Tidal bores and seiches are unique water phenomena caused by the interaction of tides and local geography, resulting in sudden and sometimes dramatic water level changes. Understanding these natural events can help you appreciate their impact on coastal and lake environments. Explore the rest of the article to learn how tidal bores and seiches form and affect your surroundings.
Table of Comparison
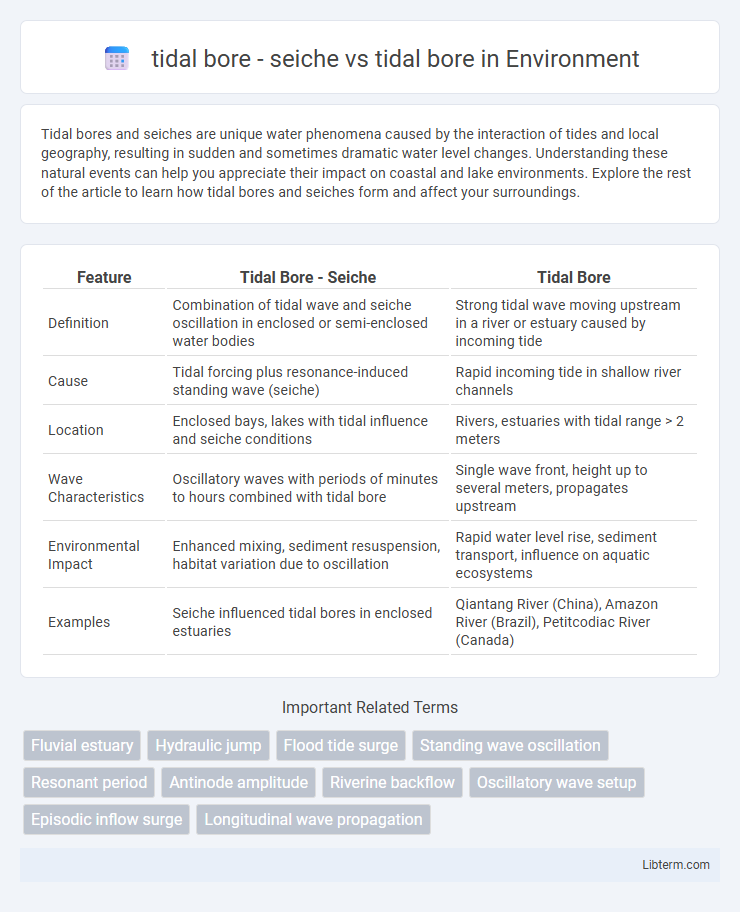
| Feature | Tidal Bore - Seiche | Tidal Bore |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combination of tidal wave and seiche oscillation in enclosed or semi-enclosed water bodies | Strong tidal wave moving upstream in a river or estuary caused by incoming tide |
| Cause | Tidal forcing plus resonance-induced standing wave (seiche) | Rapid incoming tide in shallow river channels |
| Location | Enclosed bays, lakes with tidal influence and seiche conditions | Rivers, estuaries with tidal range > 2 meters |
| Wave Characteristics | Oscillatory waves with periods of minutes to hours combined with tidal bore | Single wave front, height up to several meters, propagates upstream |
| Environmental Impact | Enhanced mixing, sediment resuspension, habitat variation due to oscillation | Rapid water level rise, sediment transport, influence on aquatic ecosystems |
| Examples | Seiche influenced tidal bores in enclosed estuaries | Qiantang River (China), Amazon River (Brazil), Petitcodiac River (Canada) |
Understanding Tidal Bores: Definition and Characteristics
Tidal bores are strong, localized waves caused by the rapid rise of the incoming tide in narrow, funnel-shaped estuaries, creating a visible wave front moving upstream. Unlike seiches, which are standing waves formed by atmospheric or seismic disturbances in enclosed or semi-enclosed bodies of water, tidal bores result from tidal forces interacting with the river's topography. Key characteristics of tidal bores include their predictable timing with tidal cycles, a sudden increase in water level, and often a turbulent, breaking wave phenomenon traveling against the river's current.
What is a Seiche? Explaining the Phenomenon
A seiche is a standing wave oscillation within an enclosed or partially enclosed body of water, caused by atmospheric pressure changes, seismic activity, or sudden shifts in wind, leading to periodic fluctuations in water levels. Unlike tidal bores, which are fast-moving waves traveling up a river or narrow bay during rising tides, seiches do not propagate but instead resonate within the water body, producing oscillations that can last from minutes to hours. This phenomenon is commonly observed in lakes, reservoirs, and harbors, where the water surface oscillates back and forth due to the natural frequency of the basin.
