The biosphere encompasses all living organisms and their interactions within Earth's atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere, forming a complex and dynamic system essential for sustaining life. This interconnected web supports biodiversity, regulates climate, and cycles nutrients crucial for ecosystems. Explore the rest of the article to understand how the biosphere influences your environment and global health.
Table of Comparison
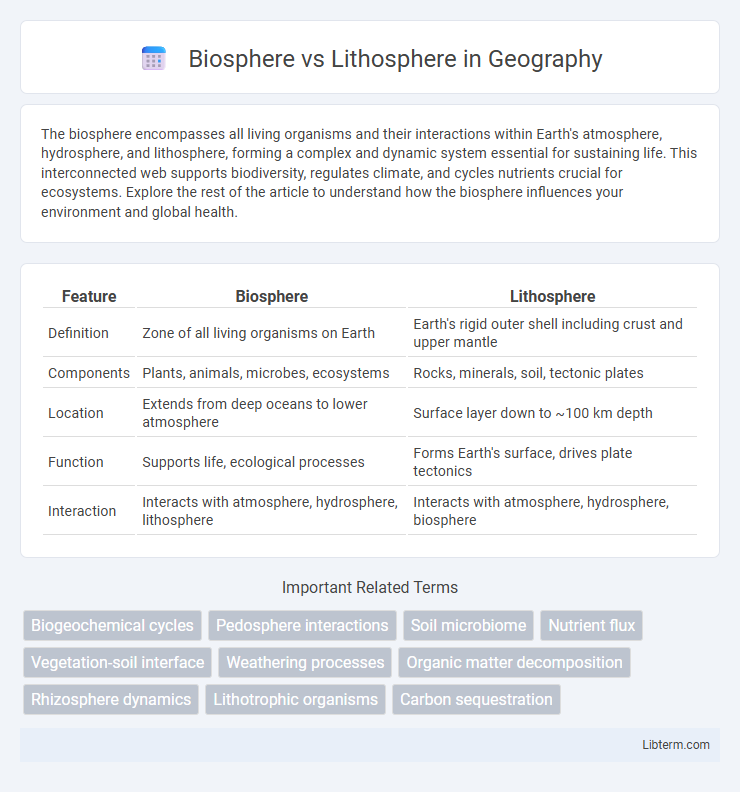
| Feature | Biosphere | Lithosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Zone of all living organisms on Earth | Earth's rigid outer shell including crust and upper mantle |
| Components | Plants, animals, microbes, ecosystems | Rocks, minerals, soil, tectonic plates |
| Location | Extends from deep oceans to lower atmosphere | Surface layer down to ~100 km depth |
| Function | Supports life, ecological processes | Forms Earth's surface, drives plate tectonics |
| Interaction | Interacts with atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere | Interacts with atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere |
Introduction to the Biosphere and Lithosphere
The biosphere encompasses all living organisms and their interactions within various ecosystems on Earth, including land, water, and air environments. The lithosphere refers to the rigid outer layer of the Earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle, which provides the physical foundation for terrestrial habitats. Understanding the biosphere's role in supporting life contrasts with the lithosphere's geophysical characteristics essential for ecosystem development and geological processes.
Defining the Biosphere: Life’s Global Realm
The biosphere encompasses all living organisms on Earth, including their interactions with the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere, forming a complex, global ecological system. It defines life's global realm by integrating diverse ecosystems where biological processes sustain biodiversity, energy flow, and nutrient cycles. Unlike the lithosphere, which consists of Earth's rigid outer shell comprising rocks and minerals, the biosphere represents the dynamic domain of life interacting with physical environments.
Understanding the Lithosphere: Earth’s Solid Outer Layer
The lithosphere is Earth's rigid outer layer comprising the crust and uppermost mantle, playing a crucial role in tectonic activity and landform creation. It differs from the biosphere, which encompasses all living organisms, by being entirely non-living and responsible for the planet's structural integrity. Understanding the lithosphere involves studying plate tectonics, rock composition, and geological processes that shape continents and ocean basins.
Key Differences Between Biosphere and Lithosphere
The biosphere encompasses all living organisms and the ecosystems they inhabit, whereas the lithosphere consists of the Earth's rigid outer layer, including the crust and upper mantle. Key differences include the biosphere's focus on biological life forms and ecological interactions, while the lithosphere primarily involves geological materials, landforms, and tectonic processes. The biosphere interacts dynamically with the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere, supporting life cycles, whereas the lithosphere provides the physical foundation and mineral resources essential for sustaining terrestrial habitats.
Interactions Between Biosphere and Lithosphere
The biosphere interacts with the lithosphere through processes such as nutrient cycling, where plants extract minerals and elements from the soil, promoting ecosystem productivity. Organisms like earthworms and microbes contribute to soil formation and aeration, enhancing lithosphere health and stability. Volcanic activity and tectonic movements in the lithosphere influence habitats and biodiversity within the biosphere by altering landscapes and nutrient availability.
Importance of the Biosphere for Life
The biosphere encompasses all ecosystems where life thrives, making it essential for sustaining biological processes and biodiversity. It regulates critical functions such as oxygen production, carbon cycling, and climate stability, directly influencing the habitability of Earth. Unlike the lithosphere, which provides the physical foundation of continents and mountains, the biosphere actively supports life through complex interactions among organisms and their environments.
Role of the Lithosphere in Earth Systems
The lithosphere plays a critical role in Earth systems by providing the rigid outer shell that supports terrestrial ecosystems and interacts dynamically with the biosphere through nutrient cycles and habitat formation. It acts as a stable platform for plant roots, influencing biodiversity and ecosystem functionality, while tectonic activity within the lithosphere drives the creation of mountains, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions that shape habitats and climate patterns. This geological layer also regulates the long-term carbon cycle by facilitating processes like weathering and volcanic outgassing, which affect atmospheric composition and global climate conditions.
Human Impacts on Biosphere and Lithosphere
Human activities drastically alter the biosphere through deforestation, habitat destruction, and pollution, leading to biodiversity loss and ecosystem imbalance. In the lithosphere, mining, urbanization, and agriculture cause soil degradation, erosion, and land subsidence, reducing land productivity and increasing vulnerability to natural disasters. These impacts underscore the interconnectedness of human actions and the health of Earth's vital systems, necessitating sustainable management practices.
Conservation Efforts for Biosphere and Lithosphere
Conservation efforts for the biosphere emphasize protecting biodiversity through habitat preservation, anti-poaching laws, and restoration of endangered ecosystems, targeting both terrestrial and marine life. In contrast, lithosphere conservation involves sustainable land use practices, soil erosion control, and reclamation of mining sites to maintain soil health and prevent land degradation. Both approaches are critical for ecosystem stability, with biosphere conservation focusing on living organisms and lithosphere efforts ensuring the physical foundation that supports life.
Future Challenges and Research Directions
Future challenges in biosphere and lithosphere studies include understanding the impact of climate change on ecosystem resilience and soil degradation. Research directions emphasize integrating satellite data with ground-based observations to model biogeochemical cycles and land-use changes more accurately. Advancements in remote sensing and machine learning will be crucial for predicting future environmental scenarios and developing sustainable management strategies.
Biosphere Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com