Traditional subject-based teaching organizes curriculum into distinct disciplines, allowing learners to focus intensively on specific areas like math, science, or literature. This method often emphasizes rote memorization and structured lessons to build foundational knowledge. Explore the rest of the article to discover how this approach compares to modern educational strategies and how it might impact Your learning journey.
Table of Comparison
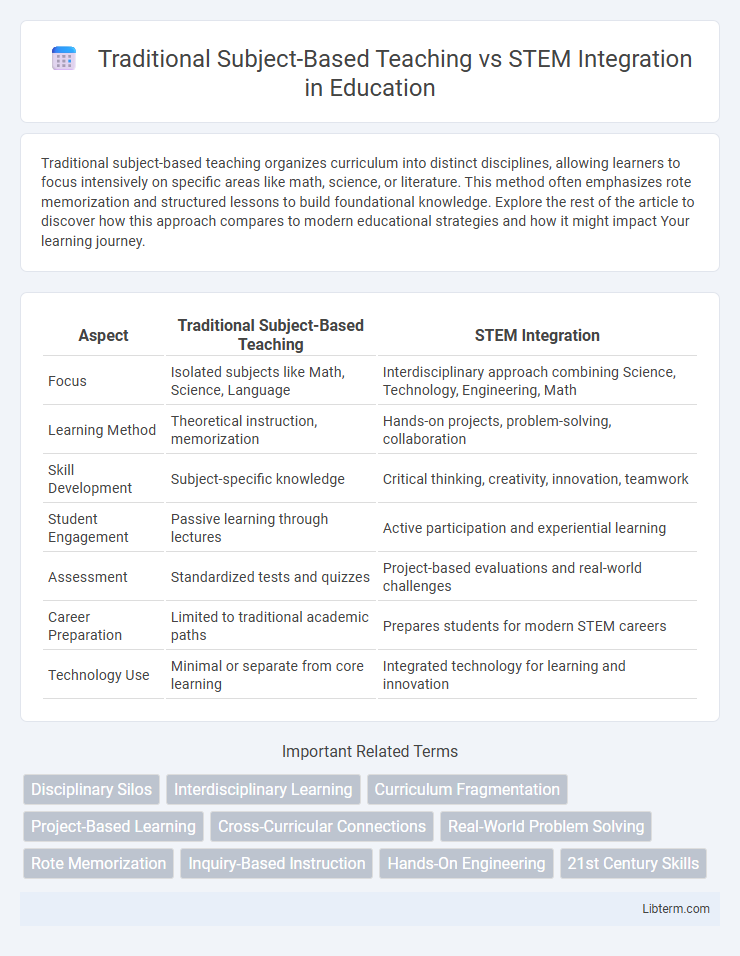
| Aspect | Traditional Subject-Based Teaching | STEM Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Isolated subjects like Math, Science, Language | Interdisciplinary approach combining Science, Technology, Engineering, Math |
| Learning Method | Theoretical instruction, memorization | Hands-on projects, problem-solving, collaboration |
| Skill Development | Subject-specific knowledge | Critical thinking, creativity, innovation, teamwork |
| Student Engagement | Passive learning through lectures | Active participation and experiential learning |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and quizzes | Project-based evaluations and real-world challenges |
| Career Preparation | Limited to traditional academic paths | Prepares students for modern STEM careers |
| Technology Use | Minimal or separate from core learning | Integrated technology for learning and innovation |
Introduction to Traditional and STEM-Based Education
Traditional subject-based teaching emphasizes isolated academic disciplines such as mathematics, science, language arts, and social studies, with a focus on rote memorization and structured, teacher-led instruction. STEM integration combines science, technology, engineering, and mathematics into interdisciplinary learning experiences that promote problem-solving, critical thinking, and real-world application. This approach fosters collaboration and innovation by connecting concepts across subjects rather than treating them as separate entities.
Defining Traditional Subject-Based Teaching
Traditional Subject-Based Teaching organizes curriculum into distinct disciplines such as math, science, language arts, and social studies, emphasizing mastery of specific content within each subject. Instruction typically follows a linear progression, focusing on memorization, standardized testing, and teacher-led lessons to ensure foundational knowledge. This approach often limits interdisciplinary connections, confining student learning to discrete, compartmentalized areas of study.
What is STEM Integration?
STEM integration combines Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics into a cohesive learning paradigm, breaking away from traditional subject-based teaching that often isolates these disciplines. This approach encourages real-world problem-solving and critical thinking by linking concepts across subjects, fostering deeper understanding and engagement. STEM integration equips students with interdisciplinary skills vital for innovation and competitiveness in the 21st-century workforce.
Key Differences Between Traditional and STEM Approaches
Traditional subject-based teaching separates disciplines into distinct categories like math, science, and language arts, emphasizing rote memorization and individual assessment. STEM integration blends science, technology, engineering, and mathematics into interconnected lessons that promote problem-solving, critical thinking, and collaboration. The key difference lies in STEM's emphasis on real-world applications and interdisciplinary learning, contrasting with the isolated, theory-driven focus of traditional methods.
Curriculum Structure: Subject Silos vs Interdisciplinary Learning
Traditional subject-based teaching organizes curriculum into distinct subject silos, such as math, science, and language arts, with limited interaction between disciplines. STEM integration restructures the curriculum around interdisciplinary learning, blending science, technology, engineering, and mathematics concepts to foster critical thinking and real-world problem-solving skills. This approach promotes collaboration across subjects, enabling students to apply knowledge in cohesive and innovative ways, contrasting with the fragmented nature of traditional curricula.
Teaching Methods: Lectures vs Hands-On Projects
Traditional subject-based teaching relies heavily on lectures, emphasizing rote memorization and theoretical knowledge delivery. STEM integration shifts the focus to hands-on projects, encouraging experiential learning, critical thinking, and real-world problem solving. This method enhances student engagement and helps develop practical skills essential for STEM careers.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Traditional subject-based teaching often leads to compartmentalized knowledge, which can limit student engagement and reduce motivation as learners struggle to see real-world applications. STEM integration promotes hands-on, interdisciplinary projects that increase student curiosity and participation by connecting concepts across science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Research shows that students in STEM-integrated environments demonstrate higher motivation levels, improved problem-solving skills, and sustained interest in learning.
Skills Development: Memorization vs Critical Thinking
Traditional subject-based teaching emphasizes memorization and repetition, often focusing on mastering discrete facts within isolated disciplines like history, math, or science. STEM integration fosters critical thinking by encouraging students to solve real-world problems through the application of interdisciplinary knowledge, combining science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. This approach enhances skills such as analytical reasoning, creativity, and collaboration, preparing students for complex, dynamic challenges beyond rote learning.
Assessment Methods and Learning Outcomes
Traditional subject-based teaching relies heavily on standardized tests and quizzes to assess discrete knowledge in subjects like math, science, and language arts, often resulting in compartmentalized learning outcomes. STEM integration employs project-based assessments and collaborative problem-solving tasks that measure critical thinking, creativity, and applied skills across science, technology, engineering, and mathematics domains. Research indicates STEM approaches enhance student engagement and improve real-world problem-solving abilities, fostering deeper conceptual understanding compared to traditional assessment methods.
Preparing Students for Future Careers
Traditional subject-based teaching often limits students to siloed knowledge, whereas STEM integration promotes interdisciplinary learning crucial for future career demands in technology and innovation sectors. Emphasizing critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving, STEM integration equips students with versatile skills aligned with workforce needs in engineering, computer science, and data analytics. Preparing students through STEM fosters adaptability and creativity required to navigate rapidly evolving industries and emerging job markets.
Traditional Subject-Based Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com