Aerial surveys use advanced drones and aircraft to capture high-resolution images and data from above, enabling precise mapping and environmental monitoring. These techniques improve accuracy in resource management and infrastructure development, reducing time and costs compared to traditional ground surveys. Explore the rest of the article to discover how aerial surveys can enhance your project outcomes and decision-making processes.
Table of Comparison
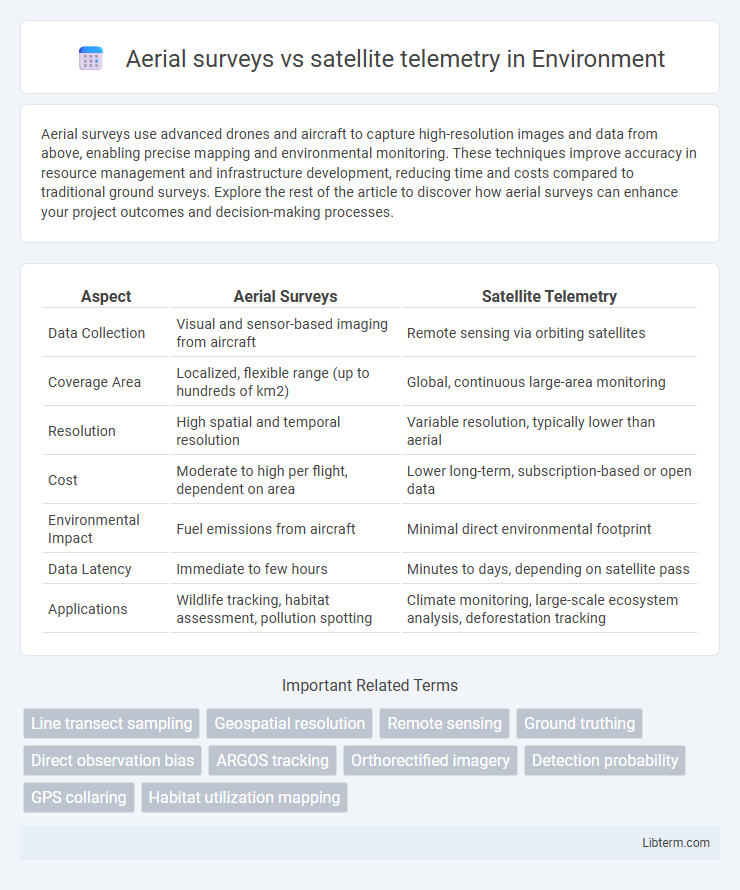
| Aspect | Aerial Surveys | Satellite Telemetry |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Visual and sensor-based imaging from aircraft | Remote sensing via orbiting satellites |
| Coverage Area | Localized, flexible range (up to hundreds of km2) | Global, continuous large-area monitoring |
| Resolution | High spatial and temporal resolution | Variable resolution, typically lower than aerial |
| Cost | Moderate to high per flight, dependent on area | Lower long-term, subscription-based or open data |
| Environmental Impact | Fuel emissions from aircraft | Minimal direct environmental footprint |
| Data Latency | Immediate to few hours | Minutes to days, depending on satellite pass |
| Applications | Wildlife tracking, habitat assessment, pollution spotting | Climate monitoring, large-scale ecosystem analysis, deforestation tracking |
Introduction to Aerial Surveys and Satellite Telemetry
Aerial surveys employ manned or unmanned aircraft equipped with sensors to collect detailed spatial data over targeted areas, offering high-resolution imagery and flexibility in data acquisition. Satellite telemetry involves tracking and monitoring wildlife or environmental variables through satellites, enabling long-term, large-scale data collection with minimal ground intervention. Both methods enhance ecological research by providing complementary perspectives--fine-scale, localized data from aerial surveys and extensive, continuous monitoring via satellite telemetry.