Tidal Bore vs Seiche: Key Differences
Tidal bores and seiches are distinct hydrodynamic phenomena influenced by tidal forces but differ fundamentally in their occurrence and mechanics. A tidal bore is a rapid, turbulent surge of seawater moving upstream in a river or estuary during rising tides, often visible as a wave front, primarily caused by the funneling shape of the river mouth and large tidal ranges. In contrast, a seiche is a standing wave oscillation within an enclosed or partially enclosed water body, such as a lake or bay, triggered by atmospheric pressure changes, seismic events, or sudden wind shifts rather than tidal ebb and flow.
Formation Processes: How Tidal Bores and Seiches Originate
Tidal bores form when incoming tides are funneled into narrow, shallow river mouths causing a sudden surge of water traveling upstream as a wave. Seiches originate from oscillations within enclosed or semi-enclosed bodies of water, triggered by factors like atmospheric pressure changes or seismic activity. The key difference lies in tidal bores being direct responses to tidal forces in confined channels, whereas seiches result from standing wave patterns induced by environmental disturbances.
Global Locations: Where Tidal Bores and Seiches Occur
Tidal bores predominantly occur in specific estuaries with large tidal ranges, such as the Qiantang River in China, the Amazon River in Brazil, and the Severn River in the UK, where incoming tides funnel into narrow, shallow channels creating a dramatic wave that travels upstream. Seiches, on the other hand, are found in enclosed or semi-enclosed bodies of water like the Great Lakes in North America, the Baltic Sea in Europe, and Lake Geneva in Switzerland, where atmospheric pressure changes and seismic activity cause oscillations in water levels. These distinct global locations highlight the different hydrodynamic conditions necessary for tidal bores versus seiches.
Physical Impacts on Waterways and Environments
Tidal bores and seiches both influence waterways but differ significantly in their physical impacts and formation mechanisms. Tidal bores occur when incoming tides create a wave that travels upstream against the current in a river or estuary, causing sudden changes in water level and flow velocity that can lead to bank erosion and habitat disruption. Seiches, on the other hand, are standing waves oscillating in enclosed or semi-enclosed bodies of water triggered by atmospheric pressure changes or seismic activity, causing periodic water level fluctuations that impact sediment distribution and aquatic ecosystems differently than the unidirectional surge of tidal bores.
Famous Examples: Notable Tidal Bores and Seiches Worldwide
Famous tidal bores include the Qiantang River in China, known for its spectacular 9-meter high wave, and the Amazon River's Pororoca, which can reach speeds up to 40 km/h. Notable seiches occur in large enclosed or semi-enclosed basins like Lake Geneva in Switzerland and the Great Lakes in North America, with oscillations lasting from minutes to hours. Tidal bores represent fast-moving, breaking tidal waves traveling upstream, whereas seiches are standing wave oscillations caused by seafloor or atmospheric disturbances within confined water bodies.
Scientific Significance and Research Focus
Tidal bores are powerful waves traveling upstream in narrow estuaries, caused by incoming tides funneling into shallow river mouths, while seiches are standing waves oscillating in enclosed or partially enclosed bodies of water due to atmospheric or seismic disturbances. Scientific research on tidal bores emphasizes hydrodynamics, sediment transport, and ecological impacts, investigating wave formation and energy dissipation mechanisms. Seiche studies focus on resonance phenomena, water level oscillations, and their influence on coastal infrastructure and aquatic ecosystems.
Safety Considerations for Observing Tidal Bores and Seiches
Tidal bores generate powerful, fast-moving waves that can pose significant hazards such as strong currents and sudden water level changes, demanding careful monitoring and strict adherence to safety protocols during observation. Seiches, typically smaller and caused by standing wave oscillations in enclosed or semi-enclosed bodies of water, present different risks primarily related to unpredictable water surges that require caution in shoreline areas. Effective safety measures include maintaining a safe distance, using proper observation equipment, and staying informed about local tidal and weather conditions to prevent accidents during these dynamic tidal phenomena.
The Future of Study: Advancing Understanding of Water Wave Phenomena
Tidal bores and seiches represent distinct water wave phenomena, with tidal bores characterized by a powerful surge moving upstream in narrow estuaries, while seiches involve stationary standing waves oscillating in enclosed or partially enclosed bodies of water. Advances in hydrodynamic modeling and real-time monitoring technologies are crucial for unraveling the complex interactions between these phenomena and their impact on coastal ecosystems and human infrastructure. Future research focuses on integrating satellite remote sensing, high-resolution numerical simulations, and machine learning algorithms to enhance prediction accuracy and support adaptive management strategies in the face of climate change and rising sea levels.
tidal bore - seiche Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com