Urbanization drives economic growth and shapes social dynamics by concentrating populations in cities, fostering innovation, and creating diverse job opportunities. It also presents challenges such as congestion, pollution, and strain on infrastructure that require sustainable planning and resource management. Explore the rest of the article to discover how urbanization impacts your daily life and the future of communities worldwide.
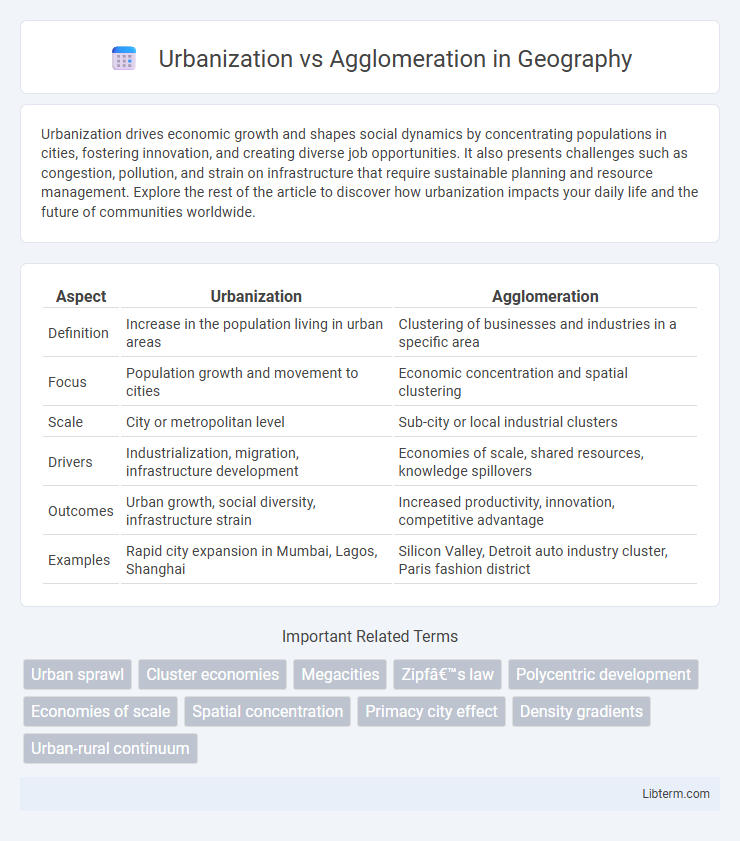
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Urbanization | Agglomeration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increase in the population living in urban areas | Clustering of businesses and industries in a specific area |
| Focus | Population growth and movement to cities | Economic concentration and spatial clustering |
| Scale | City or metropolitan level | Sub-city or local industrial clusters |
| Drivers | Industrialization, migration, infrastructure development | Economies of scale, shared resources, knowledge spillovers |
| Outcomes | Urban growth, social diversity, infrastructure strain | Increased productivity, innovation, competitive advantage |
| Examples | Rapid city expansion in Mumbai, Lagos, Shanghai | Silicon Valley, Detroit auto industry cluster, Paris fashion district |
Understanding Urbanization: Definition and Drivers
Urbanization refers to the increasing population concentration in cities, driven primarily by economic opportunities, industrialization, and improved infrastructure. Key drivers include rural-to-urban migration, technological advancements, and government policies fostering urban growth. This process reshapes social dynamics, land use, and economic activities, influencing both city expansion and regional development.
Defining Agglomeration: Key Concepts
Agglomeration refers to the spatial clustering of economic activities and industries within a specific area, leading to increased productivity and innovation due to proximity. Key concepts include economies of scale, knowledge spillovers, and shared infrastructure, which enhance efficiency and competitiveness among businesses. This concentrated growth contrasts with broader urbanization, which encompasses the overall increase in urban population and expansion of city boundaries.
Urbanization vs Agglomeration: Core Differences
Urbanization refers to the increasing population density and expansion of cities, driven by migration and economic opportunities, whereas agglomeration focuses on the spatial concentration of industries and businesses within a particular area to leverage collective efficiencies. Urbanization encompasses a broader demographic and infrastructural growth impacting housing, transportation, and social services, while agglomeration is primarily concerned with economic benefits such as reduced production costs and enhanced innovation due to proximity. The core difference lies in urbanization being a demographic phenomenon, whereas agglomeration is an economic and spatial concept that explains clustering benefits in urban environments.
Economic Impacts of Urbanization
Urbanization drives economic growth by concentrating labor, facilitating knowledge spillovers, and enhancing access to markets, which boosts productivity and innovation. The agglomeration of firms and industries in urban areas generates economies of scale, reduces transaction costs, and attracts investment, creating competitive advantages. However, rapid urbanization can also strain infrastructure and increase living costs, potentially offsetting economic gains if not managed effectively.
Economic Benefits of Agglomeration
Agglomeration economies generate significant economic benefits by concentrating firms and industries in close proximity, which enhances knowledge spillovers, reduces transportation costs, and fosters labor market pooling. These advantages lead to increased productivity, innovation, and competitive advantage for businesses within urban clusters. Compared to general urbanization, agglomeration specifically drives efficiency gains through localized networks and shared infrastructure, promoting sustained economic growth.
Social and Environmental Consequences
Urbanization drives significant social changes by intensifying population density, which often leads to overcrowded housing and strained public services, exacerbating inequality and social fragmentation. Agglomeration benefits economic productivity through concentrated resources and infrastructure but can also escalate environmental degradation, including increased pollution and loss of green spaces. Both processes contribute to challenges like urban heat islands, reduced biodiversity, and heightened social tensions due to unequal access to urban amenities.
Urban Planning: Balancing Growth and Density
Urban planning must carefully balance urbanization, characterized by population growth in cities, with agglomeration effects that enhance economic productivity and innovation through dense clustering. Effective strategies optimize land use by promoting mixed-use developments and improving public transport to mitigate congestion and environmental impact. Prioritizing sustainable infrastructure and green spaces supports livability while harnessing the benefits of urban density for economic growth.
Case Studies: Cities Exemplifying Each Model
Tokyo exemplifies urbanization with its sprawling infrastructure supporting over 37 million residents, showcasing extensive city-wide growth. In contrast, Silicon Valley represents agglomeration, where concentrated tech companies benefit from shared resources and innovation clusters. These case studies highlight urbanization's broad spatial expansion versus agglomeration's dense economic specialization.
Challenges and Opportunities in Developing Nations
Rapid urbanization in developing nations intensifies challenges such as inadequate infrastructure, strained public services, and environmental degradation, while aggressive agglomeration creates opportunities for economic growth, innovation hubs, and improved labor market efficiency. Managing these dynamics requires strategic urban planning to optimize resource allocation, reduce congestion, and promote sustainable development. Harnessing the benefits of agglomeration economies can accelerate poverty reduction and enhance quality of life if infrastructural and governance challenges are effectively addressed.
Future Trends: Urbanization and Agglomeration in the 21st Century
Future trends in urbanization and agglomeration will be shaped by rapid technological advancements, climate change adaptation, and shifting economic hubs. Smart cities integrating IoT and AI technologies will drive more efficient agglomeration economies, optimizing infrastructure and resource management. Urban growth is expected to concentrate in megaregions, intensifying both opportunities and challenges related to sustainability, housing, and transportation in the 21st century.
Urbanization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com