Drones are transforming industries by enabling efficient aerial photography, surveillance, and delivery services through advanced remote control technology. Equipped with high-resolution cameras and GPS navigation, these unmanned aerial vehicles offer precise data collection and real-time monitoring capabilities. Discover how drones can elevate your projects and explore their growing applications in the full article.
Table of Comparison
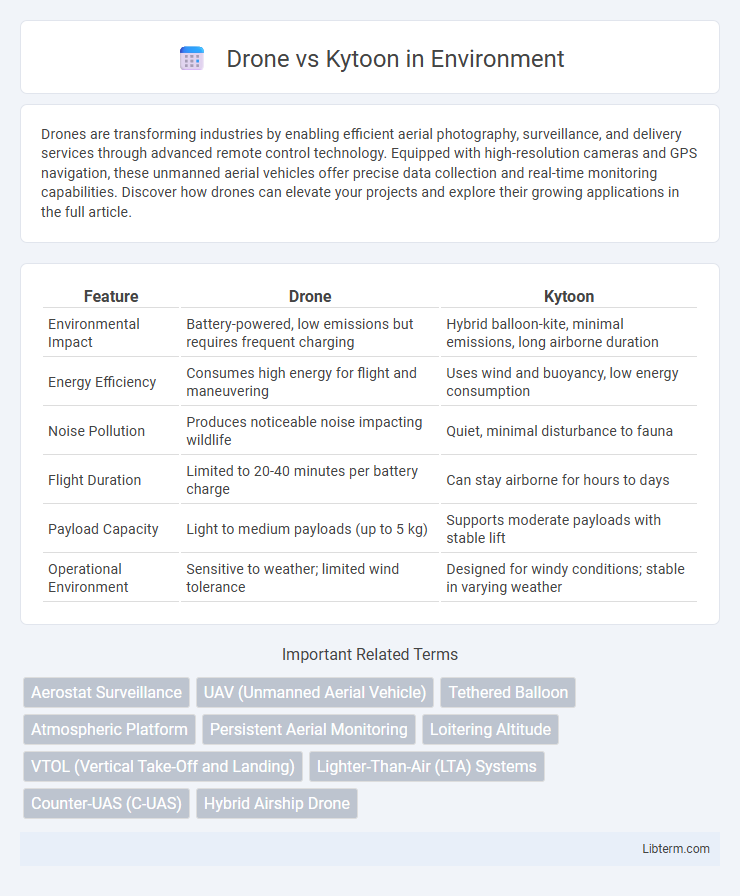
| Feature | Drone | Kytoon |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Battery-powered, low emissions but requires frequent charging | Hybrid balloon-kite, minimal emissions, long airborne duration |
| Energy Efficiency | Consumes high energy for flight and maneuvering | Uses wind and buoyancy, low energy consumption |
| Noise Pollution | Produces noticeable noise impacting wildlife | Quiet, minimal disturbance to fauna |
| Flight Duration | Limited to 20-40 minutes per battery charge | Can stay airborne for hours to days |
| Payload Capacity | Light to medium payloads (up to 5 kg) | Supports moderate payloads with stable lift |
| Operational Environment | Sensitive to weather; limited wind tolerance | Designed for windy conditions; stable in varying weather |
Introduction: Understanding Drones and Kytoons
Drones are unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with rotors and advanced navigation systems, designed for versatile applications such as aerial photography, surveying, and delivery services. Kytoons, a hybrid between kites and balloons, utilize helium for lift combined with tethered stability, making them ideal for long-duration aerial observation and communication relays. Understanding the distinct flight mechanisms and operational capabilities of drones and kytoons highlights their specialized roles in aviation technology.
Technology Overview: How Drones Work
Drones operate using integrated flight control systems, GPS navigation, and wireless communication to achieve autonomous or remote-controlled flight. Equipped with sensors such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, and cameras, drones maintain stability and capture real-time data for various applications. Unlike kytoons, which rely on buoyant gas and wind currents for aerial positioning, drones utilize electric motors and propellers to generate lift and precise maneuverability.
