Inquiry-Based Learning engages students in active exploration and critical thinking, fostering deeper understanding through questioning and investigation. This educational approach promotes curiosity and autonomy, helping learners develop problem-solving skills essential for lifelong learning. Discover how inquiry-based learning can transform Your educational experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
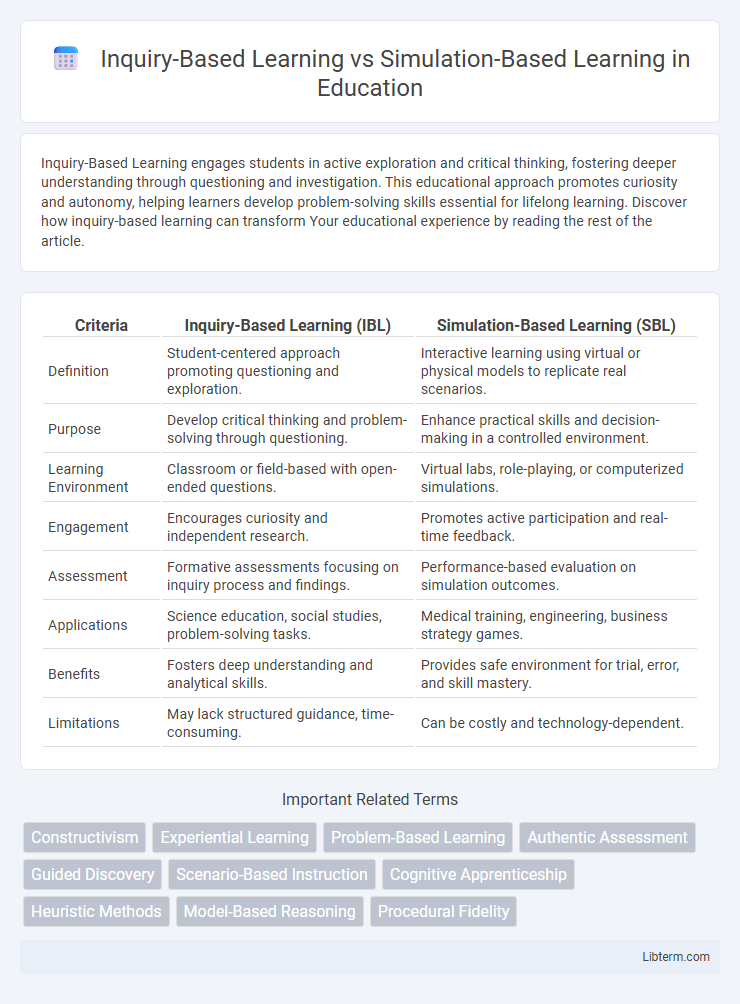
| Criteria | Inquiry-Based Learning (IBL) | Simulation-Based Learning (SBL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach promoting questioning and exploration. | Interactive learning using virtual or physical models to replicate real scenarios. |
| Purpose | Develop critical thinking and problem-solving through questioning. | Enhance practical skills and decision-making in a controlled environment. |
| Learning Environment | Classroom or field-based with open-ended questions. | Virtual labs, role-playing, or computerized simulations. |
| Engagement | Encourages curiosity and independent research. | Promotes active participation and real-time feedback. |
| Assessment | Formative assessments focusing on inquiry process and findings. | Performance-based evaluation on simulation outcomes. |
| Applications | Science education, social studies, problem-solving tasks. | Medical training, engineering, business strategy games. |
| Benefits | Fosters deep understanding and analytical skills. | Provides safe environment for trial, error, and skill mastery. |
| Limitations | May lack structured guidance, time-consuming. | Can be costly and technology-dependent. |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based Learning and Simulation-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes student-driven questioning, exploration, and critical thinking to construct knowledge actively. Simulation-Based Learning utilizes interactive, virtual environments that replicate real-world scenarios for experiential understanding and skill development. Both methods enhance engagement and deepen comprehension through immersive, hands-on educational approaches.
Core Principles of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on student-driven exploration where learners formulate questions, investigate, and construct knowledge through critical thinking and problem-solving. It emphasizes active engagement, curiosity, and reflective thinking to develop deep understanding and transferable skills. Core principles include fostering questioning, promoting hands-on investigation, and encouraging metacognition to support autonomous learning and knowledge construction.
Key Features of Simulation-Based Learning
Simulation-Based Learning immerses learners in realistic, interactive environments that replicate real-world scenarios, enabling hands-on practice and immediate feedback. Key features include high-fidelity models, risk-free experimentation, and dynamic decision-making processes that enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This approach also supports experiential learning by allowing repeated trials and adaptation without real-world consequences.
Pedagogical Differences Between Inquiry and Simulation Methods
Inquiry-based learning emphasizes student-driven exploration and questioning to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Simulation-based learning uses interactive, controlled environments to replicate real-world scenarios, allowing learners to apply knowledge and practice decision-making in a risk-free setting. Pedagogically, inquiry fosters deeper conceptual understanding through investigation, while simulation enhances experiential learning through active participation and immediate feedback.
Benefits of Inquiry-Based Learning in the Classroom
Inquiry-Based Learning boosts student engagement by encouraging active questioning and exploration, fostering critical thinking skills essential for problem-solving. It promotes deeper understanding through hands-on experiences, allowing learners to construct knowledge based on their investigations. This approach enhances retention and motivation by making learning relevant and student-centered, leading to improved academic outcomes.
Advantages of Simulation-Based Learning for Skill Development
Simulation-based learning enhances skill development by providing immersive, hands-on experiences that replicate real-world scenarios, allowing learners to practice and refine techniques without risk. It enables immediate feedback and iterative learning cycles, which accelerate competency and confidence in complex tasks. This method also supports the development of decision-making, problem-solving, and critical thinking skills through interactive, controlled environments tailored to specific training objectives.
Challenges and Limitations of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning faces challenges such as the potential for student frustration due to open-ended questions and the need for strong self-regulation skills, which may not be fully developed in all learners. Limited teacher guidance can result in misconceptions or incomplete understanding, while variability in student motivation impacts the depth of inquiry and learning outcomes. Resource constraints and the time-intensive nature of inquiry activities further limit its widespread implementation in traditional classroom settings.
Drawbacks and Constraints of Simulation-Based Learning
Simulation-Based Learning faces constraints such as high costs for advanced technology and software development, which may limit accessibility for some institutions. It often requires extensive training for both instructors and students to effectively navigate complex simulation tools, potentially hindering seamless integration into curricula. Moreover, simulations can sometimes oversimplify real-world scenarios, reducing authenticity and limiting the depth of critical thinking compared to Inquiry-Based Learning approaches.
Choosing the Right Method: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right method between Inquiry-Based Learning (IBL) and Simulation-Based Learning (SBL) depends on factors such as learning objectives, student engagement levels, and resource availability. IBL is effective for fostering critical thinking and investigative skills through open-ended exploration, while SBL excels in providing practical, hands-on experience in controlled, realistic scenarios. Consider the complexity of the subject matter and the desired balance between theory and practice to optimize educational outcomes.
Integrating Inquiry and Simulation for Optimal Learning Outcomes
Integrating inquiry-based learning with simulation-based learning creates a dynamic educational environment where students actively explore concepts through questioning while applying knowledge in realistic, simulated scenarios. This combined approach enhances critical thinking, promotes deeper understanding, and allows learners to experiment with variables in a safe space, leading to improved problem-solving skills and retention. Research shows that blending inquiry with simulation fosters engagement and supports diverse learning styles, maximizing educational effectiveness across disciplines like science, healthcare, and engineering.
Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com