Longitudinal dunes, also known as seif dunes, form parallel to prevailing wind directions through the accumulation of sand in arid environments. These elongated ridges can stretch for miles, demonstrating the dynamic processes of wind erosion and sediment deposition shaping desert landscapes. Discover how longitudinal dunes impact ecosystems and human activity by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
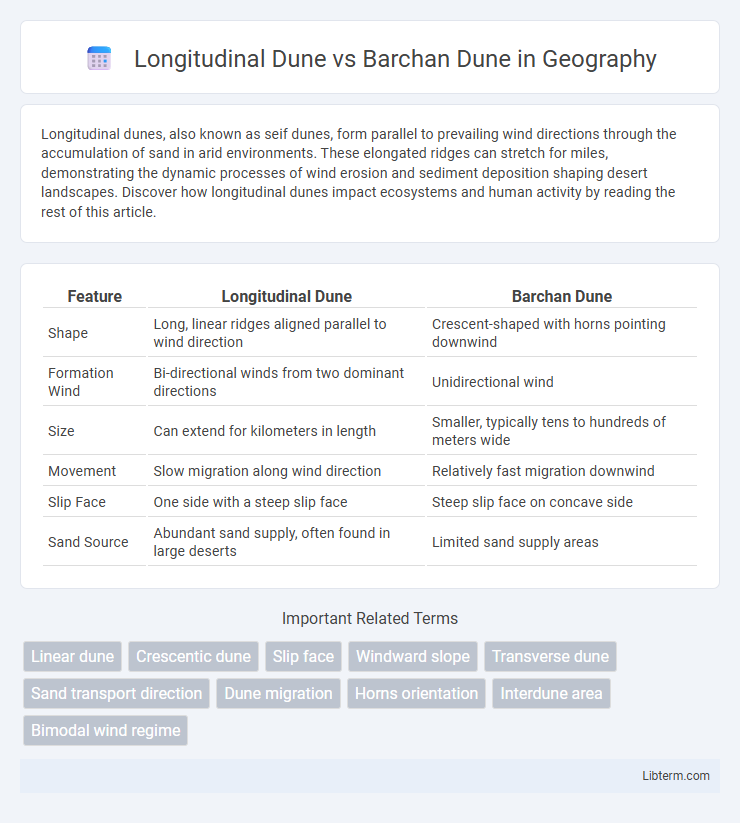
| Feature | Longitudinal Dune | Barchan Dune |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Long, linear ridges aligned parallel to wind direction | Crescent-shaped with horns pointing downwind |
| Formation Wind | Bi-directional winds from two dominant directions | Unidirectional wind |
| Size | Can extend for kilometers in length | Smaller, typically tens to hundreds of meters wide |
| Movement | Slow migration along wind direction | Relatively fast migration downwind |
| Slip Face | One side with a steep slip face | Steep slip face on concave side |
| Sand Source | Abundant sand supply, often found in large deserts | Limited sand supply areas |
Introduction to Longitudinal and Barchan Dunes
Longitudinal dunes, also known as seif dunes, form parallel to the prevailing wind direction, characterized by their long, narrow ridges that can extend for kilometers across desert landscapes. Barchan dunes are crescent-shaped, with horns pointing downwind, typically developing in environments with limited sand supply and unidirectional winds. Both dune types represent distinct aeolian processes influenced by wind patterns, sand availability, and surface conditions in arid regions.
Key Characteristics of Longitudinal Dunes
Longitudinal dunes, also known as seif dunes, are elongated sand ridges oriented parallel to the prevailing wind direction, often found in areas with bidirectional wind regimes. They typically have symmetrical or slightly asymmetrical cross-sections and can extend for kilometers, unlike barchan dunes which are crescent-shaped and form under unidirectional winds. These dunes grow by the accumulation of sand along their length, with slip faces developing on one or both sides depending on wind variability.
