Deserts are arid regions characterized by low precipitation, scorching temperatures during the day, and surprisingly cold nights. Their unique ecosystems support specially adapted plants and animals that survive extreme conditions. Discover more about the fascinating features and importance of deserts in this article.
Table of Comparison
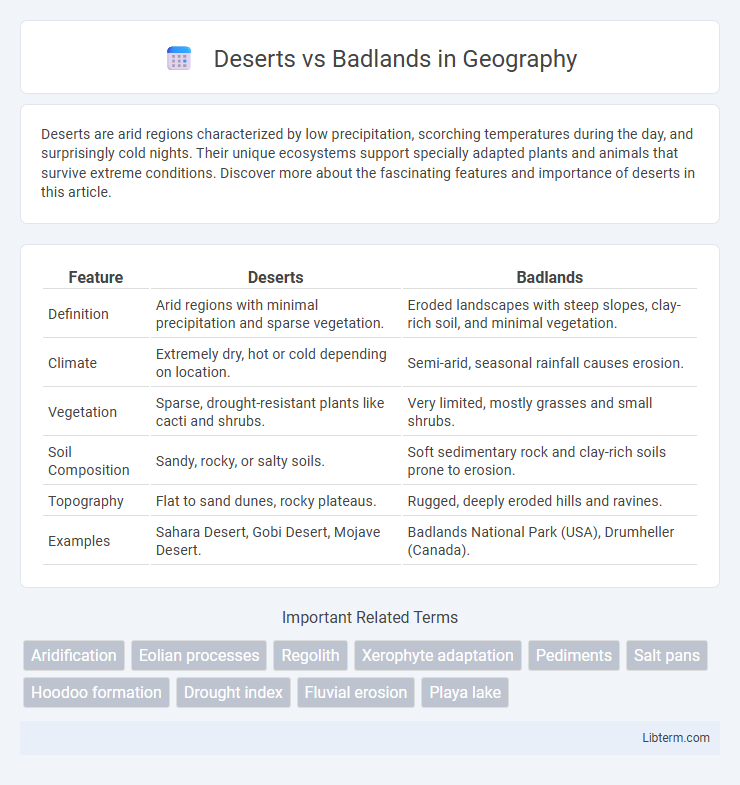
| Feature | Deserts | Badlands |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Arid regions with minimal precipitation and sparse vegetation. | Eroded landscapes with steep slopes, clay-rich soil, and minimal vegetation. |
| Climate | Extremely dry, hot or cold depending on location. | Semi-arid, seasonal rainfall causes erosion. |
| Vegetation | Sparse, drought-resistant plants like cacti and shrubs. | Very limited, mostly grasses and small shrubs. |
| Soil Composition | Sandy, rocky, or salty soils. | Soft sedimentary rock and clay-rich soils prone to erosion. |
| Topography | Flat to sand dunes, rocky plateaus. | Rugged, deeply eroded hills and ravines. |
| Examples | Sahara Desert, Gobi Desert, Mojave Desert. | Badlands National Park (USA), Drumheller (Canada). |
Introduction to Deserts and Badlands
Deserts are arid regions characterized by minimal rainfall, extreme temperature variations, and sparse vegetation, covering about one-fifth of Earth's surface. Badlands, often found in desert or semi-arid areas, are heavily eroded landscapes marked by steep slopes, clay-rich soils, and intricate drainage patterns. Both environments showcase unique geological formations shaped by erosion, but deserts primarily emphasize dryness and heat, while badlands highlight erosion and sedimentary layers.
Defining Deserts: Climate and Characteristics
Deserts are defined by their extremely low precipitation, typically receiving less than 250 millimeters of rain annually, resulting in arid conditions and sparse vegetation. These regions often experience high temperature fluctuations between day and night, with sandy or rocky terrain dominating the landscape. Unlike badlands, deserts support specialized flora and fauna adapted to drought and intense sunlight exposure.
