A compass is an essential navigation tool that uses Earth's magnetic field to determine direction, helping travelers and explorers find their way. Modern compasses often combine magnetic needles with digital technology for more precise readings in outdoor adventures or maritime navigation. Discover how understanding your compass can enhance your navigation skills by reading the rest of the article.
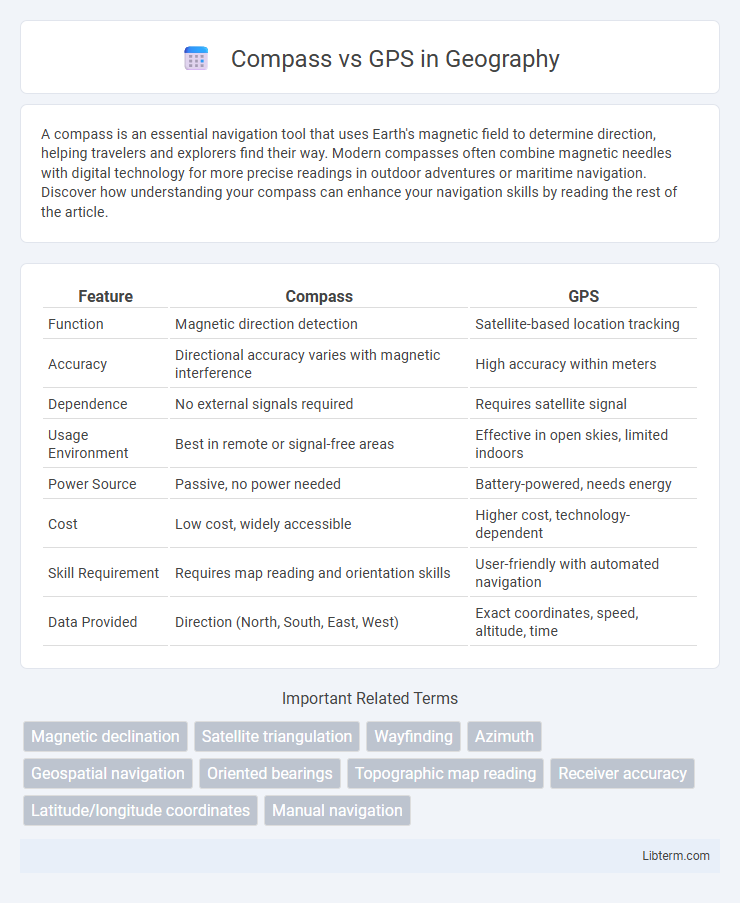
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Compass | GPS |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Magnetic direction detection | Satellite-based location tracking |
| Accuracy | Directional accuracy varies with magnetic interference | High accuracy within meters |
| Dependence | No external signals required | Requires satellite signal |
| Usage Environment | Best in remote or signal-free areas | Effective in open skies, limited indoors |
| Power Source | Passive, no power needed | Battery-powered, needs energy |
| Cost | Low cost, widely accessible | Higher cost, technology-dependent |
| Skill Requirement | Requires map reading and orientation skills | User-friendly with automated navigation |
| Data Provided | Direction (North, South, East, West) | Exact coordinates, speed, altitude, time |
Introduction: Navigational Tools in the Modern World
Navigational tools like compass and GPS play crucial roles in modern navigation by providing direction and positioning information. A compass uses Earth's magnetic field to indicate cardinal directions, offering reliable guidance without relying on batteries or satellite signals. GPS technology, based on satellite networks, delivers precise location data worldwide, enhancing navigation accuracy in various applications from hiking to aviation.
What is a Compass?
A compass is a navigational instrument that uses Earth's magnetic field to indicate direction, typically pointing toward magnetic north. It consists of a magnetized needle free to rotate on a pivot, aligning itself with the planet's magnetic lines, providing reliable orientation without the need for electrical power or satellite signals. Often used in hiking and outdoor activities, compasses offer a simple yet effective way to determine direction in environments where GPS signals may be unavailable or unreliable.
What is a GPS?
A GPS, or Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based navigation technology that provides precise location and time information anywhere on Earth. It operates through a network of at least 24 satellites that transmit signals to GPS receivers, enabling users to determine their exact position within meters. GPS is widely used in applications ranging from navigation and mapping to tracking and geotagging in various industries.
How Does a Compass Work?
A compass works by detecting the Earth's magnetic field using a magnetized needle that aligns itself with magnetic north, allowing users to determine direction accurately. Its functionality depends on the Earth's geomagnetic field rather than satellite signals, making it reliable in remote areas where GPS signals may be weak or unavailable. Unlike GPS devices that rely on satellite triangulation for location data, a compass provides real-time directional guidance based on magnetic orientation.
How Does GPS Technology Operate?
GPS technology operates by utilizing a network of at least 24 satellites orbiting Earth, which transmit precise signals to GPS receivers. These receivers calculate their exact position by measuring the time it takes for the satellite signals to reach them, using trilateration to determine latitude, longitude, and altitude. GPS provides real-time, accurate location data regardless of weather conditions, unlike a magnetic compass, which relies on Earth's magnetic field for directional guidance but cannot provide specific coordinates.
Key Differences Between Compass and GPS
A compass operates by detecting Earth's magnetic field to indicate direction, providing reliable navigation without power or signals, while GPS relies on satellites to determine precise location using trilateration, requiring a clear signal and electrical power. Unlike GPS, a compass offers only directional information (north, south, east, west) and cannot provide exact coordinates, map routes, or altitude data. GPS devices deliver real-time positioning, speed, and route tracking, essential for dynamic navigation, whereas compasses are valued for simplicity, durability, and functionality in remote or signal-limited environments.
Advantages of Using a Compass
A compass offers reliable navigation without reliance on batteries or electronic signals, making it essential for wilderness survival and remote exploration. Its simplicity and durability provide consistent directional guidance even in adverse weather conditions or dense forests where GPS signals may fail. Using a compass fosters essential map-reading and orienteering skills, enhancing user self-sufficiency and spatial awareness compared to GPS devices.
Benefits of Navigating with GPS
GPS navigation offers precise, real-time location tracking using satellite signals, enabling accurate route guidance even in complex environments. It provides dynamic updates on traffic conditions, estimated arrival times, and alternative routes, enhancing travel efficiency and convenience. Unlike a traditional compass, GPS integrates with digital maps and various applications, supporting multifunctional navigation for driving, hiking, and maritime activities.
When to Choose a Compass Over GPS
Choose a compass over GPS in remote areas where battery life and satellite signal reception are unreliable or unavailable. A compass remains effective in dense forests, deep canyons, or during severe weather conditions where GPS devices might fail. Navigators relying on traditional map reading and hands-on orientation skills benefit from the compass's simplicity and durability without dependence on electronic components.
Compass vs GPS: Which is Best for Outdoor Adventures?
A compass offers reliable, battery-free navigation essential for outdoor adventures in remote areas, while GPS devices provide precise, real-time location tracking and route planning using satellite signals. For extended trips where technology may fail or batteries deplete, a compass proves indispensable as a fail-safe navigation tool. Combining both tools ensures optimal safety and accuracy for hikers, campers, and explorers.
Compass Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com