Key Differences Between Aerial Surveys and Satellite Telemetry
Aerial surveys involve direct observation or photography from aircraft to collect spatial data, offering high-resolution imagery and real-time monitoring of specific areas. Satellite telemetry uses remote sensing technology to transmit environmental and positional data from satellites, enabling broad geographic coverage and continuous tracking over time. Key differences include resolution precision, with aerial surveys providing finer details, while satellite telemetry excels in large-scale data acquisition and long-term monitoring efficiency.
Data Accuracy and Resolution Comparison
Aerial surveys provide high-resolution data with precise spatial accuracy due to low-altitude flight paths and advanced imaging sensors, making them ideal for detailed environmental assessments and wildlife monitoring. Satellite telemetry offers broader coverage and continuous data collection over large geographic areas, but with lower spatial resolution and potential signal interruptions that may affect data precision. Combining aerial surveys with satellite telemetry enhances data accuracy by integrating high-detail local observations with extensive temporal and spatial tracking capabilities.
Cost Analysis: Aerial Surveys vs Satellite Telemetry
Aerial surveys generally involve higher operational costs due to the need for aircraft, fuel, and specialized personnel, making them less economical for large-scale or frequent monitoring. Satellite telemetry offers cost efficiency for extensive or long-term data collection by covering broad areas without repeated field deployments, despite higher initial investments in satellite technology and data processing. Comparing total expenditure, satellite telemetry provides greater value in ongoing wildlife tracking and environmental monitoring through its scalable, automated data acquisition systems.
Coverage Area and Accessibility
Aerial surveys provide high-resolution data over targeted, localized areas with flexible deployment, making them ideal for detailed studies in accessible regions. Satellite telemetry offers extensive coverage across vast and remote areas, enabling continuous monitoring regardless of ground accessibility. The choice between these methods depends on the scale of coverage required and the field conditions influencing data collection feasibility.
Application Scenarios: When to Use Each Method
Aerial surveys excel in detailed, localized assessments such as wildlife population counts, habitat mapping, and environmental monitoring where high-resolution data is essential. Satellite telemetry provides comprehensive, large-scale tracking of animal movements, migration patterns, and habitat use across vast geographic areas in real time. Use aerial surveys for focused, short-term projects requiring precise spatial detail and satellite telemetry for continuous, long-term monitoring across remote or extensive regions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aerial surveys produce minimal environmental disturbance by using manned or unmanned aircraft to collect data with low emissions and short operational periods, promoting sustainability in ecological monitoring. Satellite telemetry offers extensive, continuous environmental data coverage without physical intrusion, reducing habitat disruption and fostering long-term ecosystem management. Both methods support sustainable environmental practices, with aerial surveys suited for localized impact assessments and satellite telemetry enabling broad-scale, real-time monitoring.
Technological Advancements in Survey Methods
Technological advancements in aerial surveys include high-resolution drones equipped with LiDAR and multispectral sensors, enabling precise, real-time data collection over diverse terrains. Satellite telemetry has evolved with improved sensor accuracy, greater temporal resolution, and expansive coverage, allowing detailed monitoring of wildlife and environmental changes on a global scale. Integration of AI and machine learning in both methods enhances data analysis, improving decision-making in ecological research and resource management.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Aerial surveys face challenges such as limited coverage area, weather dependency, and high operational costs, which can restrict data collection frequency and spatial resolution. Satellite telemetry encounters limitations including signal loss in dense vegetation or rugged terrain, battery life constraints on tracking devices, and data latency issues that impact real-time monitoring. Both methods require careful consideration of species behavior and habitat characteristics to optimize survey accuracy and effectiveness.
Future Trends in Wildlife and Environmental Monitoring
Future trends in wildlife and environmental monitoring emphasize the integration of aerial surveys with satellite telemetry to enhance data accuracy and spatial coverage. Innovations in drone technology and high-resolution satellite sensors enable real-time tracking of animal movements and habitat changes, facilitating proactive conservation strategies. Machine learning algorithms are increasingly applied to large datasets from both methods, improving species population estimates and ecosystem health assessments.
Aerial surveys Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com