What Are Badlands? Unique Features Explained
Badlands are heavily eroded landscapes characterized by steep slopes, minimal vegetation, and a labyrinth of canyons, ravines, and gullies formed primarily from sedimentary rock and clay-rich soils. Unlike deserts, which are defined mainly by low precipitation and sandy terrain, badlands exhibit intricate layering of colorful rock strata and fragile earth surfaces prone to rapid erosion. These unique features create stark, rugged terrains that reveal fossil beds and ancient geological history, distinguishing badlands from the more uniform, dune-dominated desert ecosystems.
Formation Processes: Deserts vs Badlands
Deserts form primarily through prolonged arid climate conditions where minimal precipitation and high evaporation rates dominate, leading to the accumulation of sand, rocks, and sparse vegetation. Badlands develop mostly from intense erosion caused by intermittent heavy rainfall on soft sedimentary rocks, creating deeply incised gullies and rugged terrain. While deserts emphasize wind and drought in shaping landscapes, badlands are sculpted by water erosion and rapid sediment breakdown.
Geographical Locations: Where to Find Deserts and Badlands
Deserts are primarily found in regions such as the Sahara in Africa, the Arabian Desert in the Middle East, and the Mojave Desert in North America, characterized by arid climates and sparse vegetation. Badlands occur in areas like the Badlands National Park in South Dakota, USA, and the Drumheller region in Alberta, Canada, known for their eroded clay-rich soils and unique geological formations. Both landscapes exhibit extreme environmental conditions but differ significantly in their locations and geological features.
Biodiversity: Flora and Fauna Comparison
Deserts feature specialized flora like cacti and succulents adapted to extreme aridity, alongside fauna such as camels, reptiles, and nocturnal mammals that survive with minimal water. Badlands contain sparse vegetation dominated by hardy grasses, shrubs, and occasional trees, supporting diverse fauna including burrowing animals, birds, and insects adapted to unstable soil and erosion-prone terrain. Biodiversity in deserts shows extreme water conservation adaptations, while badlands present a unique ecosystem shaped by soil composition and erosion patterns influencing plant and animal life.
Human Activities and Cultural Significance
Human activities in deserts often include nomadic herding, mining, and tourism, reflecting adaptation to extreme conditions, while badlands are primarily sites for scientific research and fossil excavation due to their unique geological formations. Cultural significance in deserts is profound, with indigenous communities preserving ancient traditions and spiritual practices tied to the landscape, whereas badlands hold historical importance for paleontologists and attract visitors interested in Earth's prehistoric past. Both regions face environmental challenges from human interference, necessitating sustainable management to protect their ecological and cultural heritage.
Erosion and Weathering: Impact on Landscapes
Deserts experience intense wind erosion and occasional flash floods that shape vast sand dunes and rocky plateaus, resulting in smooth yet arid landscapes. Badlands undergo rapid weathering and water erosion due to soft sedimentary rocks, creating sharply eroded gullies, ravines, and layered formations with distinctive strata. These processes highlight the contrasting geomorphological features caused by different erosion and weathering dynamics in deserts and badlands.
Tourism and Exploration: Visiting Deserts and Badlands
Deserts offer vast, sandy landscapes ideal for activities like dune bashing, camel trekking, and stargazing, attracting adventure tourists and nature enthusiasts. Badlands feature rugged, eroded terrain with unique rock formations and fossil sites, making them popular for hiking, photography, and geological exploration. Both environments require careful preparation due to extreme temperatures and limited water sources, ensuring safe and enriching travel experiences.
Conservation Challenges and Environmental Concerns
Deserts and badlands face distinct conservation challenges due to their unique ecosystems and vulnerability to climate change. Water scarcity in deserts exacerbates habitat degradation, while badlands struggle with soil erosion and limited vegetation cover, intensifying land instability. Both landscapes require targeted strategies to mitigate human impact, preserve biodiversity, and manage fragile resources effectively.
Deserts Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com