Pedocal soil is characterized by its high calcium carbonate content and forms typically in arid and semi-arid regions with limited rainfall. This soil type has low organic matter and a distinct accumulation of calcium, making it suitable for certain drought-resistant crops but challenging for others. Explore the article to understand how pedocal soil affects agricultural practices and land management decisions in dry climates.
Table of Comparison
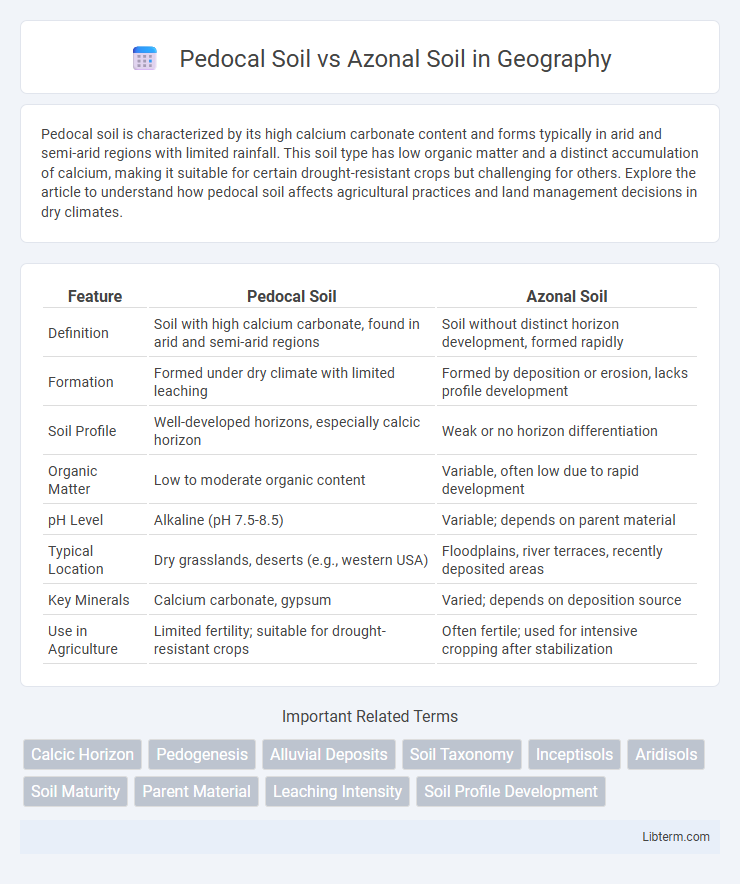
| Feature | Pedocal Soil | Azonal Soil |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Soil with high calcium carbonate, found in arid and semi-arid regions | Soil without distinct horizon development, formed rapidly |
| Formation | Formed under dry climate with limited leaching | Formed by deposition or erosion, lacks profile development |
| Soil Profile | Well-developed horizons, especially calcic horizon | Weak or no horizon differentiation |
| Organic Matter | Low to moderate organic content | Variable, often low due to rapid development |
| pH Level | Alkaline (pH 7.5-8.5) | Variable; depends on parent material |
| Typical Location | Dry grasslands, deserts (e.g., western USA) | Floodplains, river terraces, recently deposited areas |
| Key Minerals | Calcium carbonate, gypsum | Varied; depends on deposition source |
| Use in Agriculture | Limited fertility; suitable for drought-resistant crops | Often fertile; used for intensive cropping after stabilization |
Introduction to Pedocal and Azonal Soils
Pedocal soils develop in arid and semi-arid regions characterized by limited rainfall and high evaporation rates, leading to the accumulation of calcium carbonate in the soil profile. Azonal soils lack distinct horizon development due to continuous geological and climatic changes, often found in floodplains, river terraces, and areas with recent deposits. Pedocal soils exhibit well-defined calcareous layers, while Azonal soils are typically young and polymorphic, reflecting the influence of parent material rather than soil-forming factors.
Definition and Characteristics of Pedocal Soil
Pedocal soil is a type of soil characterized by high calcium carbonate content, commonly found in arid and semi-arid regions where evaporation exceeds precipitation. It typically exhibits alkaline pH, poor organic matter, and accumulation of calcium carbonate in the B horizon, contrasting with azonal soils, which lack distinct horizons and form under specific local conditions rather than climatic influences. Pedocal soils support drought-resistant vegetation and are often less fertile compared to more developed zonal soils.
