Pollen analysis offers valuable insights into past climates and ecosystems by studying preserved pollen grains in sediment layers. This method helps reconstruct environmental changes and understand how plant communities evolved over time. Explore the rest of the article to discover how pollen analysis can deepen your knowledge of natural history and ecological shifts.
Table of Comparison
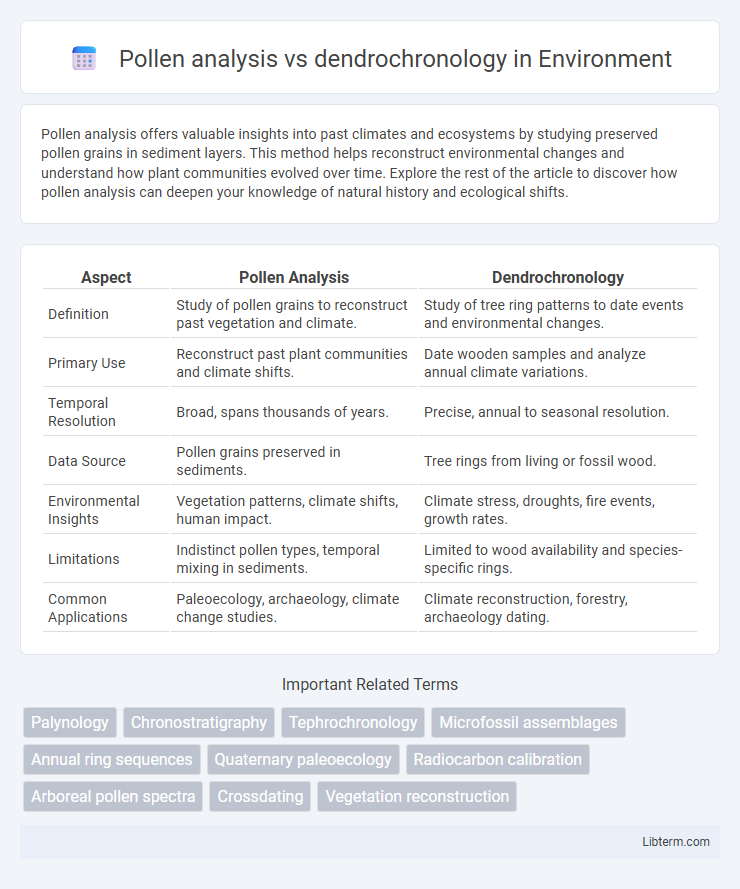
| Aspect | Pollen Analysis | Dendrochronology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of pollen grains to reconstruct past vegetation and climate. | Study of tree ring patterns to date events and environmental changes. |
| Primary Use | Reconstruct past plant communities and climate shifts. | Date wooden samples and analyze annual climate variations. |
| Temporal Resolution | Broad, spans thousands of years. | Precise, annual to seasonal resolution. |
| Data Source | Pollen grains preserved in sediments. | Tree rings from living or fossil wood. |
| Environmental Insights | Vegetation patterns, climate shifts, human impact. | Climate stress, droughts, fire events, growth rates. |
| Limitations | Indistinct pollen types, temporal mixing in sediments. | Limited to wood availability and species-specific rings. |
| Common Applications | Paleoecology, archaeology, climate change studies. | Climate reconstruction, forestry, archaeology dating. |
Introduction to Pollen Analysis and Dendrochronology
Pollen analysis, also known as palynology, studies microscopic pollen grains to reconstruct past vegetation and climate over thousands of years. Dendrochronology involves dating tree rings to determine yearly environmental conditions and historical events with annual precision. Both methods provide complementary insights into ecological changes and paleoenvironments by analyzing biological indicators preserved in natural archives.
Defining Pollen Analysis: Methods and Applications
Pollen analysis, also known as palynology, involves examining microscopic pollen grains preserved in sediments to reconstruct past vegetation and climate conditions, offering insights into ecological changes over thousands of years. Methods include extracting pollen from soil or sediment cores using chemical treatments, followed by microscopic identification and quantification to detect plant species composition and abundance. Common applications of pollen analysis span paleoecology, archaeology, and climate science, where it helps track vegetation shifts, human land use, and environmental responses over millennia, differing from dendrochronology's focus on dating and analyzing tree-ring growth patterns for precise annual climate and ecological records.