Distinct Features of Barchan Dunes
Barchan dunes are crescent-shaped sand formations characterized by their curved horns pointing downwind, typically forming in areas with limited sand supply and unidirectional wind. Unlike the elongated, parallel ridges of longitudinal dunes, barchan dunes have a steeper slip face on the concave side and migrate over time due to wind erosion on the windward side and deposition on the leeward side. Their distinctive shape and movement patterns serve as key indicators of prevailing wind direction and sand transport dynamics in arid environments.
Formation Processes: Longitudinal vs. Barchan Dunes
Longitudinal dunes form parallel to the prevailing wind direction through the alignment of sand ridges caused by bidirectional wind regimes, whereas barchan dunes develop in areas with a unidirectional wind pattern and limited sand supply, resulting in crescent-shaped dunes with horns pointing downwind. The formation of longitudinal dunes involves the sorting and elongation of sand by shifting wind patterns that create linear ridges, while barchan dunes form from sand accumulation that migrates due to consistent wind shear, leading to their characteristic crescent morphology. These distinct formation processes are influenced by variations in wind directionality, sand availability, and surface conditions, making longitudinal dunes typical of stable wind regimes and barchan dunes indicative of more dynamic, unidirectional wind environments.
Wind Patterns and Their Influence on Dune Shape
Longitudinal dunes form parallel to prevailing wind directions, typically found in areas with bidirectional wind regimes, causing them to elongate along the wind axis. Barchan dunes develop under unidirectional winds, creating crescent shapes with horns pointing downwind, indicative of consistent wind flow from one direction. Wind velocity and variability directly influence these dune shapes, with longitudinal dunes reflecting more complex wind patterns and barchan dunes indicating steady, predominant wind forces.
Typical Locations and Distribution
Longitudinal dunes typically form in areas with abundant sand supply and bidirectional wind regimes, commonly found in the Sahara Desert and Namibia's coastal regions. Barchan dunes develop in arid environments with limited sand supply and unidirectional winds, prominently distributed in the deserts of Southwestern United States and Central Asia. These distinct wind and sand conditions dictate their widespread occurrence and morphological differences across global desert landscapes.
Sediment Composition and Movement
Longitudinal dunes consist primarily of well-sorted quartz sand grains aligned parallel to prevailing wind directions, promoting linear migration patterns along dune axes. Barchan dunes feature coarser, mixed sediment sizes, including quartz and feldspar, moving laterally with crescent-shaped horns pointing downwind. Sediment composition influences dune morphology and mobility, with longitudinal dunes exhibiting slower, directional migration and barchan dunes displaying faster, transverse movement driven by wind strength and sediment supply.
Ecological Impacts of Both Dune Types
Longitudinal dunes, aligned parallel to prevailing winds, create stabilized habitats that support specialized vegetation and reduce soil erosion, enhancing local biodiversity. Barchan dunes, crescent-shaped and migrating with strong unidirectional winds, often disrupt ecosystems by shifting rapidly, which can bury plant life and alter animal habitats. Both dune types influence local microclimates and groundwater recharge, but longitudinal dunes generally promote more stable ecological conditions compared to the dynamic nature of barchan dunes.
Human Interactions and Impacts
Longitudinal dunes, aligned parallel to prevailing winds, often form extensive ridges that can impact human settlements by altering local wind patterns and contributing to sand encroachment on infrastructure. Barchan dunes, crescent-shaped and migrating rapidly with unidirectional winds, pose challenges for agriculture and transportation due to their mobility and tendency to overrun roads and farmlands. Human activities such as land development and vegetation removal can exacerbate the movement of both dune types, increasing risks to communities and necessitating targeted management strategies.
Summary: Choosing Between Longitudinal and Barchan Dunes
Longitudinal dunes form parallel to prevailing wind directions in areas with limited sand supply, creating long ridges that stabilize desert landscapes. Barchan dunes, shaped like crescent moons with horns pointing downwind, develop in environments with abundant sand and consistent unidirectional winds. Selecting between longitudinal and barchan dunes depends on wind consistency, sand availability, and terrain conditions, influencing dune morphology and desert ecosystem dynamics.
Longitudinal Dune Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com