Fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and natural gas, are primary energy sources formed from ancient organic matter over millions of years. They power industries, transportation, and electricity generation but also contribute significantly to carbon emissions and environmental pollution. Discover how shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy can impact your future and the planet by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
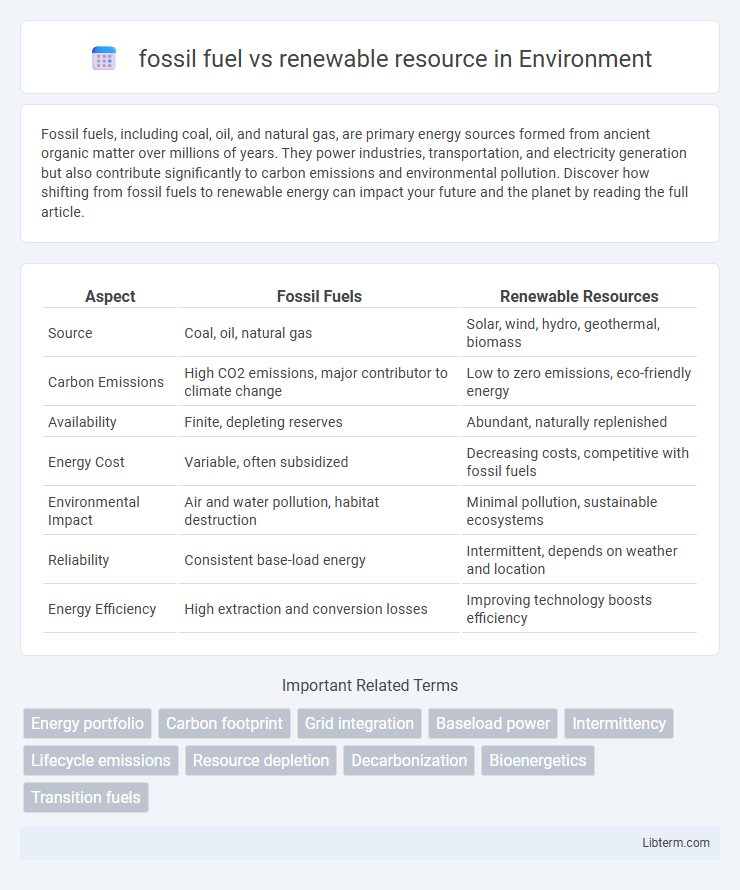
| Aspect | Fossil Fuels | Renewable Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Coal, oil, natural gas | Solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, biomass |
| Carbon Emissions | High CO2 emissions, major contributor to climate change | Low to zero emissions, eco-friendly energy |
| Availability | Finite, depleting reserves | Abundant, naturally replenished |
| Energy Cost | Variable, often subsidized | Decreasing costs, competitive with fossil fuels |
| Environmental Impact | Air and water pollution, habitat destruction | Minimal pollution, sustainable ecosystems |
| Reliability | Consistent base-load energy | Intermittent, depends on weather and location |
| Energy Efficiency | High extraction and conversion losses | Improving technology boosts efficiency |
Introduction: Understanding Energy Sources
Fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas have been primary global energy sources due to their high energy density and established infrastructure. Renewable resources, including solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy, offer sustainable alternatives with lower carbon emissions and reduced environmental impact. Transitioning from fossil fuels to renewables is critical for mitigating climate change and ensuring long-term energy security.
What Are Fossil Fuels?
Fossil fuels, including coal, oil, and natural gas, are energy resources formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals over millions of years. They are carbon-rich and release significant greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane when burned, contributing to climate change. In contrast, renewable resources such as solar, wind, and hydro energy provide cleaner alternatives by harnessing natural processes that replenish continuously without depleting Earth's reserves.
Types of Renewable Resources
Renewable resources include solar energy, wind power, hydropower, biomass, and geothermal energy, each offering sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. Solar energy harnesses sunlight through photovoltaic cells, while wind power utilizes turbines to convert wind into electricity. Hydropower generates electricity from flowing water, biomass derives energy from organic materials, and geothermal taps into the Earth's internal heat, collectively reducing carbon emissions and dependence on non-renewable fossil fuels.
Environmental Impact: Fossil Fuel vs Renewable
Fossil fuels release high levels of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane, contributing significantly to global warming and air pollution. Renewable resources like solar, wind, and hydro energy produce minimal emissions and have a lower environmental footprint, reducing the risk of climate change and ecosystem degradation. Transitioning to renewable energy sources is critical for mitigating environmental damage and promoting sustainable development.
Economic Factors and Job Creation
Fossil fuel industries historically dominate global energy markets, providing millions of jobs, but face volatility due to fluctuating oil and gas prices and regulatory pressures. Renewable energy sectors, including solar and wind, exhibit rapid growth with increasing investments and government incentives, creating diverse employment opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. Transitioning to renewables promises long-term economic resilience by reducing dependency on finite resources and fostering sustainable job creation in emerging green technologies.
Energy Efficiency and Reliability
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind offer high energy efficiency by converting natural resources directly into electricity with minimal losses compared to the combustion of fossil fuels. Fossil fuels provide consistent reliability due to established infrastructure and energy-dense properties, ensuring stable power supply even during peak demand. Advances in battery storage and smart grid technology are progressively enhancing the reliability and efficiency of renewable energy systems, narrowing the performance gap with traditional fossil fuel-based power generation.
Resource Availability and Sustainability
Fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas are finite resources formed over millions of years, leading to limited availability and concerns about long-term depletion. Renewable resources such as solar, wind, and hydropower provide sustainable energy solutions due to their natural replenishment and minimal environmental impact. Transitioning to renewables supports energy security by utilizing abundant sources that do not exhaust ecosystems or contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in renewable energy, such as improved photovoltaic cells and wind turbine designs, have significantly increased efficiency and lowered costs, making renewables more competitive with fossil fuels. Innovations in energy storage technologies, like lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, address intermittency issues associated with solar and wind power, facilitating a more reliable energy supply. Conversely, fossil fuel technologies are evolving with carbon capture and storage (CCS) systems to reduce emissions, but these methods remain costly and less sustainable compared to rapidly advancing renewable alternatives.
Government Policies and Global Trends
Government policies increasingly prioritize renewable resources through subsidies, tax incentives, and regulatory frameworks aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting clean energy adoption. Global trends indicate a significant shift from fossil fuels to renewables, driven by international agreements such as the Paris Accord and growing investments in solar, wind, and battery technologies. Nations are setting ambitious targets for renewable energy capacity, reflecting a strategic move to mitigate climate change and boost economic sustainability.
The Future of Energy: Transition and Challenges
The future of energy hinges on the transition from fossil fuels to renewable resources, driven by the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. Renewable energy technologies like solar, wind, and hydroelectric power are increasingly cost-competitive and scalable, yet infrastructure limitations and energy storage challenges remain significant barriers. Policy frameworks and innovative grid management solutions are critical to enable a reliable and sustainable energy shift that supports global economic growth and environmental resilience.
fossil fuel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com