Preserving natural resources is essential for maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem health. Effective conservation strategies help combat climate change and protect endangered species by promoting sustainable land use and habitat restoration. Explore the rest of this article to discover how your actions can contribute to global conservation efforts.
Table of Comparison
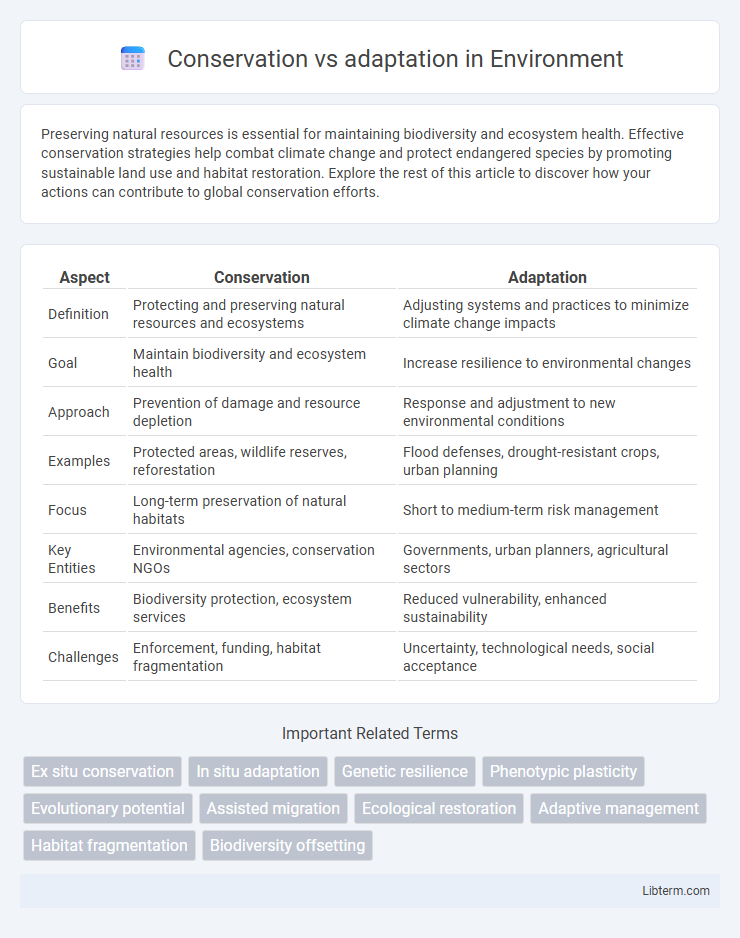
| Aspect | Conservation | Adaptation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Protecting and preserving natural resources and ecosystems | Adjusting systems and practices to minimize climate change impacts |
| Goal | Maintain biodiversity and ecosystem health | Increase resilience to environmental changes |
| Approach | Prevention of damage and resource depletion | Response and adjustment to new environmental conditions |
| Examples | Protected areas, wildlife reserves, reforestation | Flood defenses, drought-resistant crops, urban planning |
| Focus | Long-term preservation of natural habitats | Short to medium-term risk management |
| Key Entities | Environmental agencies, conservation NGOs | Governments, urban planners, agricultural sectors |
| Benefits | Biodiversity protection, ecosystem services | Reduced vulnerability, enhanced sustainability |
| Challenges | Enforcement, funding, habitat fragmentation | Uncertainty, technological needs, social acceptance |
Understanding Conservation and Adaptation
Conservation involves preserving natural resources and ecosystems to maintain biodiversity and ecological balance, ensuring the longevity of habitats and species. Adaptation refers to the process by which organisms or systems adjust to environmental changes, enhancing survival and function under new conditions. Understanding conservation and adaptation is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate climate change impacts and promote sustainable natural resource management.
