Isochim delivers innovative chemical solutions tailored for diverse industrial applications, ensuring high-quality performance and sustainability. Their expertise spans specialty chemicals, water treatment, and process additives designed to optimize your operations efficiently. Discover how Isochim's cutting-edge technologies can transform your processes by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
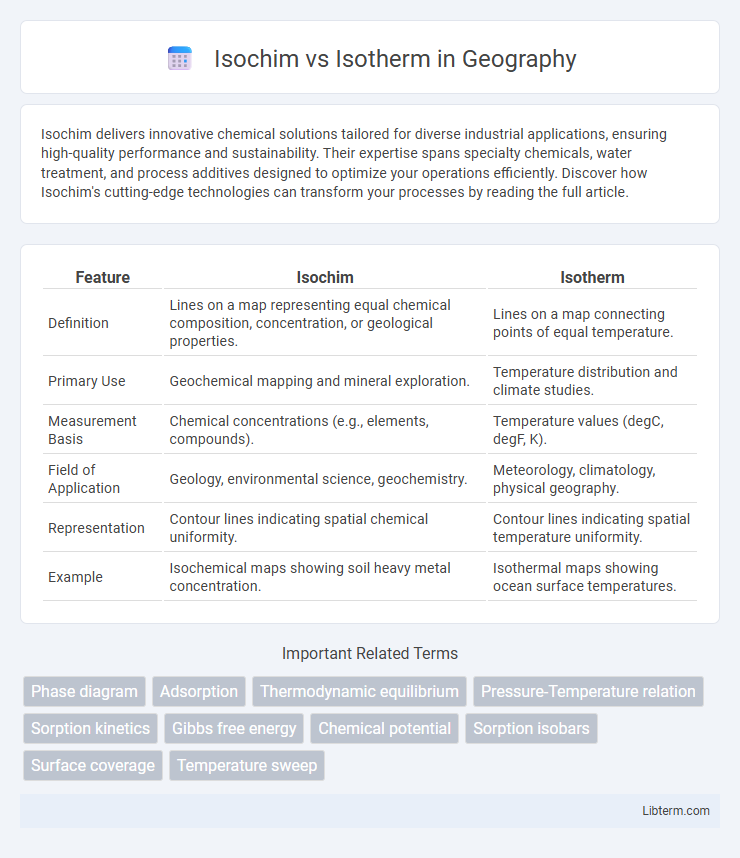
| Feature | Isochim | Isotherm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lines on a map representing equal chemical composition, concentration, or geological properties. | Lines on a map connecting points of equal temperature. |
| Primary Use | Geochemical mapping and mineral exploration. | Temperature distribution and climate studies. |
| Measurement Basis | Chemical concentrations (e.g., elements, compounds). | Temperature values (degC, degF, K). |
| Field of Application | Geology, environmental science, geochemistry. | Meteorology, climatology, physical geography. |
| Representation | Contour lines indicating spatial chemical uniformity. | Contour lines indicating spatial temperature uniformity. |
| Example | Isochemical maps showing soil heavy metal concentration. | Isothermal maps showing ocean surface temperatures. |
Introduction to Isochim and Isotherm
Isochim and Isotherm are specialized products used in chromatography for sample preparation and analysis. Isochim is a precise gas chromatographic standard designed for calibration and quality control, ensuring consistent retention times and peak accuracy. Isotherm refers to chromatographic techniques or conditions maintaining constant temperature during analysis, optimizing separation efficiency and reproducibility of components.
Defining Isochim: Meaning and Applications
Isochim refers to a line on a map or chart connecting points of equal chemical concentration, commonly used in environmental science to track pollutant distribution or nutrient levels in soil and water. This concept aids in visualizing spatial variations in chemical properties, enabling efficient monitoring and management of environmental quality. Applications of isochim include groundwater contamination studies, agricultural soil analysis, and chemical spill assessments.
