Climatology examines long-term weather patterns and their influence on Earth's environment, helping predict changes and prepare for extreme events. Understanding these patterns is crucial for addressing challenges like climate change and its impact on ecosystems and human activities. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your knowledge of how climatology shapes our planet's future.
Table of Comparison
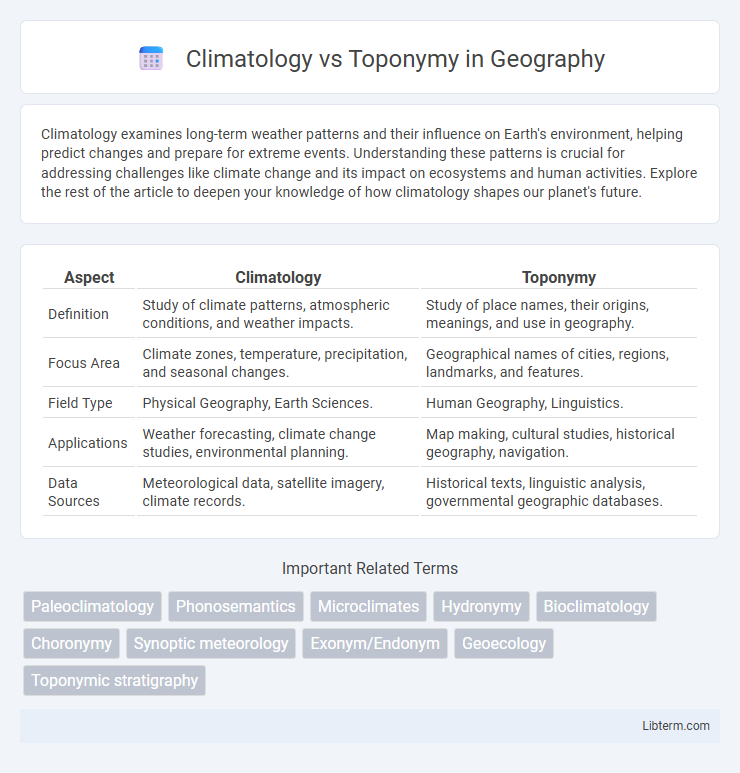
| Aspect | Climatology | Toponymy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of climate patterns, atmospheric conditions, and weather impacts. | Study of place names, their origins, meanings, and use in geography. |
| Focus Area | Climate zones, temperature, precipitation, and seasonal changes. | Geographical names of cities, regions, landmarks, and features. |
| Field Type | Physical Geography, Earth Sciences. | Human Geography, Linguistics. |
| Applications | Weather forecasting, climate change studies, environmental planning. | Map making, cultural studies, historical geography, navigation. |
| Data Sources | Meteorological data, satellite imagery, climate records. | Historical texts, linguistic analysis, governmental geographic databases. |
Understanding Climatology: A Brief Overview
Climatology examines long-term weather patterns and atmospheric conditions to understand climate variability and change, analyzing factors such as temperature, precipitation, and wind over extended periods. It utilizes data from meteorological stations, satellite observations, and climate models to predict future climate trends and assess impacts on ecosystems and human activities. Understanding climatology is crucial for addressing climate change, improving agricultural planning, and managing natural resources effectively.
Defining Toponymy and Its Significance
Toponymy, the study of place names, explores the origins, meanings, and usage of geographical names, revealing cultural, historical, and linguistic insights. It plays a crucial role in understanding human geography by linking language with physical locations, aiding in navigation, identity, and heritage preservation. Unlike climatology, which analyzes atmospheric patterns and weather phenomena, toponymy centers on the significance and evolution of geographic nomenclature across regions.
Core Concepts: Climate Patterns vs. Place Names
Climatology studies long-term climate patterns, including temperature, precipitation, and atmospheric behavior, to understand environmental changes and predict future trends. Toponymy examines place names, exploring their origins, meanings, and cultural significance within geographic and historical contexts. While climatology analyzes data-driven climate systems, toponymy focuses on linguistic and historical aspects tied to geographic locations.
The Historical Evolution of Climatology
The historical evolution of climatology traces back to ancient civilizations, where basic observations of weather patterns laid the groundwork for systematic climate studies. Over centuries, advancements in instrumentation and data analysis transformed climatology into a scientific discipline focused on understanding long-term atmospheric conditions and their global impacts. This progression contrasts with toponymy, which centers on the study of place names and their linguistic origins rather than atmospheric phenomena.
Tracing the Origins of Toponymy Studies
Tracing the origins of toponymy studies reveals its roots in early geographic and linguistic scholarship, where understanding place names provided insights into cultural history and environmental features. Climatology, while primarily focused on climate patterns and atmospheric phenomena, intersects with toponymy when analyzing how climate-related factors influence place naming conventions. The evolution of toponymy integrates interdisciplinary methods from climatology, historical linguistics, and geography to decode the etymology and significance of geographic names.
Methodologies in Climatology Research
Climatology research employs quantitative methodologies such as statistical analysis of long-term meteorological data, climate modeling, and remote sensing techniques to study atmospheric patterns and trends. Advanced tools like Geographic Information Systems (GIS) enable climatologists to visualize spatial climate variations and assess regional impacts with high precision. These methods contrast with toponymy, which primarily utilizes linguistic and historical approaches to analyze place names and their origins.
Approaches and Tools in Toponymy
Toponymy employs linguistic analysis, historical records, and geographic information systems (GIS) to study place names, emphasizing cultural, historical, and spatial contexts. Techniques such as cartographic mapping and database management facilitate the documentation and interpretation of toponyms, revealing patterns in human settlement and migration. Unlike climatology, which relies on meteorological data and atmospheric models, toponymy integrates qualitative and quantitative tools from linguistics and geography to analyze the origin and significance of geographic names.
How Climate Influences Place Naming
Climate plays a crucial role in toponymy by shaping the descriptive names assigned to locations, such as "Frost Valley" or "Desert Ridge," which reflect predominant weather patterns or environmental conditions. These climate-influenced place names provide insights into historical temperature ranges, precipitation levels, or seasonal variations that characterized the area during the naming period. Understanding the intersection of climatology and toponymy reveals how human perception of climate directly impacts geographic nomenclature and cultural identity tied to specific environments.
Interdisciplinary Connections: Climatology Meets Toponymy
Climatology provides critical insights into the impact of climate patterns on place names studied in toponymy, revealing how weather phenomena influence geographic nomenclature over time. Toponymy, by analyzing the etymology and historical context of place names, offers climatologists valuable data for reconstructing past climate conditions and understanding regional environmental changes. The interdisciplinary collaboration between climatology and toponymy enhances the accuracy of climate models and preserves cultural heritage through the interpretation of climate-related place names.
Future Directions in Climatology and Toponymy Research
Future directions in climatology emphasize enhanced climate modeling and integration of artificial intelligence to improve predictions of extreme weather patterns and climate change impacts. Toponymy research is increasingly leveraging geospatial technologies and big data analytics to refine place-name origins, cultural heritage preservation, and spatial identity mapping. Cross-disciplinary collaboration between climatologists and toponymists promises innovative approaches to understanding how climate influences geographic nomenclature and regional environmental changes.
Climatology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com