charter, private, magnet options |
| Accountability | State testing and regulations | Varies by school type; some less regulated |
| Class Size | Generally larger | Often smaller, more personalized |
| Teacher Certification | Required state certification | Varies; some schools waive certification |
| Special Programs | Special education, ESL, extracurriculars | Depends on school; may have unique programs |
| Parental Choice | Limited to district schools | Multiple options available |
Understanding Public Schools: An Overview
Public schools, funded primarily through local, state, and federal government sources, provide free education to all students within designated geographic boundaries. These institutions adhere to standardized curricula set by education departments to ensure consistent learning outcomes and equitable access to resources. Serving diverse student populations, public schools emphasize inclusivity, special education programs, and compliance with regulations like the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA).
What is School Choice? Definitions and Types
School choice encompasses various educational options allowing parents to select schools outside their assigned public institutions, including charter schools, magnet schools, voucher programs, and homeschooling. Charter schools operate autonomously with public funding, offering specialized curricula, while voucher programs provide financial aid for attending private schools. Magnet schools emphasize specific themes or programs, such as STEM or the arts, attracting students based on interest rather than geography.
Historical Evolution of Public Education
Public education in the United States evolved from locally controlled, one-room schoolhouses in the early 19th century to widespread, state-funded public school systems established during the Common School Movement led by Horace Mann. The rise of charter schools and voucher programs in the late 20th century marked a significant shift toward school choice, promoting competition and parental control within the education market. Federal legislation such as the Elementary and Secondary Education Act of 1965 further expanded access and accountability in public education while fueling debates about equity and school choice policies.
Key Arguments for Public Schooling
Public schooling provides equitable access to education for all students regardless of socioeconomic status, promoting social cohesion and diversity. State-funded resources in public schools ensure standardized curriculum and certified teachers to maintain consistent educational quality. Public education supports community accountability and transparency, fostering inclusive environments that prepare students for civic engagement.
Benefits and Challenges of School Choice
School choice offers families the opportunity to select educational environments tailored to their children's unique learning needs, potentially improving academic outcomes and satisfaction. However, challenges include resource allocation disparities, reduced funding for traditional public schools, and concerns about equitable access for all socioeconomic groups. Balancing these benefits and challenges requires careful policy design to ensure diverse educational opportunities without compromising public education quality.
Comparing Academic Outcomes: Public vs. Choice Schools
Public schools often demonstrate consistent academic outcomes due to standardized curriculums and state funding, while school choice options such as charter and voucher schools offer diverse educational models that can lead to varied performance results. Research indicates that some school choice programs improve standardized test scores and graduation rates, especially in underserved communities, although outcomes widely depend on implementation quality and accountability measures. Comparative studies highlight that while school choice can foster innovation and competition, public schools continue to provide equitable access to comprehensive education critical for broader student populations.
Funding and Resource Allocation: Who Benefits?
Public schools receive the majority of funding from local property taxes, state budgets, and federal grants, resulting in uneven resource allocation based on community wealth. School choice programs, including vouchers and charter schools, redirect public funds to private or alternative institutions, raising debates about the impact on public school budgets. The beneficiaries of funding shifts depend on policy design, with public schools often facing financial strains while school choice options can access resources with potentially less accountability.
Equity, Access, and Social Implications
Public schools aim to provide equitable education by offering universal access regardless of socioeconomic status, fostering diverse learning environments that reflect community demographics. School choice programs, including charter schools, vouchers, and magnet schools, can increase access to specialized curricula but may inadvertently widen educational disparities by diverting resources from traditional public schools. Social implications include potential stratification and reduced social cohesion when school choice options create socioeconomically segregated learning spaces, challenging the equity goals foundational to public education systems.
Parental Perspectives and Student Experiences
Parental perspectives on public schools often emphasize stability, community involvement, and standardized curricula, while school choice advocates highlight personalized learning and increased educational opportunities. Students in public schools benefit from diverse peer interactions and established support systems; those in school choice programs frequently experience tailored instruction but may face variability in resources. Research indicates that parental satisfaction tends to increase with options that align closely with their child's learning style and needs, impacting overall student engagement and academic outcomes.
The Future of Education: Policy Trends and Predictions
Public schools remain the backbone of the education system, with over 50 million students enrolled nationwide, but school choice programs, including charter schools, vouchers, and education savings accounts, are rapidly expanding, influencing policy decisions. Emerging trends emphasize personalized learning, technology integration, and increased parental control, aiming to enhance educational outcomes and equity. Policy predictions indicate continued funding shifts toward school choice initiatives, paired with accountability measures to ensure quality and accessibility across diverse communities.
Public Schools Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com