Mulching improves soil moisture retention, suppresses weed growth, and regulates soil temperature, creating optimal conditions for plant health. Organic mulches also enrich the soil with nutrients as they decompose, promoting sustainable gardening practices. Explore the full article to discover the best mulching techniques and materials tailored for your garden's needs.
Table of Comparison
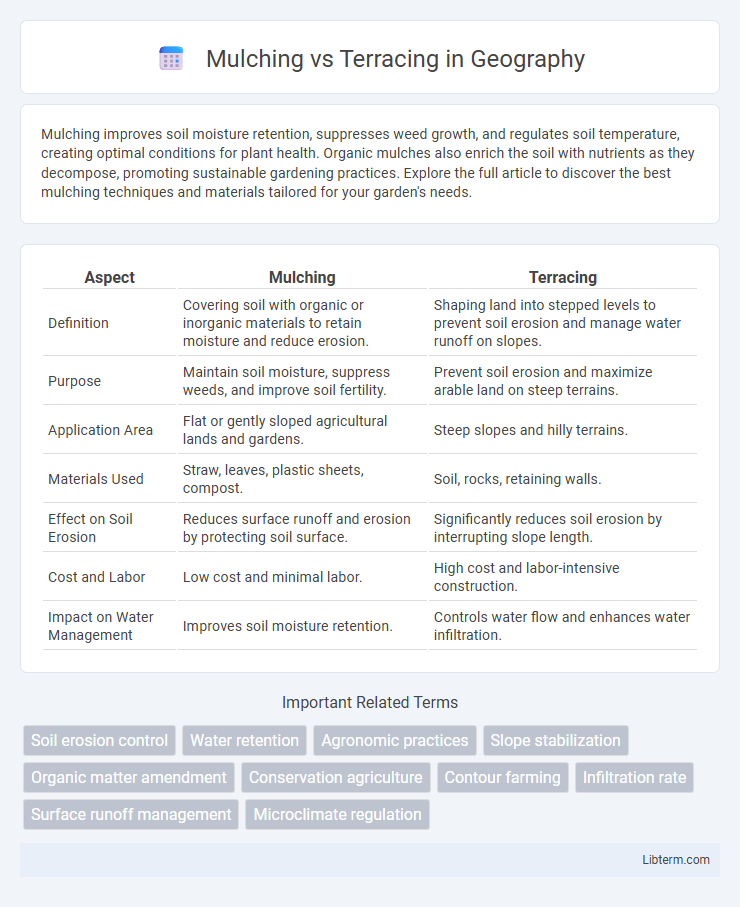
| Aspect | Mulching | Terracing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Covering soil with organic or inorganic materials to retain moisture and reduce erosion. | Shaping land into stepped levels to prevent soil erosion and manage water runoff on slopes. |
| Purpose | Maintain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and improve soil fertility. | Prevent soil erosion and maximize arable land on steep terrains. |
| Application Area | Flat or gently sloped agricultural lands and gardens. | Steep slopes and hilly terrains. |
| Materials Used | Straw, leaves, plastic sheets, compost. | Soil, rocks, retaining walls. |
| Effect on Soil Erosion | Reduces surface runoff and erosion by protecting soil surface. | Significantly reduces soil erosion by interrupting slope length. |
| Cost and Labor | Low cost and minimal labor. | High cost and labor-intensive construction. |
| Impact on Water Management | Improves soil moisture retention. | Controls water flow and enhances water infiltration. |
Understanding Mulching and Terracing
Mulching involves covering the soil surface with organic or inorganic materials like straw, leaves, or plastic to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and improve soil health. Terracing is an agricultural technique that creates stepped levels on steep slopes to reduce soil erosion, manage water runoff, and increase arable land for crop cultivation. Both methods enhance soil conservation but serve different purposes: mulching primarily improves soil conditions, while terracing focuses on landscape modification for erosion control.
Key Benefits of Mulching
Mulching improves soil moisture retention by reducing evaporation and regulating ground temperature, which promotes healthier plant growth. It suppresses weed growth by blocking sunlight, reducing the need for chemical herbicides and manual weeding. Mulching also enhances soil fertility through organic matter decomposition, boosting nutrient availability and supporting sustainable agriculture.
Core Advantages of Terracing
Terracing offers significant soil erosion control by creating leveled steps that reduce water runoff and increase water infiltration, which is crucial for maintaining soil fertility on steep slopes. The method enhances agricultural productivity by stabilizing land, allowing for efficient water usage and preventing nutrient loss, making it ideal for hilly regions. Unlike mulching, terracing provides permanent structural landscape modification that supports sustainable farming and long-term soil conservation.
Differences in Application and Suitability
Mulching involves covering soil with organic or inorganic materials to retain moisture, reduce erosion, and improve soil fertility, making it suitable for small-scale gardens and orchards. Terracing reshapes steep slopes into stepped levels to prevent soil erosion and manage water runoff, ideal for hilly or mountainous agricultural lands. While mulching is primarily a surface treatment enhancing soil health, terracing is a landform modification designed for large-scale cultivation and erosion control.
Soil Erosion Control: Mulching vs Terracing
Mulching effectively reduces soil erosion by providing a protective cover that minimizes water runoff and soil displacement, enhancing moisture retention and organic matter content. Terracing controls soil erosion on steep slopes by creating level steps that slow down water flow, allowing increased water infiltration and preventing soil loss. Both methods significantly contribute to soil conservation, with mulching suitable for flat or gently sloping land and terracing ideal for steep terrain.
Impact on Soil Fertility
Mulching enhances soil fertility by retaining moisture, moderating temperature, and adding organic matter through decomposition, which improves nutrient availability and microbial activity. Terracing prevents soil erosion on slopes, preserving topsoil and nutrients essential for plant growth, but may require supplemental organic inputs to maintain long-term fertility. Both practices contribute to sustainable agriculture by stabilizing soil structure and enhancing nutrient cycling, though mulching directly enriches soil organic content more rapidly.
Water Management Strategies
Mulching conserves soil moisture by reducing evaporation and enhancing water infiltration, making it ideal for small-scale water management in gardens and agricultural plots. Terracing transforms sloped land into stepped levels, effectively slowing runoff and increasing water retention on hilly terrains, which prevents soil erosion and improves moisture distribution. Both strategies optimize water management, but mulching suits flat or gently sloping areas, while terracing is essential for controlling water flow on steep slopes.
Cost and Labor Considerations
Mulching offers a cost-effective solution with lower initial expenses and minimal labor requirements compared to terracing, which involves significant investment in materials and intensive manual work. Terracing demands skilled labor and machinery, increasing overall costs, but provides long-term soil erosion control and water management benefits. Mulching serves best for small-scale or temporary projects, while terracing suits large-scale, sustainable land management despite higher upfront labor and cost commitments.
Environmental Impacts Compared
Mulching improves soil moisture retention and reduces erosion by covering the ground with organic materials, enhancing soil fertility and supporting biodiversity. Terracing effectively controls soil erosion on steep slopes by creating flat platforms, reducing runoff and sediment loss while allowing water infiltration and crop cultivation. Both methods conserve soil and water, but terracing has a more significant impact on preventing landslides and degradation in hilly terrains compared to mulching's benefits in soil nutrient enhancement and microclimate regulation.
Choosing Between Mulching and Terracing
Choosing between mulching and terracing depends on the specific landscape and soil erosion challenges. Mulching is ideal for conserving soil moisture, preventing weed growth, and improving soil organic matter on gentle slopes or flat areas. Terracing suits steep terrain by creating level steps that reduce runoff and soil erosion while enabling more effective water retention and crop cultivation.
Mulching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com