Technology Overview: How Kytoons Operate
Kytoons utilize a hybrid technology combining lighter-than-air gas with aerodynamic lift generated by tethered kites, enabling stable altitude maintenance and minimal power consumption compared to drones. Their tether system provides continuous power and data transmission, contrasting with battery-dependent drones which have limited flight durations. Kytoons are ideal for applications requiring prolonged airborne monitoring and communications without the operational constraints of drone flight times.
Lift Mechanisms: Propellers vs. Buoyant Lift
Drones generate lift through rapidly spinning propellers that push air downward, creating thrust sufficient for vertical takeoff and maneuverability. Kytoons achieve lift via a buoyant gas envelope, like helium, providing static lift that reduces the energy needed to stay aloft while using minimal propulsion for stability. The combination of propeller-generated thrust and buoyant lift in kytoons enables longer endurance and payload capacity compared to drones relying solely on propeller lift.
Energy Efficiency and Endurance Comparison
Kytoons demonstrate superior energy efficiency by harnessing both aerostatic lift and aerodynamic lift, significantly reducing power consumption compared to drones that rely solely on battery-powered rotors. The combined buoyancy and tethered design of kytoons allow for prolonged endurance, maintaining flight for days or even weeks without refueling, unlike drones which typically sustain flight for 20 to 60 minutes per battery cycle. This energy-efficient hybrid system enables kytoons to support continuous surveillance or communication tasks with minimal energy input, offering a more sustainable solution than conventional drones.
Payload Capacity and Applications
Drones typically offer payload capacities ranging from a few hundred grams to several kilograms, suitable for applications like aerial photography, agriculture monitoring, and delivery services. Kytoons, which combine features of kites and balloons, can carry heavier payloads up to several hundred kilograms, making them ideal for long-duration surveillance, communication relays, and scientific research. The choice between a drone and a kytoon depends on mission-specific requirements, including payload weight, flight duration, and environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis: Drones vs. Kytoons
Drone costs typically range from $500 to over $5,000 depending on technology and payload capacity, while Kytoons, combining balloon and kite features, often cost between $1,000 and $3,000 with lower operational expenses. Drones require frequent battery replacements and maintenance, adding to long-term costs, whereas Kytoons benefit from passive lift and minimal power consumption, reducing ongoing expenses significantly. The total cost of ownership favors Kytoons for extended aerial monitoring, while drones offer flexibility and advanced features at higher investment and upkeep.
Environmental Impact and Noise Levels
Drones generate higher noise levels due to their rotating propellers, which can disturb wildlife and contribute to noise pollution, while kytoons operate quietly with minimal sound, making them more environmentally friendly. The environmental impact of drones is amplified by their battery production and disposal, leading to potential soil and water contamination, whereas kytoons use helium or hydrogen for lift, which has a lower environmental footprint when sourced sustainably. Kytoons also consume less energy for prolonged periods compared to drones, reducing overall carbon emissions in aerial operations.
Safety, Stability, and Regulatory Considerations
Drones offer agile maneuverability but face limited flight duration and higher risk of mechanical failure compared to kytoons, which provide enhanced stability and extended airborne time by combining helium lift with tethered support. Safety concerns with drones include potential collisions, battery fires, and loss of control, whereas kytoons reduce such risks due to their controlled tether and less complex propulsion systems. Regulatory frameworks often impose stricter weight, altitude, and no-fly zone restrictions on drones, while kytoons benefit from more lenient oversight given their lower speed and tethered operation, influencing operational planning and compliance strategies.
Choosing the Right Platform: Key Use Cases and Recommendations
Drones offer agile aerial surveillance and rapid deployment, ideal for tasks like real-time mapping and inspection in industries such as agriculture and construction. Kytoons provide stable, long-duration airborne platforms suitable for persistent communication relays, weather monitoring, and surveillance over extended periods. Selecting the right platform depends on mission duration, payload requirements, and environmental conditions, with drones favored for mobility and kytoons preferred for endurance and stability.
Drone Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com