Understanding Dendrochronology: Techniques and Uses
Dendrochronology, the scientific method of dating tree rings, provides precise year-by-year data on past climate conditions and environmental changes. This technique analyzes the pattern of annual growth rings in trees, offering insights into historical droughts, volcanic eruptions, and archaeological chronologies. Unlike pollen analysis, which reveals broad vegetation trends over time, dendrochronology delivers exact temporal resolution for studying ecological and climatic events.
Historical Development of Both Methods
Pollen analysis, also known as palynology, emerged in the early 20th century with contributions from Lennart von Post, who developed techniques to reconstruct past vegetation and climate from pollen grains preserved in sediments. Dendrochronology, pioneered by A.E. Douglass in the early 1900s, involves dating tree rings to understand chronological sequences of climatic events and historical timelines. Both methods advanced through the 20th century, integrating laboratory improvements and statistical techniques, with pollen analysis emphasizing paleoecological reconstructions and dendrochronology focusing on precise annual dating of environmental changes.
Types of Data Collected in Pollen Analysis vs Dendrochronology
Pollen analysis collects data on microscopic pollen grains preserved in sediment layers, revealing past vegetation types and climatic conditions over thousands of years. Dendrochronology gathers precise annual growth ring data from tree trunks, providing exact dates and information on environmental factors such as rainfall, drought, and temperature variations. Both methods contribute complementary datasets for reconstructing historical ecological and climate changes.
Accuracy and Limitations of Each Approach
Pollen analysis provides detailed insights into past vegetation and climate conditions but can be limited by pollen dispersal and preservation biases, affecting accuracy in pinpointing precise timelines. Dendrochronology offers highly accurate annual dating through tree-ring patterns, yet its limitations include regional applicability and susceptibility to environmental disturbances that may obscure growth signals. Combining both methods enhances chronological and ecological reconstructions by compensating for individual constraints in temporal resolution and environmental factors.
Temporal Resolution: Yearly Rings vs Stratigraphic Layers
Dendrochronology provides high temporal resolution through the precise dating of annual tree rings, allowing for year-by-year environmental and climatic reconstructions. Pollen analysis offers broader temporal scales by examining stratigraphic layers, where each layer represents an accumulation of pollen over longer periods, often spanning decades to centuries. This difference makes dendrochronology ideal for detailed, short-term climate events, while pollen analysis suits long-term vegetation and ecological changes.
Environmental and Climate Reconstruction Capabilities
Pollen analysis provides detailed insights into past vegetation and climate by examining pollen grains preserved in sediment layers, offering high-resolution data on plant species distribution and environmental changes over thousands of years. Dendrochronology, through the study of tree ring patterns, delivers precise annual records of climate variables such as temperature, precipitation, and drought events, enabling exact dating of environmental fluctuations. Combining both methods enhances the reconstruction of historical ecosystems and climate dynamics by integrating long-term vegetation trends with fine-scale temporal climate data.
Case Studies: Comparing Research Outcomes
Pollen analysis and dendrochronology both provide critical insights into past environmental conditions, with case studies revealing their complementary strengths. Pollen analysis excels in reconstructing vegetation history and climate changes over long timescales, while dendrochronology offers precise annual data on tree growth and climate variability. Comparative research demonstrates that integrating pollen data with tree-ring records enhances understanding of ecological dynamics and improves the accuracy of paleoclimate reconstructions.
Choosing the Right Method for Paleoenvironmental Studies
Pollen analysis excels in reconstructing long-term vegetation changes by examining microscopic pollen grains in sediment layers, providing detailed insights into past climates and ecosystems. Dendrochronology offers precise annual climate records through tree ring patterns, ideal for studying more recent environmental variations and extreme events. Selecting between these methods depends on the study's temporal scale and resolution needs, with pollen analysis suited for millennial trends and dendrochronology for high-resolution, annual data.
Pollen analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com