Definition and Characteristics of Azonal Soil
Azonal soil forms in regions where soil formation processes are weak or disrupted, often near rivers, lakes, or floodplains, and lacks well-developed horizons. Unlike pedocal soils, which are rich in calcium carbonate and develop in arid to semi-arid climates, azonal soils are primarily characterized by their immature profile and high variability due to frequent sediment deposition. These soils tend to have poor structure and fertility but are often fertile due to regular nutrient replenishment from alluvial deposits.
Formation Processes of Pedocal Soils
Pedocal soils form primarily in arid and semi-arid regions through the process of limited leaching, which allows calcium carbonate to accumulate within the soil profile, creating a hardpan or caliche layer. The dry climate reduces water percolation, causing soluble minerals to precipitate and concentrate near the surface. This process contrasts with azonal soils, which develop rapidly and are heavily influenced by parent material and topography rather than climatic factors.
Formation Processes of Azonal Soils
Azonal soils form primarily through the influence of parent material and topography rather than long-term climatic or biological factors, resulting in minimal horizon development and rapid formation processes. These soils often develop on steep slopes or floodplains where erosion or deposition dominates, preventing typical soil profile differentiation seen in pedocal soils. Unlike pedocal soils, which accumulate calcium carbonate in arid or semi-arid climates, azonal soils retain characteristics closely linked to their immediate environmental conditions and geomorphological processes.
Pedocal vs Azonal: Key Differences
Pedocal soil forms in arid and semi-arid climates with calcium carbonate accumulation, resulting in high pH and poor leaching, whereas Azonal soil develops rapidly with minimal horizon formation, typically influenced by local factors like topography or parent material. Pedocal is characterized by well-defined layers and stable mineral composition, contrasting Azonal soil's immature, unstructured profile often found in floodplains and steep slopes. The key differences emphasize pedocal's climatic dependence versus azonal's dominance by environmental processes and lack of soil horizon development.
Geographic Distribution of Pedocal Soils
Pedocal soils predominantly form in arid and semi-arid regions, mainly across the western United States, parts of Mexico, and Central Asia, where low rainfall limits leaching and calcium carbonate accumulates. These soils contrast with azonal soils, which develop without strong horizon development, often found in floodplains, mountain slopes, and areas with rapid sediment deposition worldwide. The geographic distribution of pedocal soils aligns closely with dry climates, influencing vegetation patterns and land use in these regions.
Geographic Distribution of Azonal Soils
Azonal soils are predominantly found in regions with varying climatic and topographic conditions, often occurring along river valleys, deltas, and floodplains where soil formation is influenced more by deposition and erosion than by climatic factors. Unlike Pedocal soils, which are common in arid and semi-arid regions characterized by calcium carbonate accumulation, Azonal soils lack well-developed horizons and are typically situated in geographically diverse environments such as alluvial plains, mountainous regions, and young landscapes. Their widespread geographic distribution includes areas with dynamic physical processes that prevent long-term soil profile development, contrasting with the more stable and climate-dependent distribution of Pedocal soils.
Impacts on Agriculture and Plant Growth
Pedocal soils, rich in calcium carbonate and found in arid regions, tend to have alkaline pH levels that limit nutrient availability, affecting crop yield and requiring careful management to improve soil fertility for agriculture. Azonal soils, forming rapidly without strong horizon development, often retain nutrients better and support diverse plant growth but can be vulnerable to erosion and require conservation practices to maintain productivity. Effective agricultural strategies must tailor fertilization and irrigation to the specific chemical and physical properties of pedocal and azonal soils to optimize plant growth and sustainable crop production.
Environmental and Ecological Implications
Pedocal soils, rich in calcium carbonate, typically develop in arid and semi-arid regions, influencing local vegetation by supporting drought-tolerant plant species and contributing to limited organic matter accumulation. In contrast, azonal soils form quickly due to factors like erosion, river deposits, or volcanic activity, often leading to highly variable nutrient availability and unstable ecosystems. The distinct formation processes and nutrient profiles of pedocal and azonal soils significantly impact regional biodiversity, water retention, and land use sustainability.
Pedocal Soil Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com