Definitions: Conservation vs Adaptation
Conservation refers to the protection and preservation of natural resources, ecosystems, and biodiversity to maintain ecological balance and prevent depletion. Adaptation involves adjusting practices, behaviors, or systems in response to environmental changes, such as climate change, to reduce negative impacts and enhance resilience. Both strategies are critical in environmental management, with conservation focusing on maintaining existing natural conditions and adaptation emphasizing dynamic responses to evolving environmental challenges.
Historical Context of Environmental Approaches
Conservation emerged prominently in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, focusing on preserving natural resources like forests and wildlife through legislation and protected areas. Adaptation gained emphasis in the late 20th century as climate change impacts became evident, prioritizing flexible strategies to adjust human and ecological systems to environmental shifts. The historical context shows a transition from resource preservation to dynamic responses addressing ongoing and future environmental challenges.
Importance of Conservation Strategies
Conservation strategies play a crucial role in preserving biodiversity by protecting ecosystems, species, and genetic diversity essential for ecological balance. Effective conservation efforts mitigate habitat loss, combat climate change impacts, and maintain ecosystem services vital for human well-being. Implementing targeted conservation plans ensures long-term sustainability and resilience of natural habitats against environmental disruptions.
The Role of Adaptation in Changing Climates
Adaptation plays a crucial role in enabling ecosystems and communities to survive and thrive amid rapidly changing climates by fostering resilience against extreme weather events, shifting temperature regimes, and altered precipitation patterns. Unlike conservation, which aims to preserve current conditions and biodiversity, adaptation emphasizes dynamic strategies such as habitat restoration, species migration corridors, and sustainable resource management to cope with inevitable environmental shifts. This proactive approach integrates scientific data on climate projections and socio-economic factors to design interventions that reduce vulnerability and promote long-term ecological balance.
Key Differences Between Conservation and Adaptation
Conservation focuses on preserving existing natural resources and ecosystems to maintain their current state, while adaptation involves making adjustments in response to environmental changes to reduce vulnerability and enhance resilience. Conservation strategies prioritize protection and sustainable management of biodiversity, whereas adaptation emphasizes flexibility through practices like habitat restoration, species migration facilitation, and infrastructure modification. Both approaches are crucial for addressing climate impacts but serve distinct roles in environmental management frameworks.
Benefits and Limitations of Conservation
Conservation efforts help preserve biodiversity, protect ecosystems, and maintain natural resources essential for human survival and climate stability, ensuring long-term ecological balance. However, conservation can face limitations such as restricted land availability, high financial costs, and conflicts with human development needs. Despite these challenges, conservation remains critical for safeguarding endangered species and sustaining ecosystem services that support agriculture, water quality, and air purification.
Benefits and Limitations of Adaptation
Adaptation in environmental management allows ecosystems and communities to adjust to changing conditions, enhancing resilience and reducing vulnerability to climate impacts such as flooding or drought. Benefits include increased flexibility in response to unforeseen changes and the promotion of innovative solutions tailored to local contexts. Limitations of adaptation involve potential high costs, time delays in implementation, and the risk that adaptive measures may not fully counteract severe or rapid environmental changes.
Integrating Conservation and Adaptation Efforts
Integrating conservation and adaptation efforts enhances ecosystem resilience by combining strategies that protect biodiversity while enabling species to adjust to climate change. Effective integration involves using adaptive management practices, habitat restoration, and climate-smart conservation planning to address shifting environmental conditions. Collaboration among scientists, policymakers, and local communities ensures that conservation goals align with adaptive responses, securing long-term ecological and socio-economic benefits.
Future Directions for Sustainable Environmental Management
Future directions for sustainable environmental management emphasize the integration of conservation and adaptation strategies to address climate change impacts effectively. Innovations in ecosystem-based approaches prioritize preserving biodiversity while enhancing resilience through adaptive land use and resource management practices. Embracing adaptive governance frameworks enables dynamic policy adjustments that balance ecological preservation with community needs and economic development.
Conservation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com