Understanding Isotherm: Concept and Usage
Isotherms represent curves on a graph depicting the relationship between pressure and adsorption capacity at a constant temperature, crucial for analyzing gas or liquid adsorption on solids. Understanding isotherm models, such as Langmuir or Freundlich, helps in predicting adsorption behavior and designing industrial applications like gas storage and water purification. Accurate interpretation of isotherm data enables optimization of material properties for enhanced efficiency in environmental and chemical engineering processes.
Key Differences Between Isochim and Isotherm
Isochim emphasizes precise chemical concentration control in industrial processes, while Isotherm specializes in maintaining constant temperature conditions during reactions. Isochim systems integrate advanced sensor technology for dynamic adjustment, whereas Isotherm units rely on robust thermal insulation and accurate heat exchange mechanisms. The key difference lies in Isochim's focus on chemical equilibrium versus Isotherm's focus on thermal stability.
Scientific Principles Behind Isochim
Isochim relies on advanced chemical equilibrium modeling to accurately simulate phase behavior in multiphase systems, enhancing the prediction of solubility and adsorption processes. Its foundation is rooted in thermodynamics and molecular interactions, enabling precise calculations of component distribution under varying temperature and pressure conditions. This scientific rigor distinguishes Isochim from Isotherm approaches, which primarily focus on adsorption equilibrium without integrating comprehensive thermodynamic state variables.
Scientific Foundations of Isotherm
Isotherms represent curves depicting the relationship between gas adsorption and pressure at constant temperature, grounded in the principles of thermodynamics and surface chemistry. The scientific foundation of isotherms involves analyzing the equilibrium states of adsorbate molecules on solid surfaces, characterized by models such as Langmuir, Freundlich, and BET isotherms. These models provide critical insights into adsorption capacity, surface area, and pore structure, enabling precise understanding of material interactions and adsorption mechanisms.
Practical Examples of Isochim in Science
Isochim refers to lines or surfaces representing equal chemical concentrations in a given medium, commonly used in environmental chemistry to track pollutant dispersion in water bodies. Isotherm, on the other hand, denotes lines of constant temperature, frequently applied in meteorology to map temperature distribution in atmospheric studies. Practical examples of Isochim include modeling the distribution of dissolved oxygen in lakes to assess aquatic health and tracing nitrate levels in groundwater to monitor agricultural runoff impacts.
Real-World Applications of Isotherm
Isotherms play a crucial role in real-world applications such as adsorption processes in environmental engineering, where they model the interactions between adsorbates and adsorbents to optimize pollutant removal. Unlike Isochim, which focuses on chemical equilibrium constants in vapor-liquid systems, isotherms specifically describe how adsorbate concentration correlates with pressure or concentration at constant temperature, essential for designing industrial gas purification and water treatment systems. Accurate isotherm models like Langmuir and Freundlich provide vital data for scaling adsorption technologies in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to wastewater management.
Isochim vs Isotherm: Comparative Analysis
Isochim and Isotherm are leading providers of high-performance membranes used in gas separation and water treatment technologies, each offering distinct material compositions and operational efficiencies. Isochim membranes typically feature advanced polymeric structures optimized for durability and selective permeability, whereas Isotherm membranes emphasize thermal stability and enhanced surface area for improved filtration rates. Comparative analysis reveals that Isochim membranes excel in long-term chemical resistance and energy efficiency, while Isotherm membranes deliver superior thermal resilience and rapid throughput, making the choice dependent on specific industrial process requirements.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Isochim and Isotherm
Isochim offers superior thermal insulation with advanced phase change materials, providing enhanced energy efficiency in temperature regulation compared to Isotherm's conventional insulation solutions. Isotherm remains a cost-effective option for less demanding applications, delivering reliable performance with established technology. Selecting between Isochim and Isotherm depends on specific project requirements, budget constraints, and the desired balance between innovation and proven insulation methods.
Isochim Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com