Delta represents change or difference in mathematics, science, and finance, often symbolized by the Greek letter D. Understanding how delta impacts your calculations or investments is crucial for accurate results and informed decisions. Explore the full article to discover how delta influences various fields and why it matters to you.
Table of Comparison
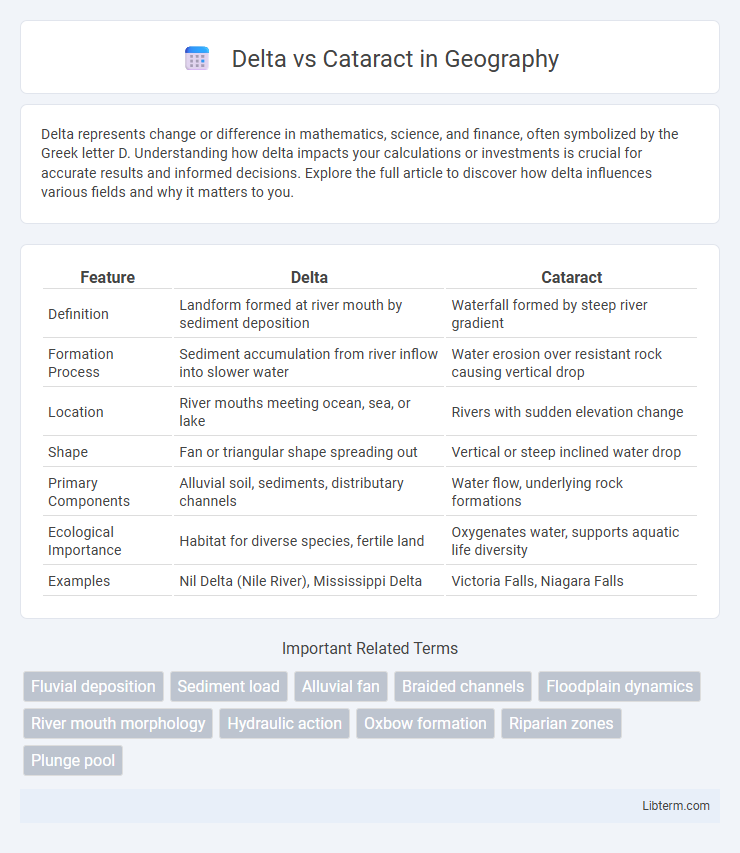
| Feature | Delta | Cataract |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Landform formed at river mouth by sediment deposition | Waterfall formed by steep river gradient |
| Formation Process | Sediment accumulation from river inflow into slower water | Water erosion over resistant rock causing vertical drop |
| Location | River mouths meeting ocean, sea, or lake | Rivers with sudden elevation change |
| Shape | Fan or triangular shape spreading out | Vertical or steep inclined water drop |
| Primary Components | Alluvial soil, sediments, distributary channels | Water flow, underlying rock formations |
| Ecological Importance | Habitat for diverse species, fertile land | Oxygenates water, supports aquatic life diversity |
| Examples | Nil Delta (Nile River), Mississippi Delta | Victoria Falls, Niagara Falls |
Introduction to Delta and Cataract
Delta is a landform created by sediment deposition at the mouth of a river, characterized by intricate networks of distributaries and rich biodiversity. Cataracts are large, powerful waterfalls or rapids formed where a river flows over a steep drop, often creating significant obstacles to navigation. Both geological features play vital roles in shaping river ecosystems and influencing local human settlements.
Defining Delta and Cataract
Delta in medical imaging refers to the angular deviation or change in wavefront measurements used to assess optical aberrations in the eye. Cataract is a clouding of the eye's natural lens, leading to decreased vision and light scattering, often evaluated through slit-lamp examination or optical coherence tomography (OCT). Defining delta in the context of cataracts involves quantifying changes in optical properties that indicate lens opacity and visual impairment.
Key Differences Between Delta and Cataract
Delta refers to a landform created by sediment deposits at the mouth of a river, characterized by its triangular shape and rich biodiversity, while cataract is a large, powerful waterfall or rapid in a river, marked by steep drops and turbulent water flow. Deltas form gradually over time through sediment accumulation, influencing ecosystems and agriculture, whereas cataracts result from geological activity causing abrupt changes in river elevation. Unlike cataracts, deltas are typically flat and expansive, serving as crucial habitats and fertile areas, whereas cataracts are notable for their dramatic scenic and energetic water features.
Causes of Delta and Cataract
Delta refers to a specific medical condition or entity not commonly associated with eye diseases, whereas cataract is characterized by the clouding of the eye's natural lens. The primary causes of cataracts include aging, ultraviolet radiation exposure, diabetes, smoking, and prolonged use of corticosteroids. In contrast, if "Delta" refers to a distinct medical condition, its causes would depend on the specific context, but it is not linked to lens opacity like cataracts.
Symptoms Comparison: Delta vs Cataract
Delta syndrome primarily causes neurological symptoms such as muscle weakness, coordination issues, and visual disturbances including double vision, while cataracts manifest as clouding of the eye lens leading to blurred vision, glare sensitivity, and difficulty seeing at night. Delta syndrome-related visual symptoms stem from nerve damage affecting eye movement, contrasting with cataract symptoms that result from lens opacity impairing light transmission. Recognizing the distinct symptom profiles--neurological deficits in Delta versus progressive vision loss in cataracts--is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis Methods for Delta and Cataract
Delta diagnosis involves advanced imaging techniques such as Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and fluorescein angiography to assess retinal abnormalities and vascular changes. Cataract diagnosis primarily relies on slit-lamp examination and visual acuity tests to evaluate lens opacity and its impact on vision. Both conditions require precise clinical evaluation to determine the extent and appropriate treatment approach.
Treatment Options for Delta and Cataract
Treatment options for Delta primarily involve corrective lenses, such as glasses or contact lenses, to manage the refractive error caused by the irregular corneal shape. Advanced options include orthokeratology and corneal cross-linking, which aim to reshape or strengthen the cornea to improve vision. Cataract treatment requires surgical removal of the cloudy lens, typically replaced with an artificial intraocular lens, offering a definitive solution to restore clarity and improve vision.
Risk Factors Associated with Delta and Cataract
Risk factors for cataracts include aging, prolonged UV exposure, diabetes, smoking, and corticosteroid use, which contribute to lens clouding and vision impairment. Delta, or Angle Delta syndrome, involves structural abnormalities in the eye's anterior chamber angle, with risk factors such as genetic predisposition, ocular trauma, and chronic inflammation leading to impaired aqueous humor drainage. Understanding these distinct risk profiles assists in early diagnosis and targeted treatment strategies to prevent vision loss.
Prevention Strategies for Delta and Cataract
Delta variant prevention strategies center on widespread vaccination, mask-wearing in crowded or indoor settings, and maintaining physical distancing to reduce transmission. Cataract prevention focuses on protecting eyes from ultraviolet (UV) light by wearing sunglasses, maintaining a healthy diet rich in antioxidants, and managing chronic conditions like diabetes to slow lens clouding. Both conditions benefit from early detection and regular health check-ups to minimize complications and improve outcomes.
Prognosis and Outlook: Delta vs Cataract
Delta variant infections generally result in a more severe prognosis compared to cataract conditions, primarily due to respiratory complications and potential long-term lung damage. Cataracts usually have an excellent outlook with timely surgical intervention, restoring vision and significantly improving quality of life. While Delta variant recovery varies widely, cataract surgery boasts a high success rate, making its prognosis comparatively favorable.
Delta Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com